The pleura is a serous membrane that lines the walls of the thoracic cavity and the surface of the lungs Lungs Lungs are the main organs of the respiratory system. Lungs are paired viscera located in the thoracic cavity and are composed of spongy tissue. The primary function of the lungs is to oxygenate blood and eliminate CO2. Lungs: Anatomy. This structure of mesodermal origin covers both lungs Lungs Lungs are the main organs of the respiratory system. Lungs are paired viscera located in the thoracic cavity and are composed of spongy tissue. The primary function of the lungs is to oxygenate blood and eliminate CO2. Lungs: Anatomy, the mediastinum Mediastinum The mediastinum is the thoracic area between the 2 pleural cavities. The mediastinum contains vital structures of the circulatory, respiratory, digestive, and nervous systems including the heart and esophagus, and major thoracic vessels. Mediastinum and Great Vessels: Anatomy, the thoracic surface of the diaphragm Diaphragm The diaphragm is a large, dome-shaped muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity. The diaphragm consists of muscle fibers and a large central tendon, which is divided into right and left parts. As the primary muscle of inspiration, the diaphragm contributes 75% of the total inspiratory muscle force. Diaphragm: Anatomy, and the inner part of the thoracic cage. The pleura is divided into a visceral pleura and parietal pleura Parietal pleura Pleuritis. Between both layers, there is a well-lubricated potential space called the pleural cavity, which eases the respiratory movements of the lungs Lungs Lungs are the main organs of the respiratory system. Lungs are paired viscera located in the thoracic cavity and are composed of spongy tissue. The primary function of the lungs is to oxygenate blood and eliminate CO2. Lungs: Anatomy and helps avoid friction.
Last updated: Nov 19, 2024
The pleura is a double-layered serous membrane that lines the walls of the thoracic cavity and the surface of the lungs Lungs Lungs are the main organs of the respiratory system. Lungs are paired viscera located in the thoracic cavity and are composed of spongy tissue. The primary function of the lungs is to oxygenate blood and eliminate CO2. Lungs: Anatomy. Thus, it extends virtually as far and wide as the thoracic cavity.
Boundaries:
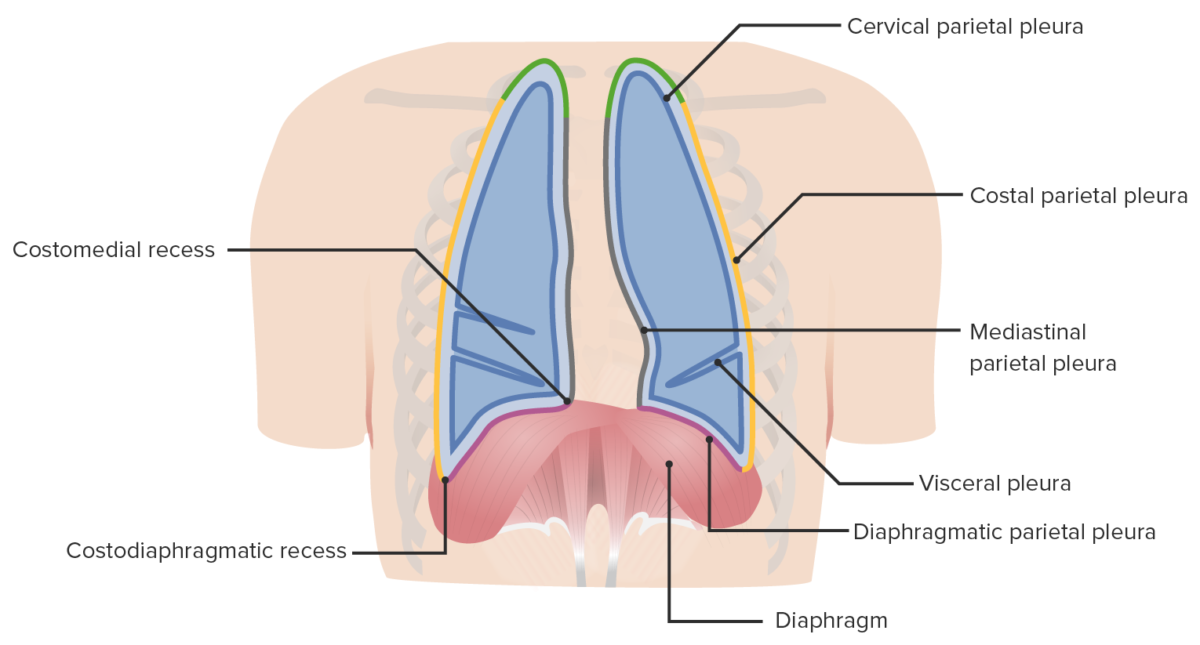
Boundaries and parts of the pleura within the thoracic cavity
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Each lung is enclosed in a serous pleural sac that consists of 2 continuous membranes of visceral and parietal pleura Parietal pleura Pleuritis.
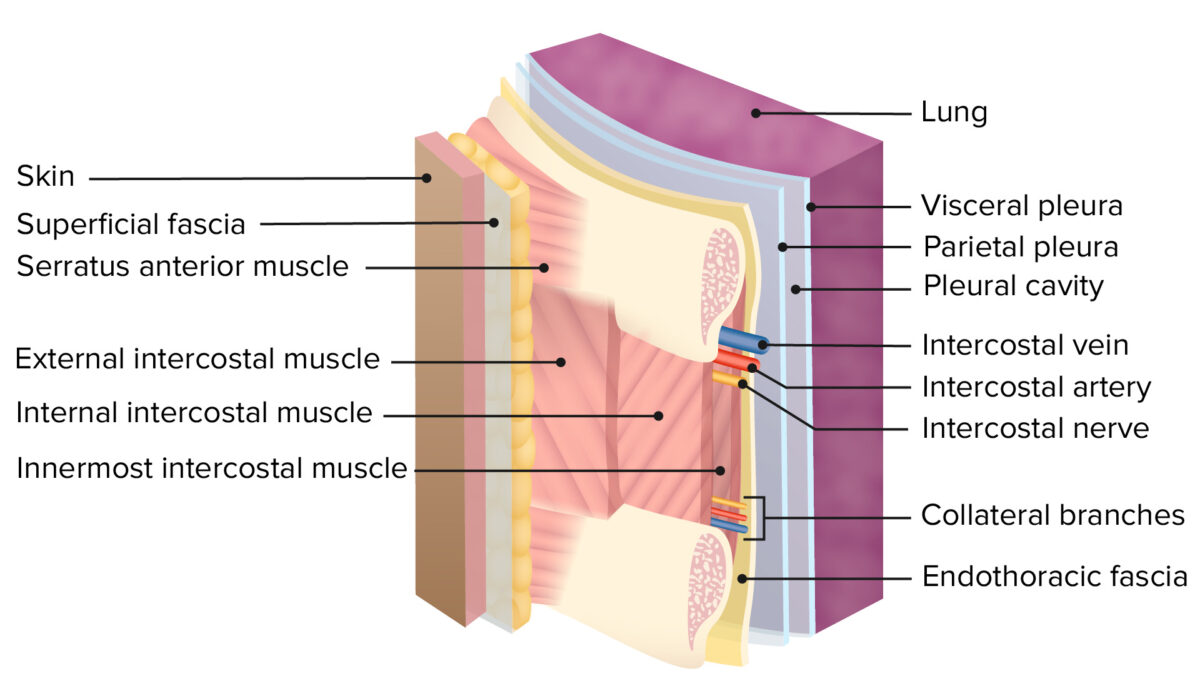
Layers of the thoracic wall:
Note the double layer of pleura and the pleural cavity, separated from the rib cage by the endothoracic fascia.
Pleural cavity:
| Irrigation | Innervation | |
|---|---|---|
| Parietal pleura Parietal pleura Pleuritis | Costal portion is supplied by:
Diaphragmatic portion is supplied by: superficial part of the diaphragmatic microcirculation |
Receives somatic
afferent
Afferent
Neurons which conduct nerve impulses to the central nervous system.
Nervous System: Histology (
sensory
Sensory
Neurons which conduct nerve impulses to the central nervous system.
Nervous System: Histology) innervation from:
|
| Visceral pleura |
|
Receives visceral afferent Afferent Neurons which conduct nerve impulses to the central nervous system. Nervous System: Histology (autonomic) innervation from: pulmonary plexus |
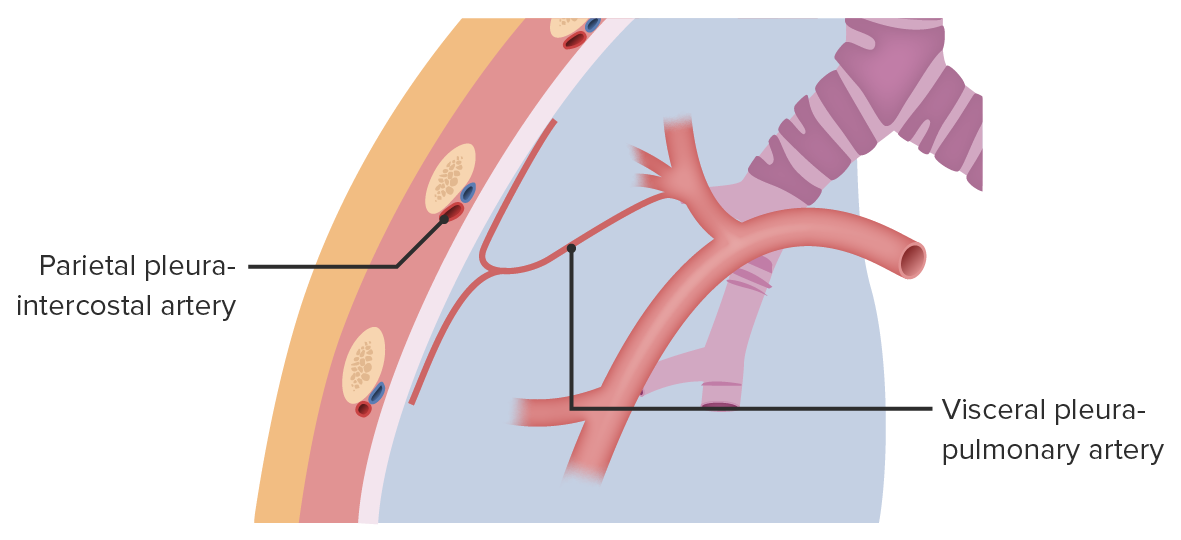
Blood supply of the pleurae:
The parietal pleura receives blood supply from the intercostal, diaphragmatic, mediastinal, and internal thoracic arteries. The visceral pleura receives blood supply from the bronchial and pulmonary vessels.