Retropharyngeal abscesses occur in the retropharyngeal space, which extends from the base of the skull Base of the skull The inferior region of the skull consisting of an internal (cerebral), and an external (basilar) surface. Skull: Anatomy to the posterior mediastinum Posterior mediastinum Mediastinum and Great Vessels: Anatomy. The abscesses occur due to extension Extension Examination of the Upper Limbs of local infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease, including upper respiratory infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease or localized infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease from trauma such as dental procedures. Infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease most commonly occur in children. Key clinical features include trismus Trismus Spasmodic contraction of the masseter muscle resulting in forceful jaw closure. This may be seen with a variety of diseases, including tetanus, as a complication of radiation therapy, trauma, or in association with neoplastic conditions. Tetanus, dysphagia Dysphagia Dysphagia is the subjective sensation of difficulty swallowing. Symptoms can range from a complete inability to swallow, to the sensation of solids or liquids becoming "stuck." Dysphagia is classified as either oropharyngeal or esophageal, with esophageal dysphagia having 2 sub-types: functional and mechanical. Dysphagia, and an inability to extend the neck Neck The part of a human or animal body connecting the head to the rest of the body. Peritonsillar Abscess. Diagnosis is confirmed by computed tomography of the neck Neck The part of a human or animal body connecting the head to the rest of the body. Peritonsillar Abscess. Management is primarily through antibiotics and surgical drainage. Complications include airway Airway ABCDE Assessment compromise, mediastinitis Mediastinitis Mediastinitis refers to an infection or inflammation involving the mediastinum (a region in the thoracic cavity containing the heart, thymus gland, portions of the esophagus, and trachea). Acute mediastinitis can be caused by bacterial infection due to direct contamination, hematogenous or lymphatic spread, or extension of infection from nearby structures. Mediastinitis, and internal jugular vein Internal jugular vein Parapharyngeal Abscess thrombosis Thrombosis Formation and development of a thrombus or blood clot in the blood vessel. Epidemic Typhus.
Last updated: May 20, 2025
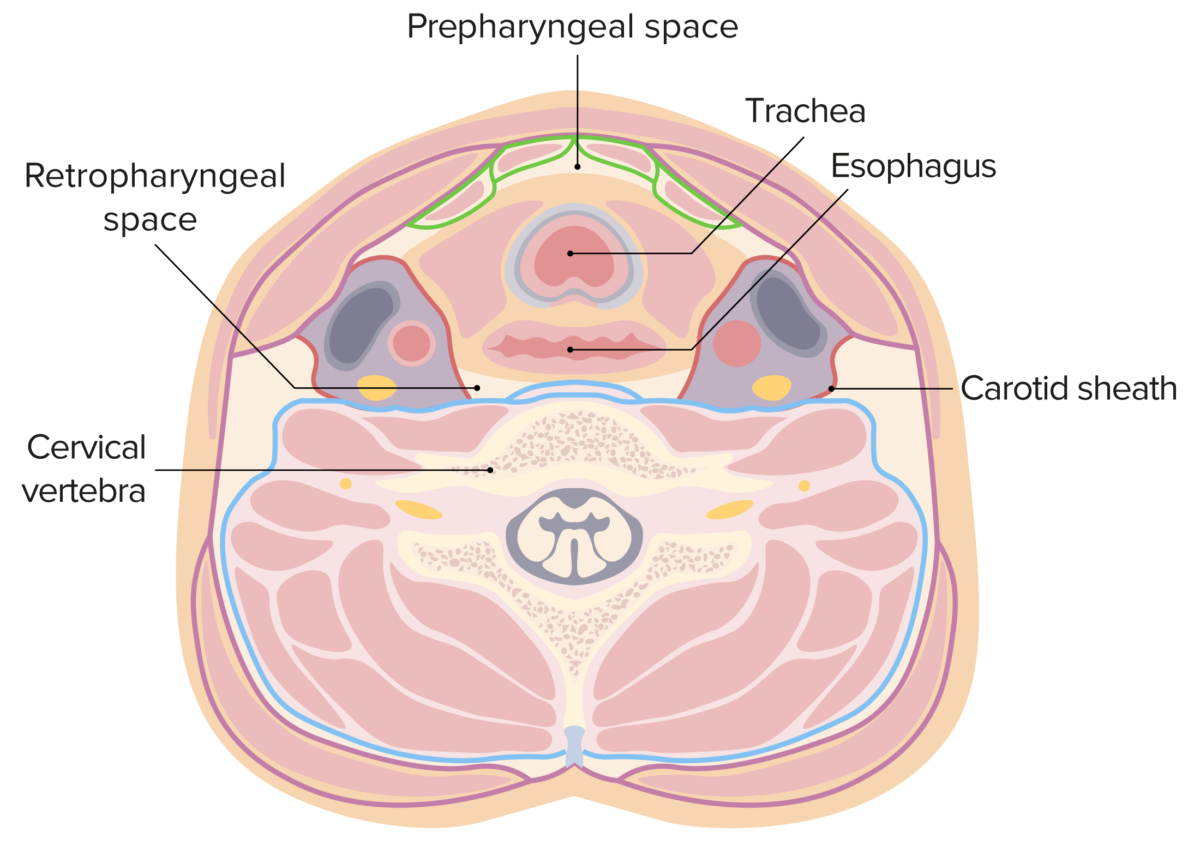
The retropharyngeal space in this figure is located between the yellow (buccopharyngeal fascia) and blue (prevertebral fascia) lines. The lateral borders are formed by the carotid sheath (red lines).
Image by Lecturio.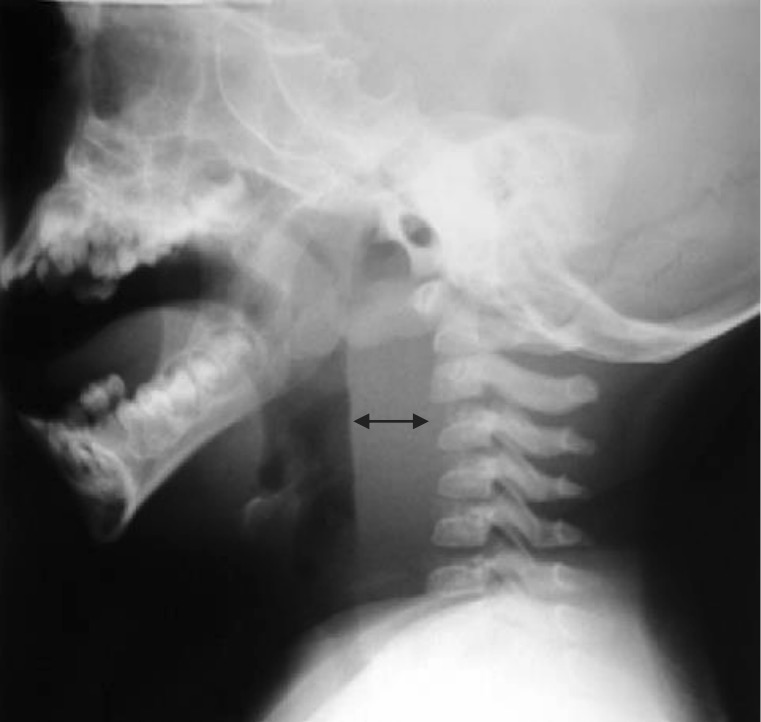
Thickening of soft tissue between the esophagus and cervical vertebrae is highly predictive of tissue edema and abscess in the retropharyngeal space.
David Swenson; Widlus DM.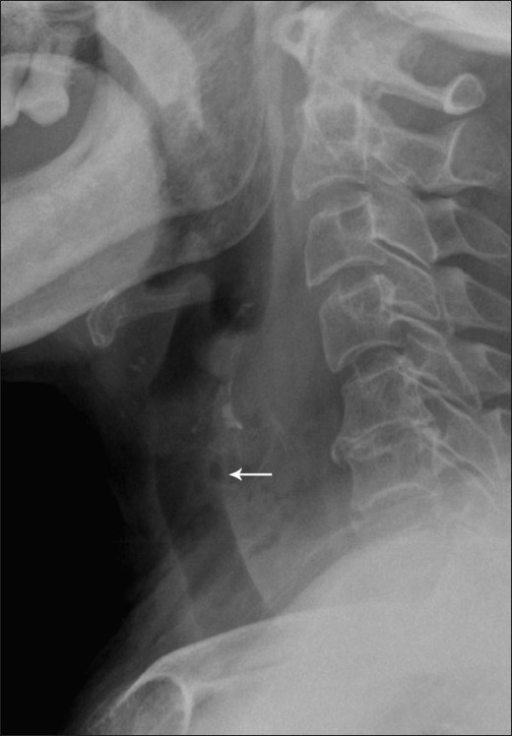
Lateral radiograph showing widening of the prevertebral space with small locules (arrow):
The findings are consistent with a retropharyngeal abscess. In this case, the abscess was caused by ingestion of a foreign body.
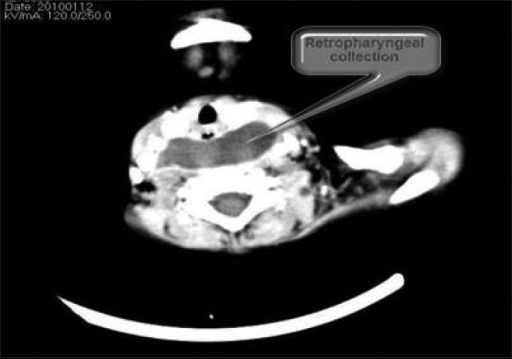
Retropharyngeal abscess:
a CT scan of the neck showing a retropharyngeal collection suggestive of an abscess
Retropharyngeal abscesses are considered the most deadly deep neck Neck The part of a human or animal body connecting the head to the rest of the body. Peritonsillar Abscess infection.
The most common complications include: