Aminoglycosides are a class of antibiotics including gentamicin, tobramycin, amikacin, neomycin, plazomicin, and streptomycin. The class binds the 30S ribosomal subunit to inhibit bacterial protein synthesis Synthesis Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). Unlike other medications with a similar mechanism of action, aminoglycosides are bactericidal Bactericidal Penicillins. Aminoglycosides provide coverage against aerobic gram-negative pathogens, including Pseudomonas Pseudomonas Pseudomonas is a non-lactose-fermenting, gram-negative bacillus that produces pyocyanin, which gives it a characteristic blue-green color. Pseudomonas is found ubiquitously in the environment, as well as in moist reservoirs, such as hospital sinks and respiratory equipment. Pseudomonas. Aminoglycosides can also be used synergistically with inhibitors of bacterial cell wall Cell wall The outermost layer of a cell in most plants; bacteria; fungi; and algae. The cell wall is usually a rigid structure that lies external to the cell membrane, and provides a protective barrier against physical or chemical agents. Cell Types: Eukaryotic versus Prokaryotic synthesis Synthesis Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) (e.g., β lactams) for gram-positive Gram-Positive Penicillins pathogens. Use is limited by serious side effects, including nephrotoxicity Nephrotoxicity Glycopeptides and ototoxicity Ototoxicity Damage to the ear or its function secondary to exposure to toxic substances such as drugs used in chemotherapy; immunotherapy; or radiation. Glycopeptides.
Last updated: Aug 18, 2022
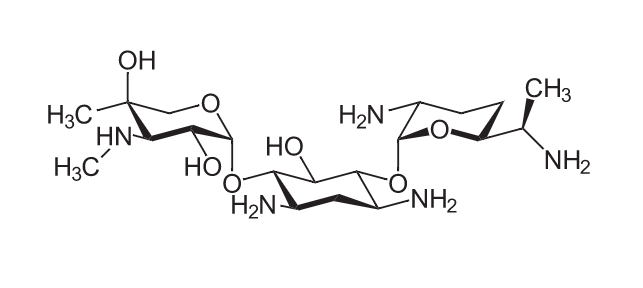
Chemical structure of gentamicin:
a core hexose ring (2-deoxystreptamine in the center) with 2 amino sugar molecules attached
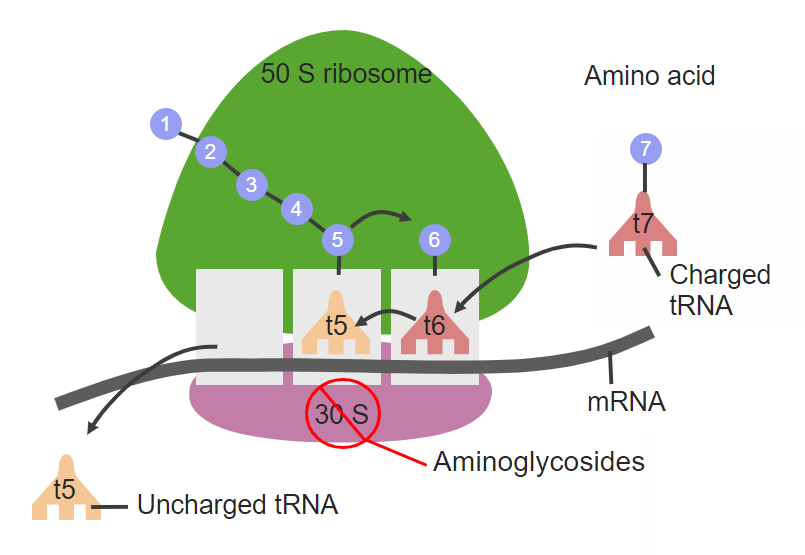
The site of action for aminoglycosides, which target the 30S ribosomal subunit
tRNA: transfer RNA
mRNA: messenger RNA
Several mechanisms of aminoglycoside resistance Resistance Physiologically, the opposition to flow of air caused by the forces of friction. As a part of pulmonary function testing, it is the ratio of driving pressure to the rate of air flow. Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing:
The following table compares antibiotics, which inhibit bacterial protein synthesis Synthesis Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR):
| Drug class | Mechanism of action | Coverage | Adverse effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amphenicols |
|
|
|
| Lincosamides Lincosamides The lincosamides, lincomycin and clindamycin, are inhibitors of bacterial protein synthesis. Drugs in this class share the same binding site as that of macrolides and amphenicols; however, they differ in chemical structure. Lincosamides target the 50S ribosomal subunit and interfere with transpeptidation. Lincosamides |
|
|
|
| Macrolides Macrolides Macrolides and ketolides are antibiotics that inhibit bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit and blocking transpeptidation. These antibiotics have a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity but are best known for their coverage of atypical microorganisms. Macrolides and Ketolides |
|
|
|
| Oxazolidinones Oxazolidinones The oxazolidinones (linezolid and tedizolid) are bacterial protein synthesis inhibitors. Their unique binding site on the 23S ribosomal RNA of the 50S ribosome gives them zero cross-resistance with other antibiotics. Oxazolidinones |
|
Gram-positive
Gram-Positive
Penicillins
cocci
Cocci
Bacteriology:
|
|
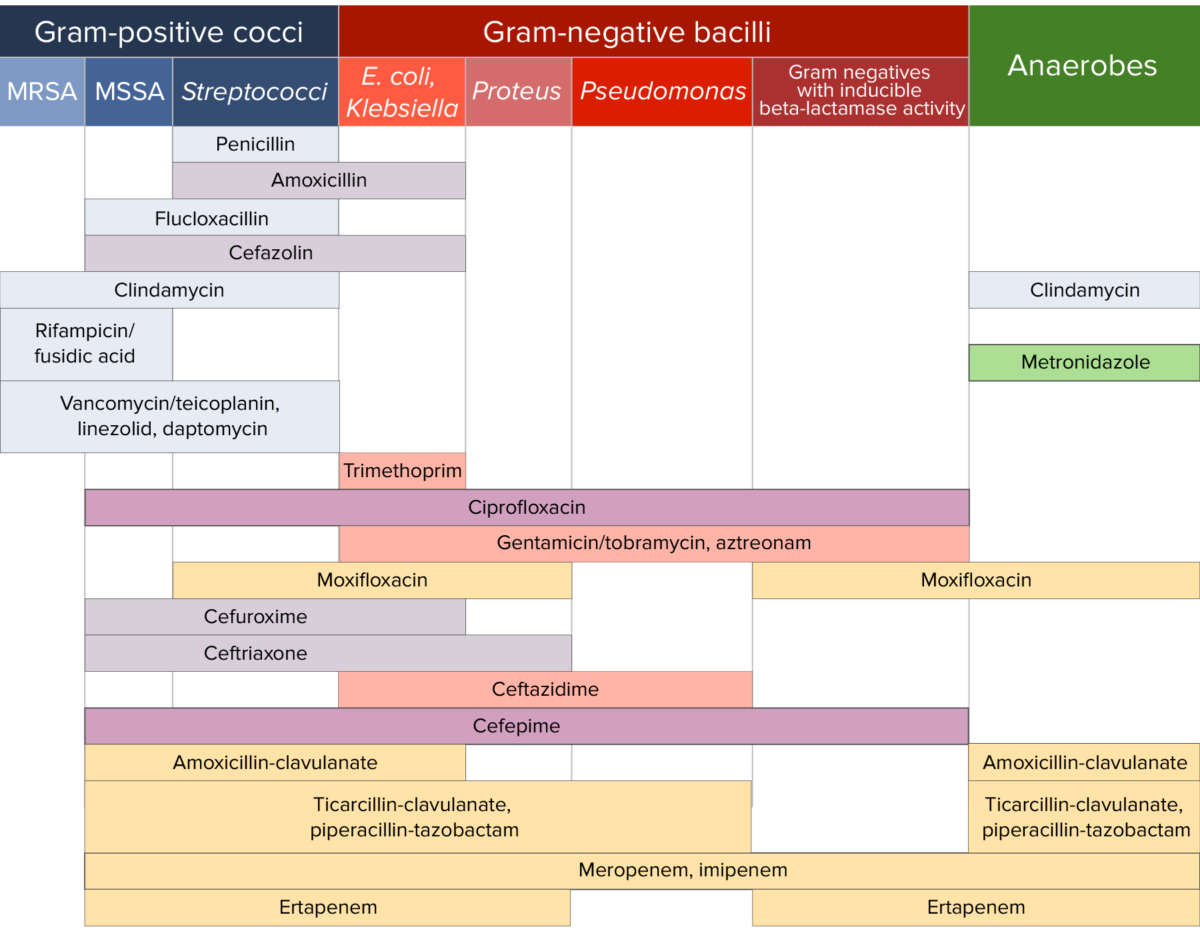
Antibiotic sensitivity:
Chart comparing the microbial coverage of different antibiotics for gram-positive cocci, gram-negative bacilli, and anaerobes.