Coccidioidomycosis, commonly known as San Joaquin Valley fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever, is a fungal disease caused by Coccidioides immitis or Coccidioides posadasii. When Coccidioides spores Spores The reproductive elements of lower organisms, such as bacteria; fungi; and cryptogamic plants. Anthrax are inhaled, they transform into spherules that result in infection. Coccidioidomycosis is also a common cause of community-acquired pneumonia Community-Acquired Pneumonia Pneumonia in Children and can cause severe disease in the immunocompromised immunocompromised A human or animal whose immunologic mechanism is deficient because of an immunodeficiency disorder or other disease or as the result of the administration of immunosuppressive drugs or radiation. Gastroenteritis. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship may present with fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever, chills Chills The sudden sensation of being cold. It may be accompanied by shivering. Fever, cough, chest pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, and shortness of breath Shortness of breath Dyspnea is the subjective sensation of breathing discomfort. Dyspnea is a normal manifestation of heavy physical or psychological exertion, but also may be caused by underlying conditions (both pulmonary and extrapulmonary). Dyspnea. The diagnosis is supported by clinical history, radiology, microscopy, fungal culture, and serological data. Management involves antifungals and supportive care. In severe disease, addressing the etiology of immunosuppression is critical.
Last updated: Oct 31, 2022
Taxonomy:
Forms:
Reproduction:
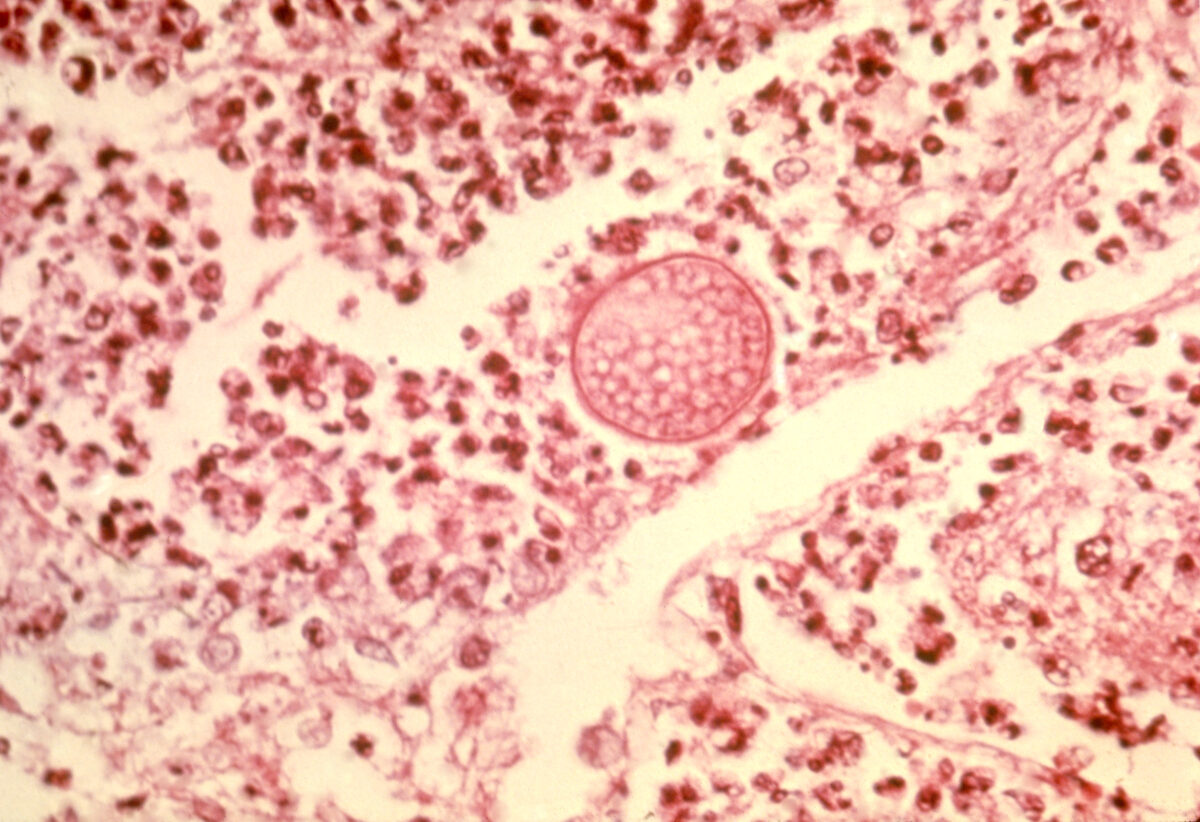
This image depicts a photomicrograph of a lung tissue specimen, revealing some of the ultrastructural histopathology exhibited in a case of pulmonary coccidioidomycosis.
Note the mature spherule with its contents of Coccidioides immitis endospores, as well as an intense infiltrate of neutrophils.
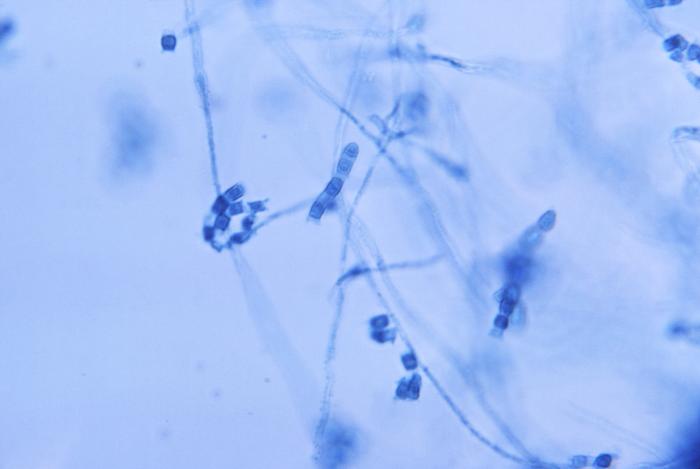
Photomicrograph showing the presence of thin, septate, hyaline hyphae, from which numerous thick-walled Coccidioides immitis arthroconidia had evolved
Image: “Photomicrograph showing the presence of thin, septate, hyaline hyphae, from which numerous, thick walled, Coccidioides immitis arthroconidia had evolved” by CDC/ Lucille Georg. License: Public DomainCoccidioidomycosis (also known as San Joaquin Valley fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever) can be caused by:
Coccidioides arthroconidia can become airborne when soil is disturbed, allowing transmission via inhalation.
The clinical presentation can vary from asymptomatic to life-threatening. The incubation Incubation The amount time between exposure to an infectious agent and becoming symptomatic. Rabies Virus period is 1–4 weeks after exposure.
Cutaneous involvement may occur in conjunction with pulmonary involvement, with direct inoculation, or from disseminated disease.
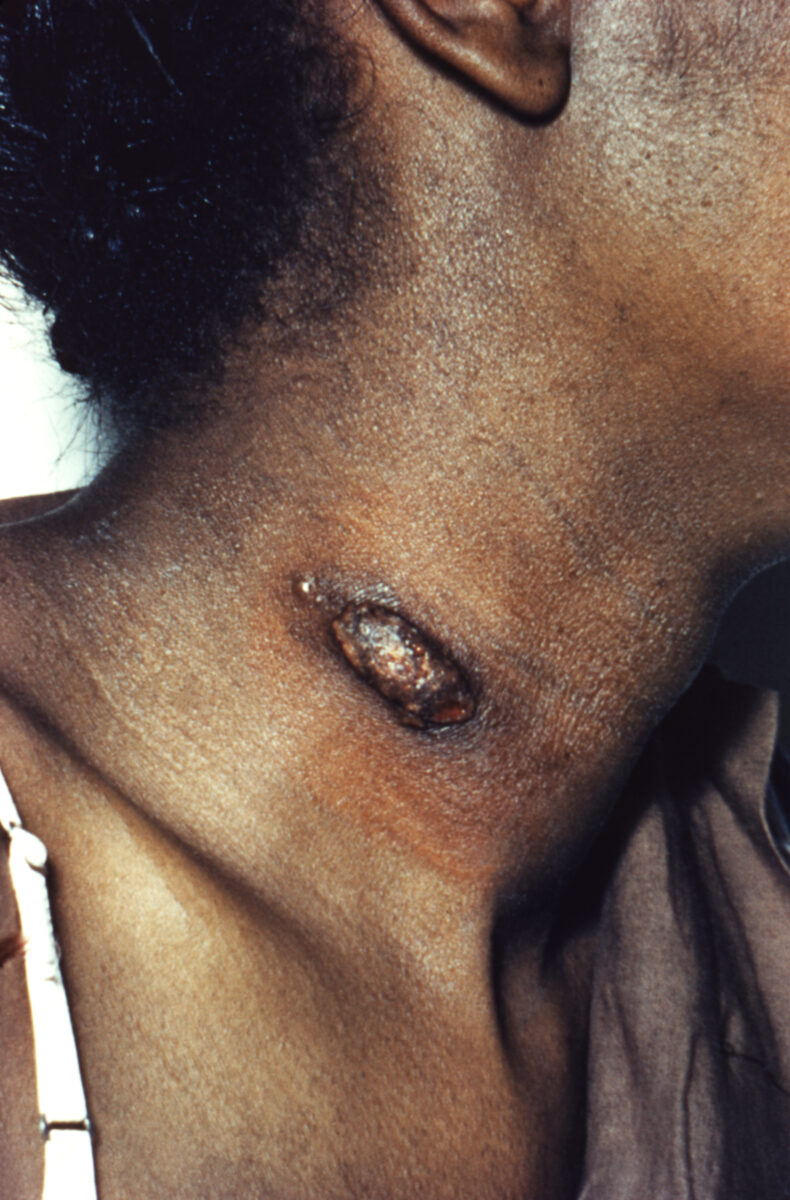
Skin lesions caused by Coccidioides infection
Image: “A skin lesion due to Coccidioides infection” by CDC/Dr. Lucille K. Georg. License: Public Domain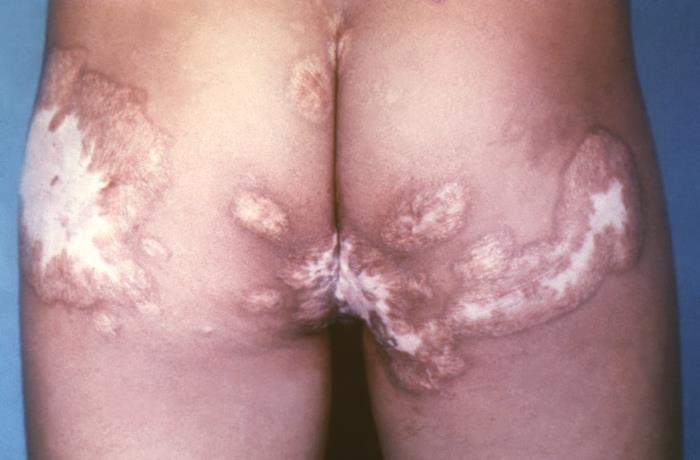
A posterior view of a patient’s torso with marked cutaneous scarring over both buttocks after treatment for coccidioidomycosis
Image: “This image depicts a posterior view of a patient’s torso, who had undergone treatment with amphotericin B, in this case of coccidioidomycosis, also known as valley fever, caused by the fungal organism, Coccidioides immitis” by CDC/Dr. Brodsky. License: Public DomainDisseminated infection is defined as disease outside the thoracic cavity and is considered an AIDS-defining illness. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship can present with the following (this list is not exhaustive):
“Desert rheumatism” is often defined by the presence of:
The diagnosis is made based on history and physical exam with supporting imaging and laboratory data.
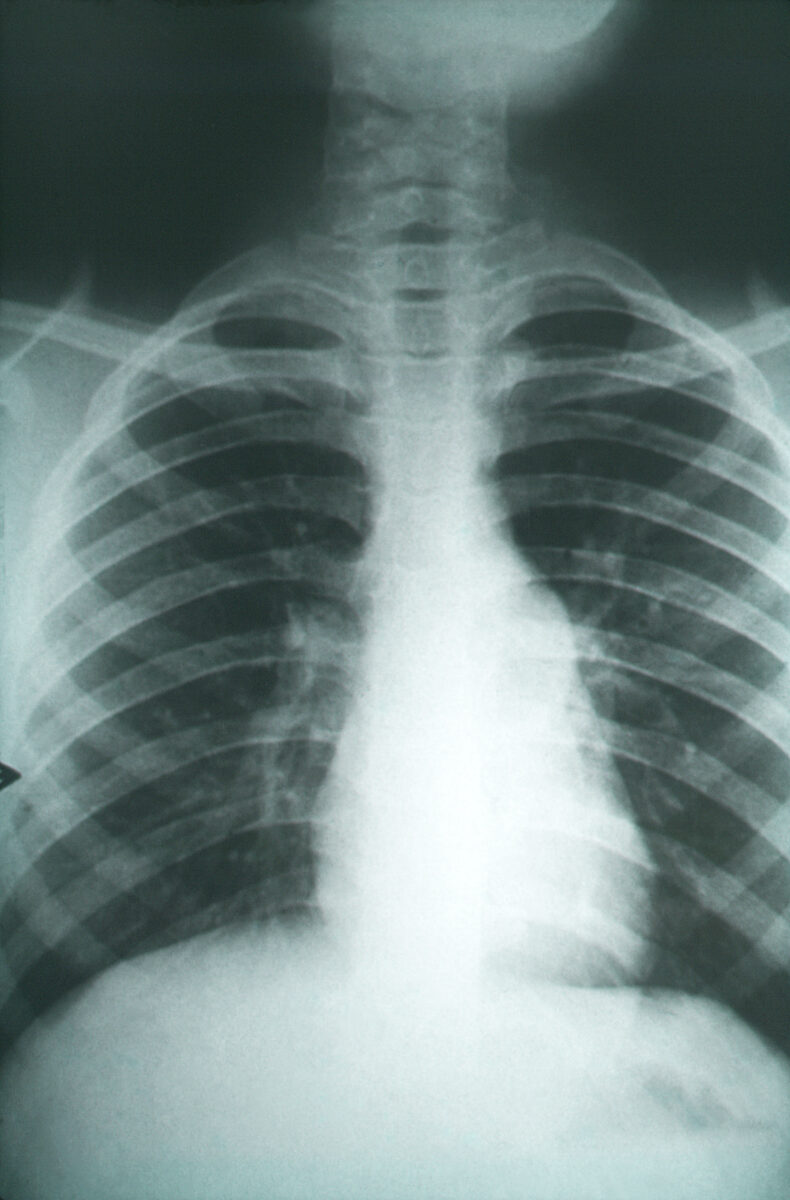
This anteroposterior chest X-ray revealed pulmonary changes indicative of pulmonary fibrosis in a case of coccidioidomycosis, caused by fungal organisms of the genus Coccidioides:
Because these changes also resemble those seen in other lung infections, including tuberculosis, the findings uncovered with a chest X-ray need to be coupled with serologic testing as well as possible tissue biopsy. The degree of fibrotic changes, indicative of scarring found on X-ray, can be directly correlated to the severity of the fungal infection.
Listed complications are associated with being immunocompromised immunocompromised A human or animal whose immunologic mechanism is deficient because of an immunodeficiency disorder or other disease or as the result of the administration of immunosuppressive drugs or radiation. Gastroenteritis and/or delay in treatment:
It is difficult to prevent coccidioidomycosis when living in an endemic area. General strategies include: