Pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia is a disease of the lower airways characterized by inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body's defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation of the alveolar and/or interstitial tissue of the lungs Lungs Lungs are the main organs of the respiratory system. Lungs are paired viscera located in the thoracic cavity and are composed of spongy tissue. The primary function of the lungs is to oxygenate blood and eliminate CO2. Lungs: Anatomy. Pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia has numerous potential etiologies, the most common of which is infectious, and is classified according to several factors. Pathogens that commonly affect the pediatric population often differ from those seen in adults. Diagnosis is based on a history and exam. In some cases, supportive information is obtained by labs and imaging. Management involves supportive care and antimicrobial agents based on the etiology. Prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas is generally good.
Last updated: Oct 6, 2022

Causal pathogens in community-acquired pneumonia according to age group and special circumstances
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Clinical presentation varies by age of patient and by course of the illness.
By age:
By clinical course:
Diagnosis made based on history and exam and can be confirmed or refined with imaging.
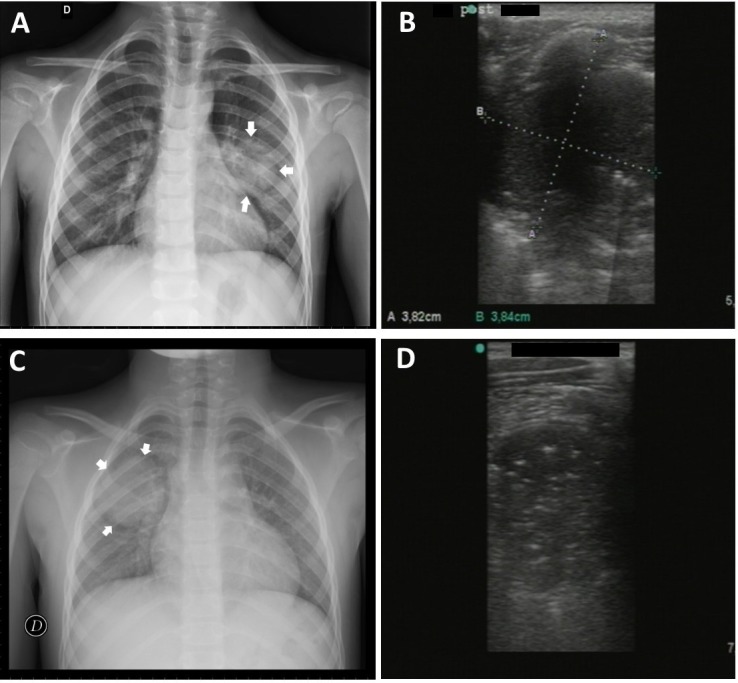
Round pneumonia:
Case 1: 5-year-old boy with evidence of round pneumonia by chest X-ray in middle region of the left lung (A) detected by lung ultrasound (B)
Case 2: 8-year-old boy with round pneumonia in middle/upper region of right lung by chest X-ray (C) and corresponding ultrasound image (D)
Most children with pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia recover without long-term sequelae; however, some complications can occur.
Other complications of pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia in children include: