Acute respiratory distress syndrome is characterized by the sudden onset of hypoxemia Hypoxemia Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome and bilateral pulmonary edema Pulmonary edema Pulmonary edema is a condition caused by excess fluid within the lung parenchyma and alveoli as a consequence of a disease process. Based on etiology, pulmonary edema is classified as cardiogenic or noncardiogenic. Patients may present with progressive dyspnea, orthopnea, cough, or respiratory failure. Pulmonary Edema without cardiac failure Cardiac failure Congestive heart failure refers to the inability of the heart to supply the body with normal cardiac output to meet metabolic needs. Echocardiography can confirm the diagnosis and give information about the ejection fraction. Heart Failure. Sepsis Sepsis Systemic inflammatory response syndrome with a proven or suspected infectious etiology. When sepsis is associated with organ dysfunction distant from the site of infection, it is called severe sepsis. When sepsis is accompanied by hypotension despite adequate fluid infusion, it is called septic shock. Sepsis and Septic Shock is the most common cause of ARDS. The underlying mechanism and histologic correlate is diffuse alveolar damage (DAD). Diffuse alveolar damage involves damage to the endothelial and alveolar epithelial cells and is associated with inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body's defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation and the development of hyaline membranes lining the inner alveolar walls. The reparative stage follows after weeks, with fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans possibly occurring later. Clinically, the following triad of findings favors a diagnosis of ARDS: acute or rapidly progressive dyspnea Dyspnea Dyspnea is the subjective sensation of breathing discomfort. Dyspnea is a normal manifestation of heavy physical or psychological exertion, but also may be caused by underlying conditions (both pulmonary and extrapulmonary). Dyspnea, hypoxic respiratory failure Respiratory failure Respiratory failure is a syndrome that develops when the respiratory system is unable to maintain oxygenation and/or ventilation. Respiratory failure may be acute or chronic and is classified as hypoxemic, hypercapnic, or a combination of the two. Respiratory Failure ( partial pressure Partial pressure The pressure that would be exerted by one component of a mixture of gases if it were present alone in a container. Gas Exchange of O2/fraction of inspired O2 ratio < 300 mm Hg), and bilateral alveolar opacities on chest imaging. Management involves determination and treatment of the cause while providing adequate oxygen, reducing further lung damage, and avoiding fluid overload. Most patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship require mechanical ventilation Ventilation The total volume of gas inspired or expired per unit of time, usually measured in liters per minute. Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing. Acute respiratory distress syndrome is associated with high mortality Mortality All deaths reported in a given population. Measures of Health Status or long-term complications potentially developing even after treatment.
Last updated: Apr 30, 2025
Acute respiratory distress syndrome is a clinical syndrome (not a pathological diagnosis) characterized by a sudden onset of hypoxemia Hypoxemia Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome and bilateral pulmonary edema Pulmonary edema Pulmonary edema is a condition caused by excess fluid within the lung parenchyma and alveoli as a consequence of a disease process. Based on etiology, pulmonary edema is classified as cardiogenic or noncardiogenic. Patients may present with progressive dyspnea, orthopnea, cough, or respiratory failure. Pulmonary Edema without cardiac failure Cardiac failure Congestive heart failure refers to the inability of the heart to supply the body with normal cardiac output to meet metabolic needs. Echocardiography can confirm the diagnosis and give information about the ejection fraction. Heart Failure.
The underlying mechanism of ARDS is diffuse alveolar damage (DAD):
Acute respiratory distress syndrome is clinically diagnosed using the Berlin diagnostic criteria.
Acute respiratory distress syndrome results from clinical disorders that affect the lungs Lungs Lungs are the main organs of the respiratory system. Lungs are paired viscera located in the thoracic cavity and are composed of spongy tissue. The primary function of the lungs is to oxygenate blood and eliminate CO2. Lungs: Anatomy either directly or indirectly.
Direct lung injury:
Indirect lung injury:
Risk of ARDS:
Acute respiratory distress syndrome begins with an initial injury to the pneumocytes and pulmonary endothelium Endothelium A layer of epithelium that lines the heart, blood vessels (vascular endothelium), lymph vessels (lymphatic endothelium), and the serous cavities of the body. Arteries: Histology, which starts a chain reaction of increasing inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body’s defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation and pulmonary damage that can have an uneven/patchy distribution.
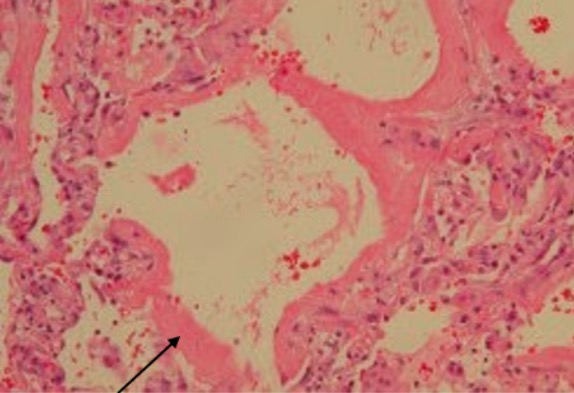
Acute respiratory distress syndrome:
A 68-year-old man had mantle cell lymphoma and received chemotherapy. He was admitted to the hospital for fever and respiratory failure. Lung involvement by mantle cell lymphoma was excluded. Video-assisted thoracoscopic lung biopsy revealed diffuse alveolar damage with hyaline membranes lining the alveolar surfaces (arrow) consistent with ARDS.
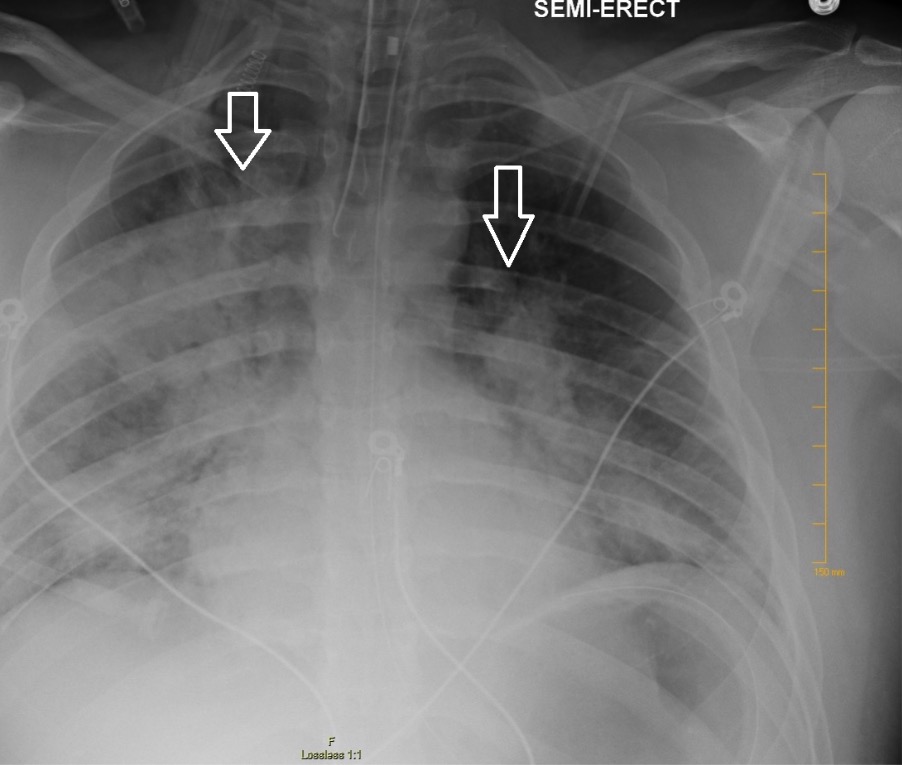
Chest X-ray showing bilateral patchy infiltrates suggestive of ARDS
Image: “Chest radiography demonstrating bilateral hilar opacities” by Ologun G O, Ridley D, Chea N D, et al. (September 08, 2017). Severe ARDS after laparoscopic appendectomy in a young adult. Cureus 9(9): e1664. doi:10.7759/cureus.1664. License: CC BY 4.0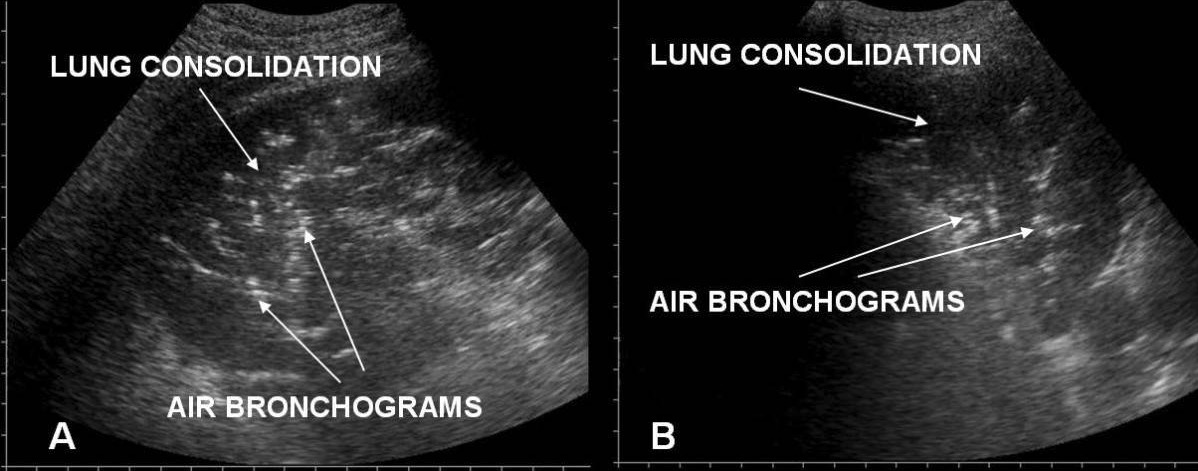
Acute respiratory distress syndrome versus acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema on chest/lung ultrasound:
A: irregular pleural line in ARDS
B: an even pleural line in acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema
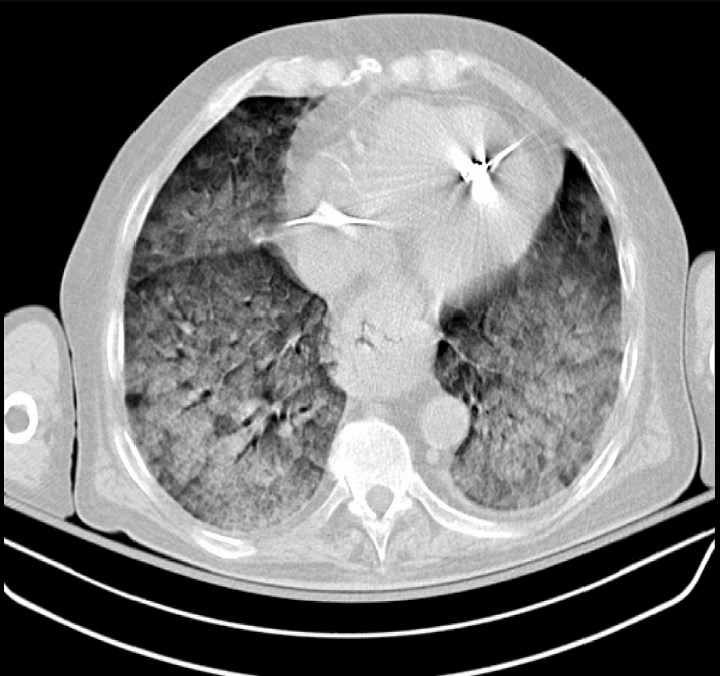
A CT scan showing severe ARDS: diffuse pulmonary opacifications present bilaterally
Image: “Chest CT scan indicative of severe ARDS” by Zagkotsis G, Markou M, Papanikolaou P, et al. (January 24, 2021). Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Induced by Parathyroid Storm. Cureus 13(1): e12881. doi:10.7759/cureus.12881. License: CC BY 4.0Almost all patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship are managed in the ICU ICU Hospital units providing continuous surveillance and care to acutely ill patients. West Nile Virus
Acute respiratory distress syndrome is a serious condition that is usually associated with high mortality Mortality All deaths reported in a given population. Measures of Health Status and morbidity Morbidity The proportion of patients with a particular disease during a given year per given unit of population. Measures of Health Status.
Several risk factors have been identified that can estimate the prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual’s condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas in a patient with ARDS:
The majority of patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship recover most of their lung function, but will take months.
Long-term complications: