Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body's defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation Chronic Inflammation Inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology, viruses Viruses Minute infectious agents whose genomes are composed of DNA or RNA, but not both. They are characterized by a lack of independent metabolism and the inability to replicate outside living host cells. Virology, or fungi Fungi A kingdom of eukaryotic, heterotrophic organisms that live parasitically as saprobes, including mushrooms; yeasts; smuts, molds, etc. They reproduce either sexually or asexually, and have life cycles that range from simple to complex. Filamentous fungi, commonly known as molds, refer to those that grow as multicellular colonies. Mycology. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Pneumonia is the infection of the lung parenchyma.
| MDR gram-negative bacteria gram-negative bacteria Bacteria which lose crystal violet stain but are stained pink when treated by gram’s method. Bacteriology and MRSA MRSA A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins. Staphylococcus | Nosocomial (HAP and VAP) MRSA MRSA A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins. Staphylococcus | Community-acquired MRSA MRSA A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins. Staphylococcus |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Common pathogens that cause CAP to vary based on the severity of CAP (i.e., requiring treatment as an outpatient or as an inpatient outside or inside the ICU ICU Hospital units providing continuous surveillance and care to acutely ill patients. West Nile Virus) (see Table 2):
| Outpatient | Non-intensive care unit ( ICU ICU Hospital units providing continuous surveillance and care to acutely ill patients. West Nile Virus) Inpatient | ICU ICU Hospital units providing continuous surveillance and care to acutely ill patients. West Nile Virus |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| Newly identified pathogens | ||
|
||
An anaerobic etiology is suggested only when a history of aspiration is present days to weeks before the diagnosis of pneumonia.
General
Specific
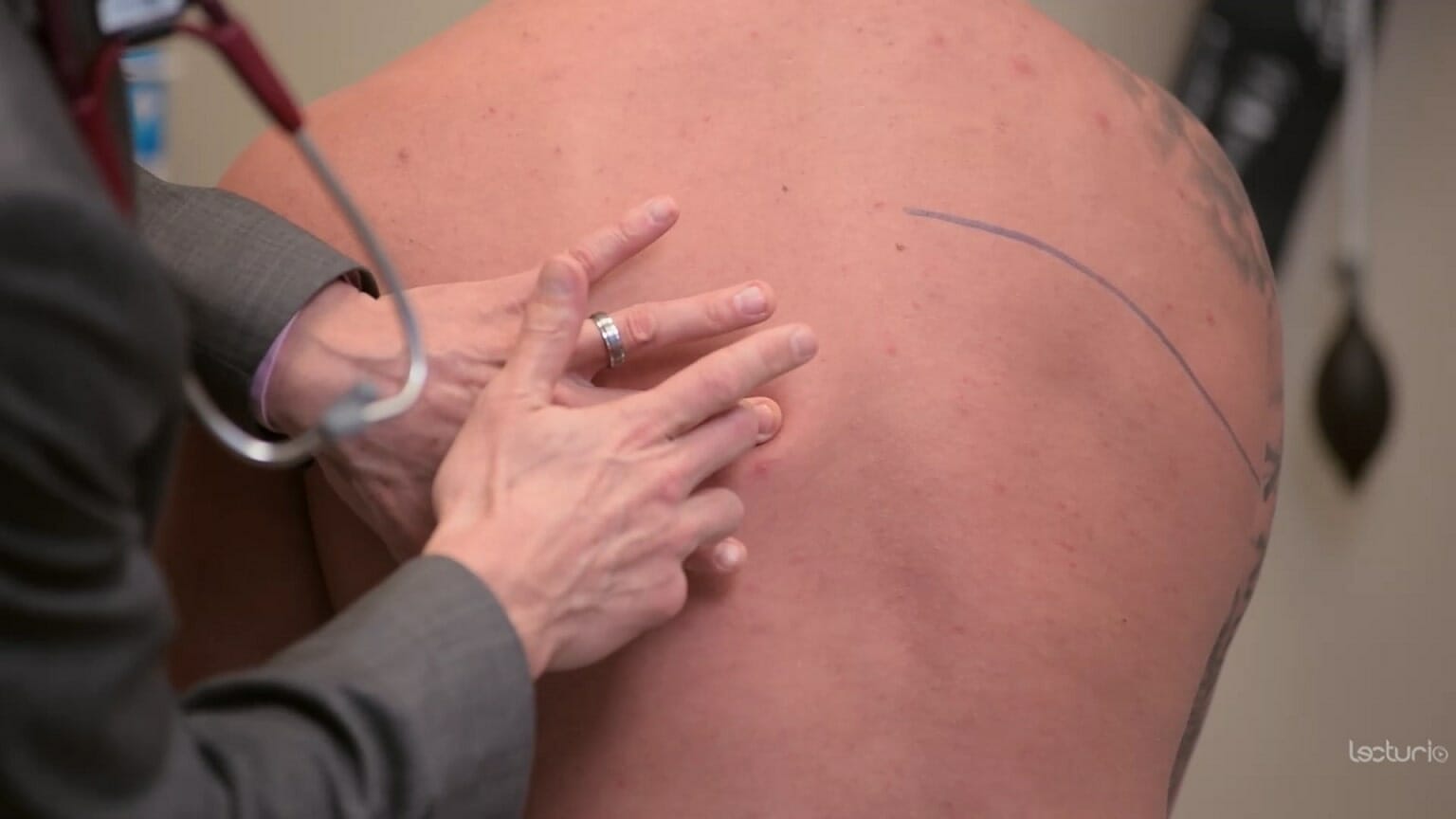
Percussion technique:
The clinician’s middle finger is placed on the area of interest. The other hand strikes the middle finger at the distal interphalangeal joint. A consolidation from pneumonia may sound dull to percussion.
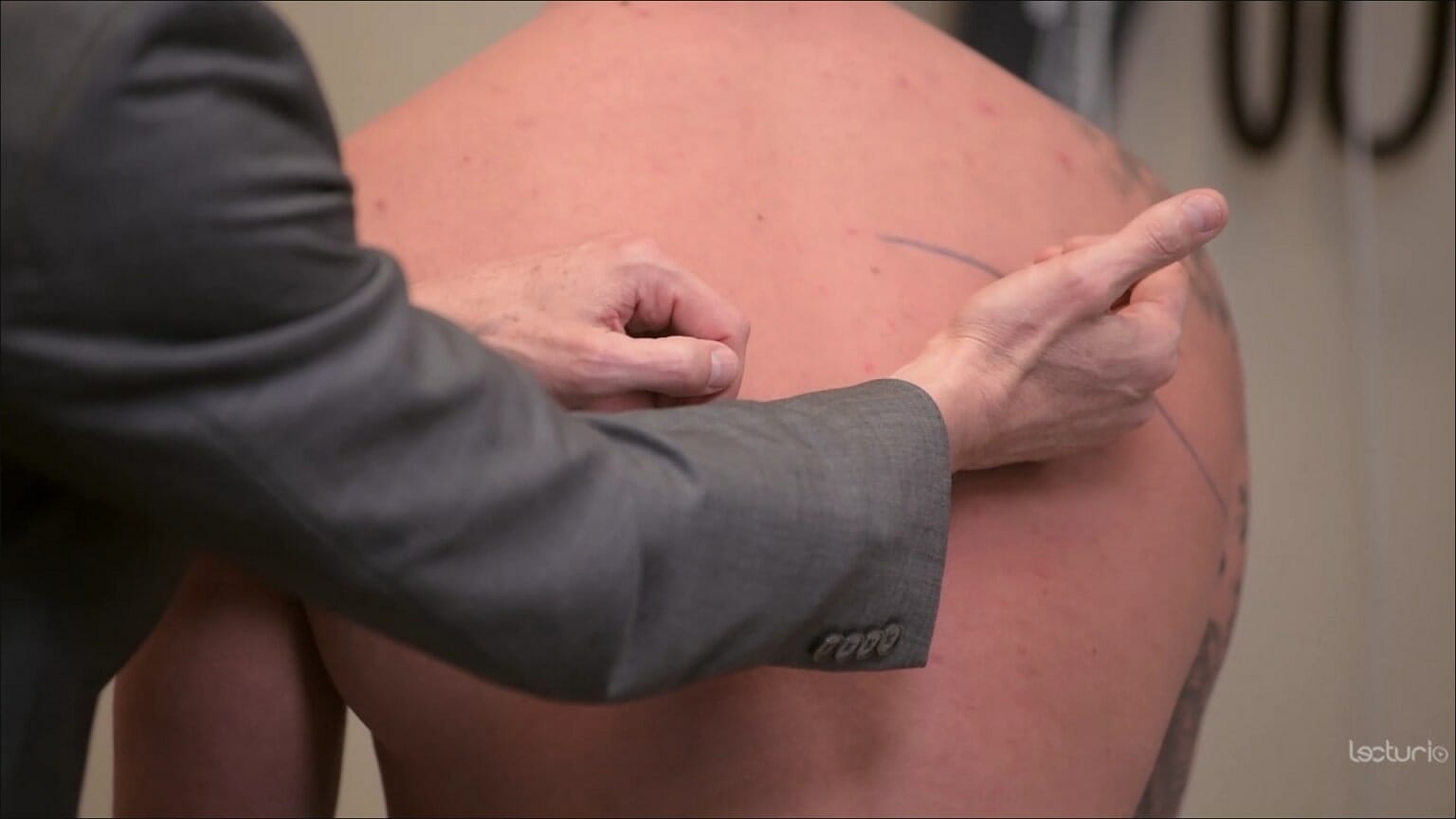
Tactile fremitus:
The clinician places the ulnar surface of their hands on both sides of the back to compare vibration transmission while the individual speaks. In pneumonia, increased fremitus may signal a consolidation (due to increased density of the lung tissue). Decreased fremitus may be due to a pleural effusion.
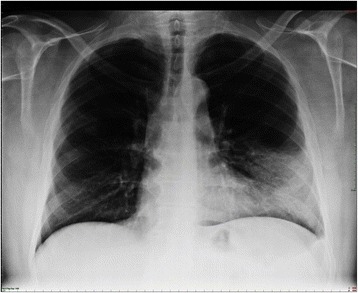
Lobar pneumonia. Dense infiltration in the left lower lobe has caused a silhouette of the left cardiac border (dashed line). Air bronchogram is a typical feature of consolidation.
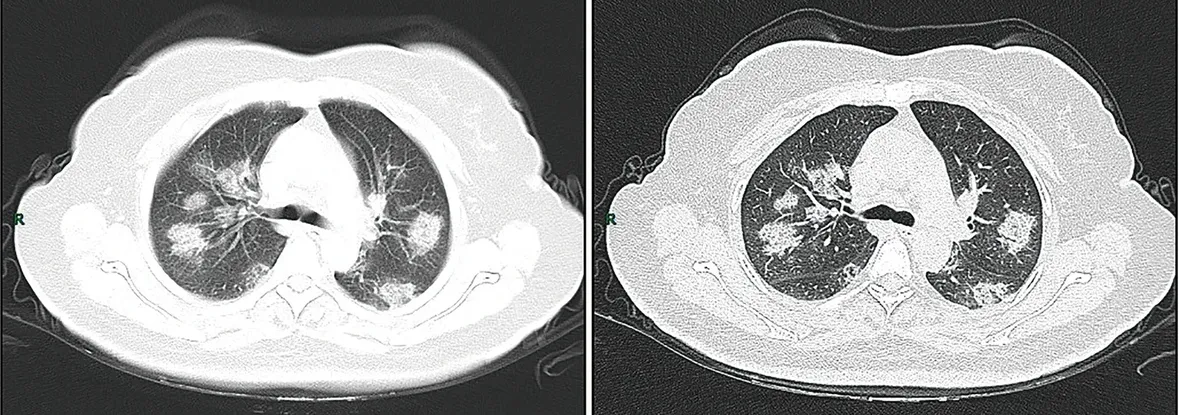
CT imaging of rapid progression stage. A 50-year-old female with anorexia, fatigue, muscle soreness, nasal congestion, and runny nose for 1 week, sore and itching throat for 2 days. Laboratory test: increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate (25 mm/h), normal white blood cells (4.08 × 109/L), decreased lymphocytes (0.96 × 109/ L), increased C-reaction protein (60.8 mg/L). Imaging examination: a (thin layer CT) and b (high-resolution CT) showed multiple patchy and light consolidation in both lungs and grid-like thickness of interlobular septa.
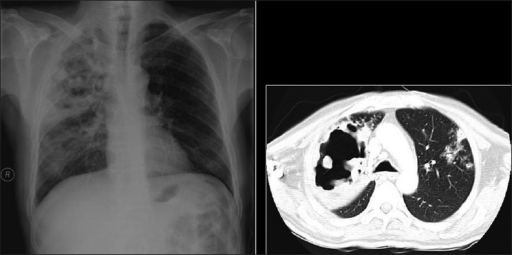
Necrotizing cavitating pneumonia. Chest X-ray and CT depicting necrotizing cavitating pneumonia due to Staphylococcus aureus in a 29-year-old man with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.
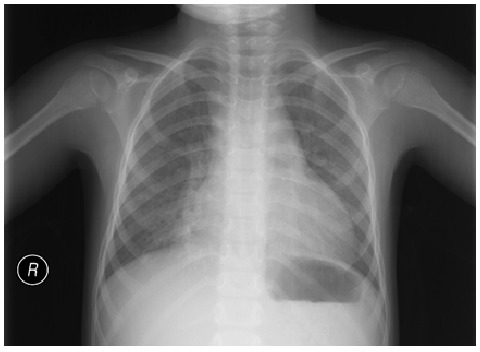
Atypical pneumonia: mild diffuse interstitial infiltration. No lobar consolidation, effusion, or pneumothorax is observed.
In addition to clinical judgment Judgment The process of discovering or asserting an objective or intrinsic relation between two objects or concepts; a faculty or power that enables a person to make judgments; the process of bringing to light and asserting the implicit meaning of a concept; a critical evaluation of a person or situation. Psychiatric Assessment, a validated prediction tool is recommended to determine the need for hospitalization Hospitalization The confinement of a patient in a hospital. Delirium:
Severe CAP or CAP requiring ICU ICU Hospital units providing continuous surveillance and care to acutely ill patients. West Nile Virus admission is defined by CAP plus at least 1 of the following:
VAP is the most common form of ICU-acquired pneumonia.