Blastomycosis is an infection caused by inhalation of the spores Spores The reproductive elements of lower organisms, such as bacteria; fungi; and cryptogamic plants. Anthrax of the fungus, Blastomyces. Blastomyces species thrive in moist soil and decaying material and are common in the Ohio and Mississippi River valleys and the Great Lakes regions of the United States and Canada. Although most patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship are asymptomatic, some can develop pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia. Extrapulmonary disease, such as skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions lesions, osteomyelitis Osteomyelitis Osteomyelitis is an infection of the bone that results from the spread of microorganisms from the blood (hematogenous), nearby infected tissue, or open wounds (non-hematogenous). Infections are most commonly caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Osteomyelitis, genitourinary infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease, and meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis can occur. The diagnosis is made by identifying the organism in sputum or tissue samples using culture, PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), or antigen Antigen Substances that are recognized by the immune system and induce an immune reaction. Vaccination testing. Antifungals are used for treatment.
Last updated: Jan 20, 2025
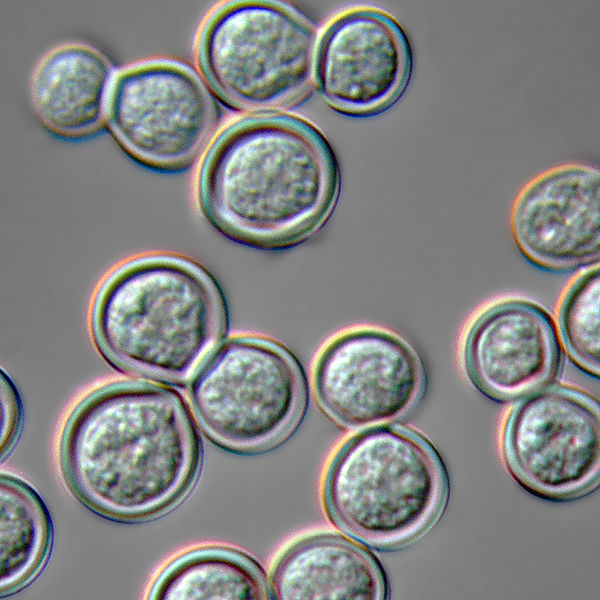
Blastomyces dermatitidis yeast form at 37°C
Image: “Blastomyces dermatitidis yeast form” by Medmyco. License: CC0 1.0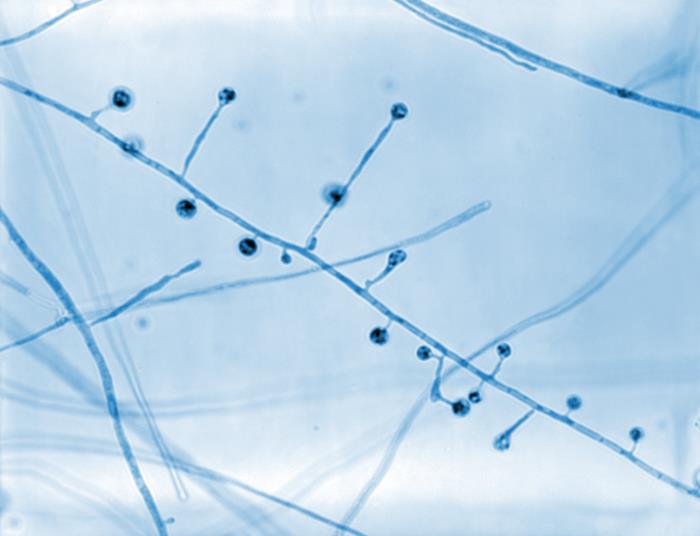
Photomicrograph showing the ultrastructural morphology exhibited by Blastomyces dermatitidis:
In this view, there are a number of conidiophores. Note how each conidiophore sprouts directly from the filamentous hyphae in a perpendicular arrangement, and that each is topped by a spherical conidium.
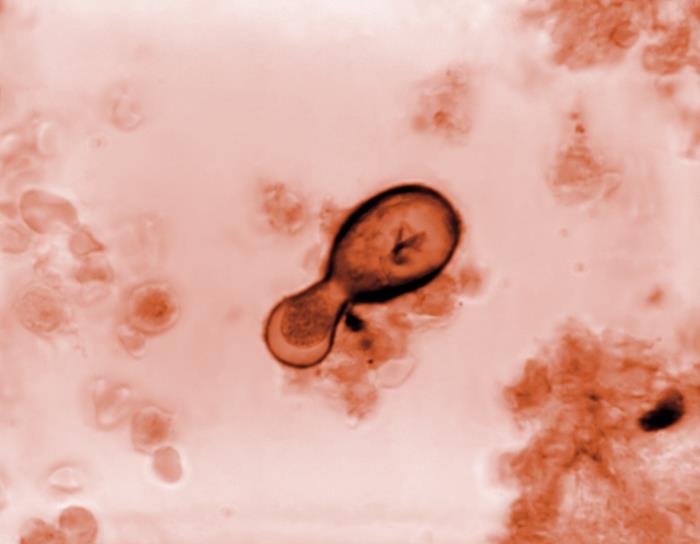
Photomicrograph of a Blastomyces dermatitidis fungal cell:
The yeast form of the organism is undergoing an asexual reproductive method known as budding, where the contents of its cell wall and internal contents are being extruded, thereby, producing a new cell.
Blastomycosis is caused by Blastomyces dermatitidis.
The conidia Conidia Mycology form of B. dermatitidis can be aerosolized by disturbing the fungal colony followed by inhalation.
Blastomycosis is more common in individuals who are immunocompromised immunocompromised A human or animal whose immunologic mechanism is deficient because of an immunodeficiency disorder or other disease or as the result of the administration of immunosuppressive drugs or radiation. Gastroenteritis, but can occur in immunocompetent individuals too.
Severity of the infection depends on a person’s immune system Immune system The body’s defense mechanism against foreign organisms or substances and deviant native cells. It includes the humoral immune response and the cell-mediated response and consists of a complex of interrelated cellular, molecular, and genetic components. Primary Lymphatic Organs.
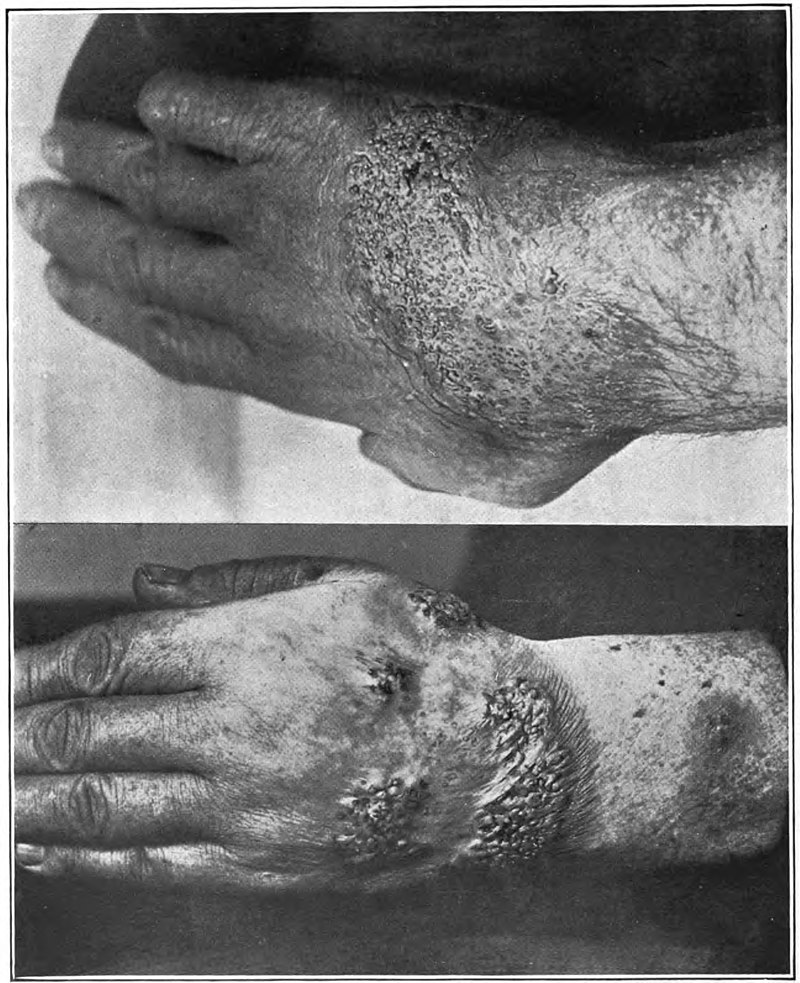
Verrucous (wart-like) lesions in the hands of a patient with blastomycosis
Image: “Blastomycosis” by Norman Purvis Walker. License: Public Domain
Nodular skin lesions from blastomycosis
Image: “Nodular skin lesions of blastomycosis” by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. License: Public DomainSpontaneous remission Remission A spontaneous diminution or abatement of a disease over time, without formal treatment. Cluster Headaches can occur, but patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship should be indicated antifungal Antifungal Azoles therapy to reduce the chances of dissemination or recurrence.