Genetic mutations Genetic Mutations Carcinogenesis are errors in DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure that can cause protein misfolding and dysfunction. There are various types of mutations, including chromosomal, point, frameshift, and expansion mutations. Chromosomal mutations occur when an abnormal number of chromosomes Chromosomes In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. DNA Types and Structure is inherited. Point mutations occur when a nucleotide is swapped for another nucleotide and can be missense, nonsense, or silent mutations. Frameshift mutations occur when a nucleotide is added or deleted, and expansion mutations occur when a given trinucleotide sequence is repeated along the chromosome Chromosome In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. Basic Terms of Genetics. Genetic mutations Genetic Mutations Carcinogenesis are the basis for most inherited diseases. Common disorders caused by DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure mutations include sickle cell disease Sickle cell disease Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of genetic disorders in which an abnormal Hb molecule (HbS) transforms RBCs into sickle-shaped cells, resulting in chronic anemia, vasoocclusive episodes, pain, and organ damage. Sickle Cell Disease, Huntington disease Huntington disease Huntington disease (HD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder with an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance and poor prognosis. It is caused by cytosine-adenine-guanine (CAG) trinucleotide repeats in the huntingtin gene (HTT). The most common clinical presentation in adulthood is a movement disorder known as chorea: abrupt, involuntary movements of the face, trunk, and limbs. Huntington Disease, and Tay-Sachs disease Tay-Sachs disease Tay-Sachs disease is an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorder caused by genetic mutations in the hexosaminidase A (HEXA) gene, leading to progressive neurodegeneration. Classic symptoms in infants include rapid degeneration of cognitive and neuromuscular abilities, progressive blindness, and a macular cherry-red spot on physical examination. Tay-Sachs Disease.
Last updated: Apr 4, 2023
Chromosomal numerical abnormalities occur when there is a gain or loss of an entire chromosome Chromosome In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. Basic Terms of Genetics.
Monosomy is a loss of 1 chromosome Chromosome In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. Basic Terms of Genetics (pair becomes 1 chromosome Chromosome In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. Basic Terms of Genetics):
Trisomy is a gain of 1 chromosome Chromosome In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. Basic Terms of Genetics (pair becomes 3 chromosomes Chromosomes In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. DNA Types and Structure):
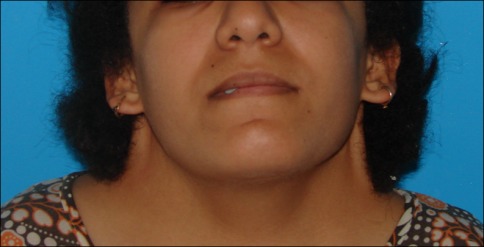
Webbed neck, seen in Turner syndrome
Image: “Preoperative photo” by Imen Mehri Turki. License: CC BY 4.0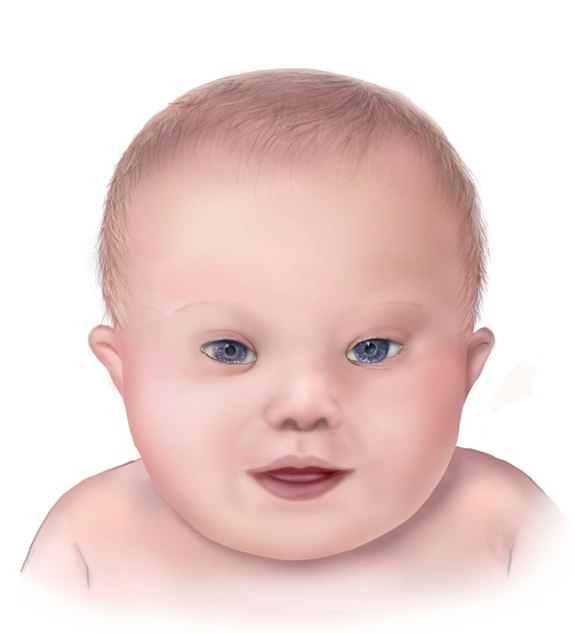
Facial features of a baby with Down syndrome
Image: “A drawing of the facial features of Down syndrome” by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities. License: Public DomainA point mutation is a mutation that affects only 1 nucleotide in a DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure sequence. The nucleotide change can lead to the following outcomes:

Silent mutation:
A silent mutation is a single nucleotide substitution that results in the translation of the same amino acid. Thus, protein function is not affected.
Met: methionine
Pro: proline
Thr: threonine
Arg: arginine
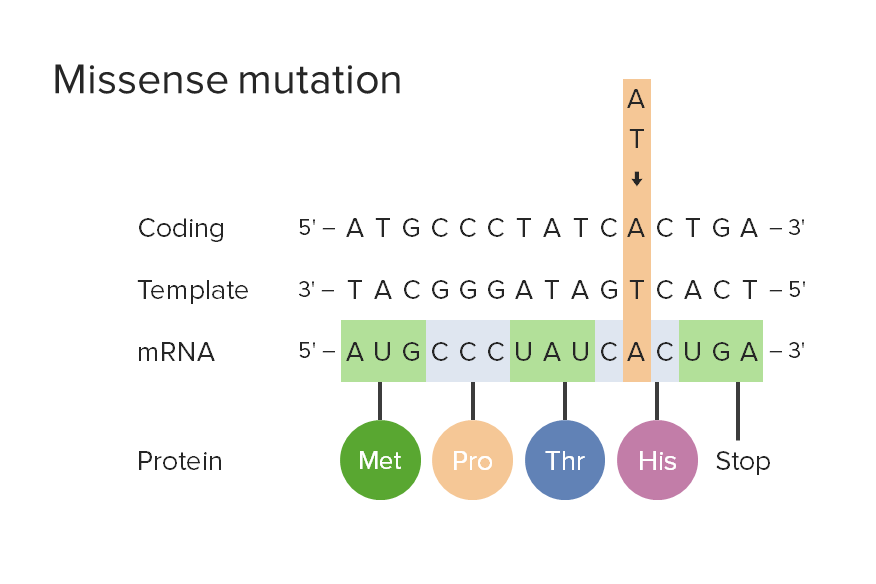
Missense mutation:
Missense mutations result when a change of a single base pair causes the substitution of a different amino acid in the resulting protein. Amino acid substitution may have no effect or may render the protein nonfunctional.
Met: methionine
Pro: proline
Thr: threonine
His: histidine
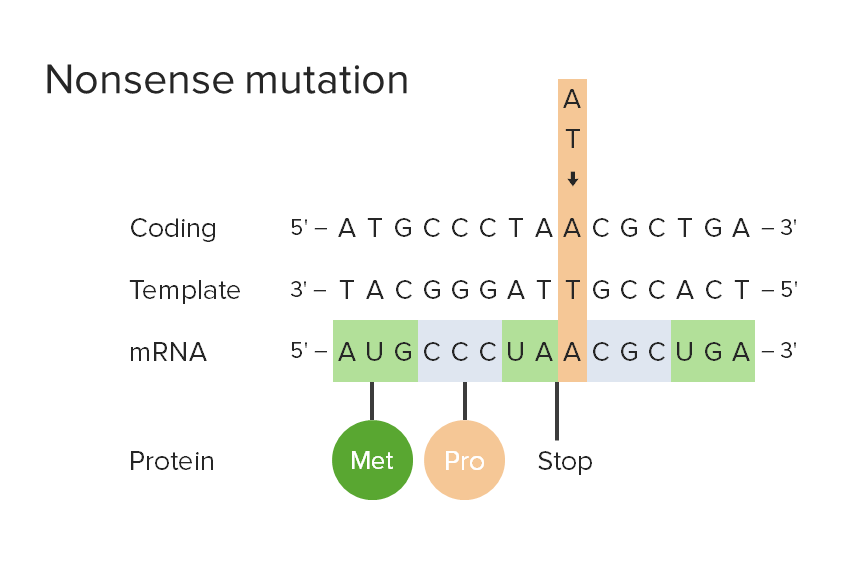
Nonsense mutation:
A sense codon that corresponds to 1 of the 20 amino acids specified by the genetic code is changed to a stop codon.
Met: methionine
Pro: proline
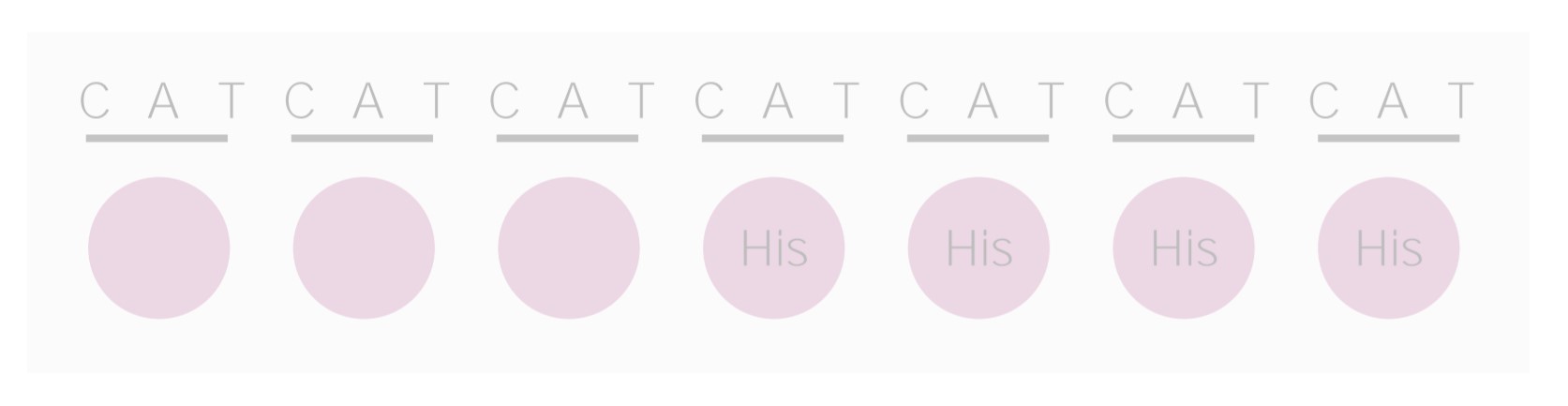
Frameshift mutation:
Frameshift mutations can be due to the addition or insertion of nucleotides that changes the length of the gene, thus affecting protein synthesis.
His: histidine
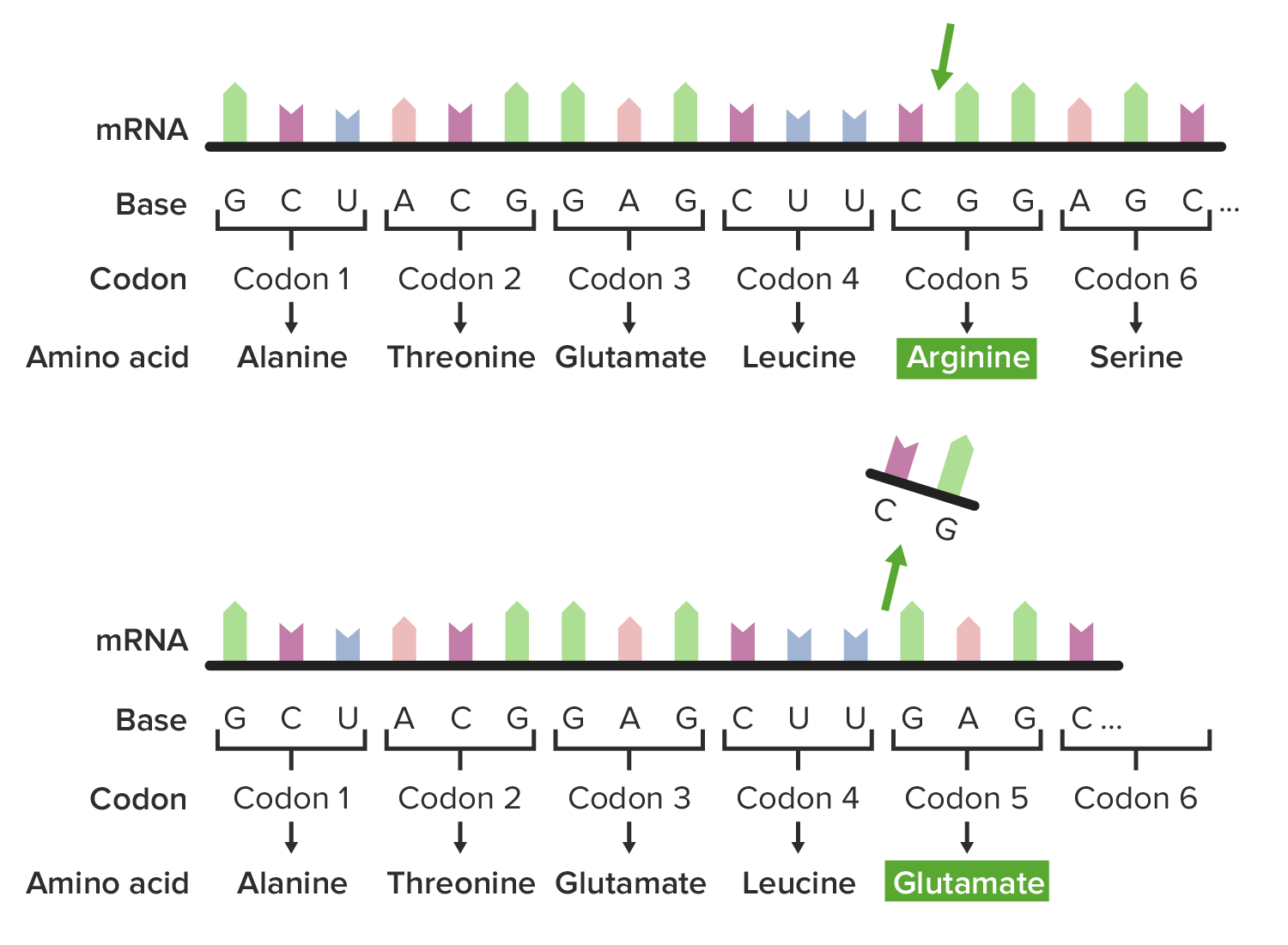
A frameshift mutation in which deletion of CG alters the amino acid sequence:
The 5th amino acid, arginine, is now translated to glutamate.
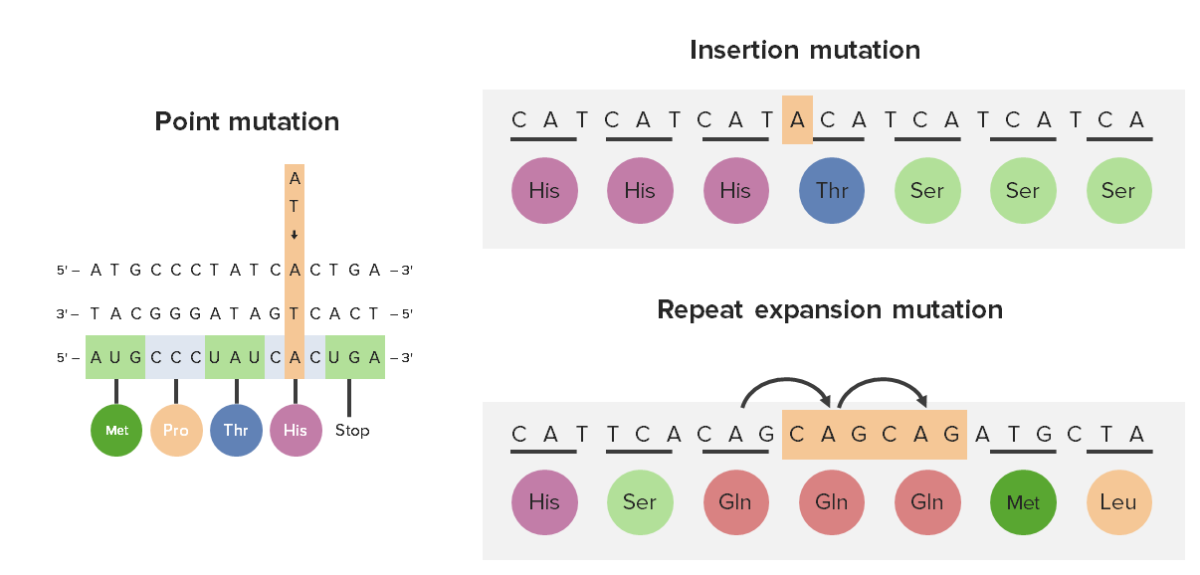
Trinucleotide repeat expansion (repeat expansion mutation) in relation to point mutations and insertion mutations
Met: methionine
Pro: proline
Thr: threonine
His: histidine
Ser: serine
Gln: glutamine
Leu: leucine