Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a sign observed in several medical conditions. Fluid dynamics in the body depend on body fluid compartments Body fluid compartments The adult human body is made up of 60% water and is divided into extracellular and intracellular fluid compartments. Extracellular fluid is present outside the cells and makes up two-thirds of the total body water. Intracellular fluid is present inside the cells and makes up two-thirds of the total body water. Body Fluid Compartments, fluid osmolarity Osmolarity The concentration of osmotically active particles in solution expressed in terms of osmoles of solute per liter of solution. Osmolality is expressed in terms of osmoles of solute per kilogram of solvent. Hypernatremia, and Starling forces Starling Forces Capillaries: Histology. Edema can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Symptoms vary depending on location of the edema.
Last updated: May 17, 2024
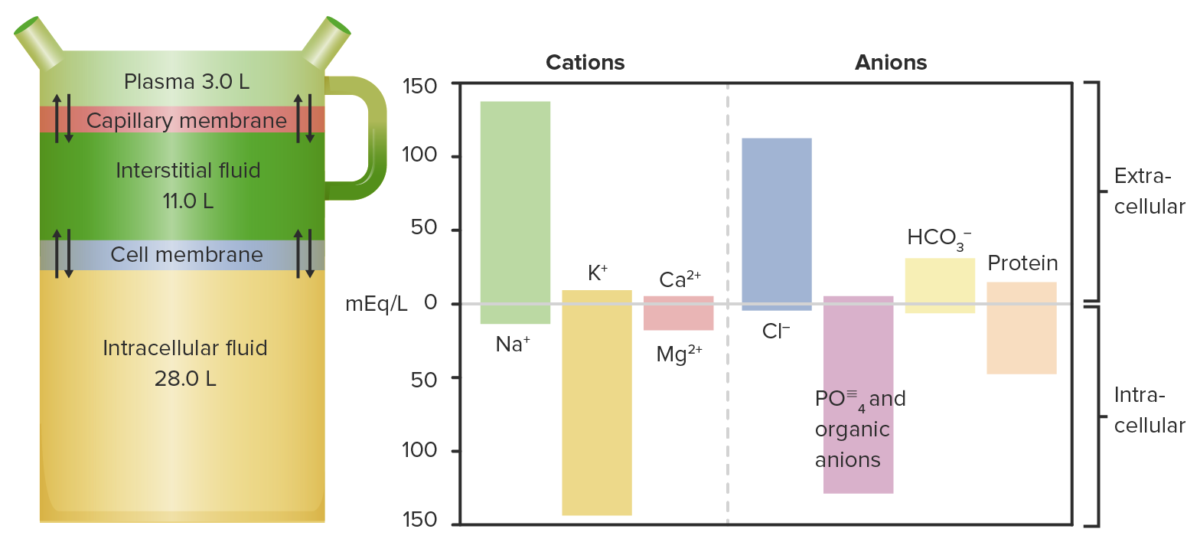
Diagram and chart showing fluid distribution and their respective cations and anions:
Notice that K+ levels are the highest in cells and Na+ levels are the highest in the plasma.
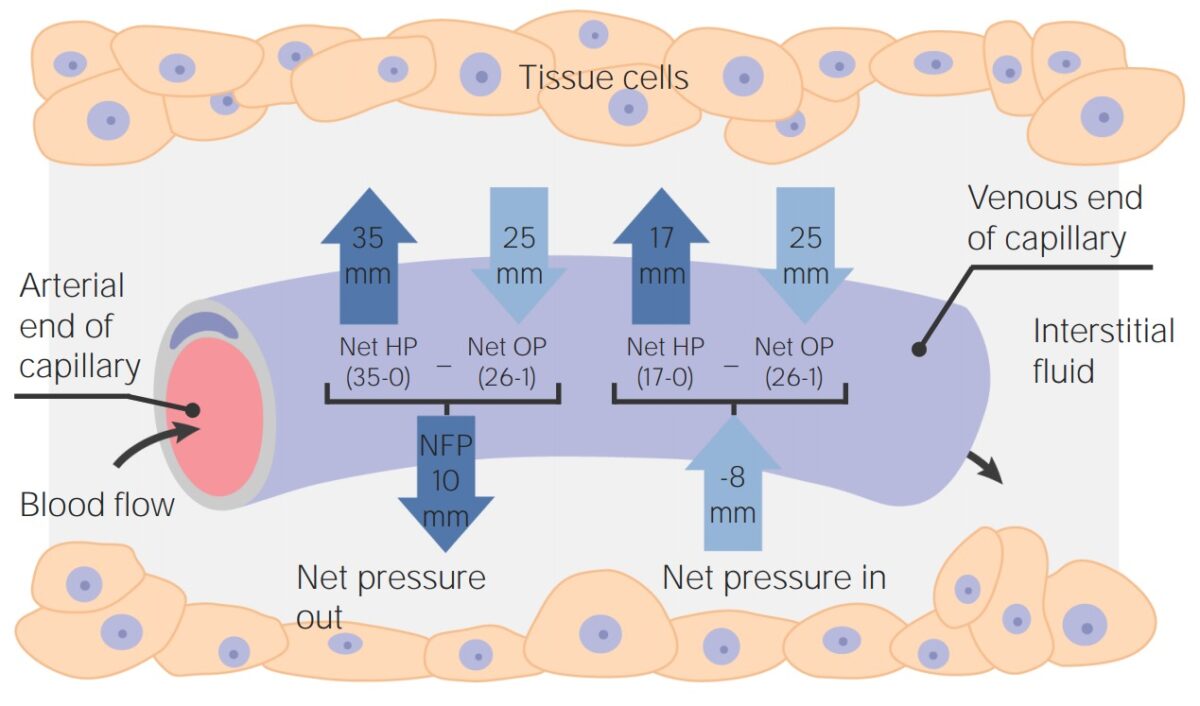
Diagram of Starling’s Law in a systemic capillary:
Shows the location and computation of intra and extraluminal forces to calculate pressures of filtration and of absorption.
HP: hydrostatic pressure
OP: oncotic pressure
Peripheral edema is the swelling Swelling Inflammation of the gravity-dependent extremities (more common in the lower limbs, distal > proximal). Although peripheral edema is typically painless, it can cause discomfort from swelling Swelling Inflammation and pose difficulty in walking.
Subtypes:
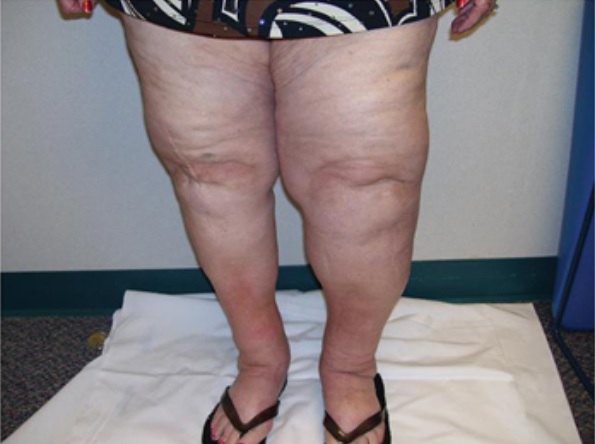
Lymphedema: Notice the asymmetrical deposition of fluid.
Image: “Lymphedema” by Cannon S. License: CC BY 3.0, cropped by Lecturio.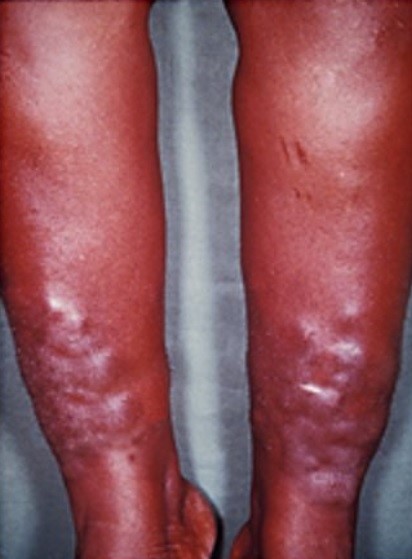
Myxedema
Image: “Myxedema” by Herbert L et al. License: CC BY 2.0, cropped by Lecturio.The following conditions commonly lead to edema: