The phases of the cell cycle include interphase (G1, S, and G2) and mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase). The cell’s progression through these phases is punctuated by checkpoints regulated by cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases Kinases Macrolides and Ketolides, tumor Tumor Inflammation suppressors, and their antagonists.
Last updated: Apr 25, 2025
The cell cycle describes the cyclic sequence of events through which a eukaryotic Eukaryotic Eukaryotes can be single-celled or multicellular organisms and include plants, animals, fungi, and protozoa. Eukaryotic cells contain a well-organized nucleus contained by a membrane, along with other membrane-bound organelles. Cell Types: Eukaryotic versus Prokaryotic, proliferating parent cell splits into 2 identical daughter cells.
G1, S, and G2 phases are grouped together as interphase.
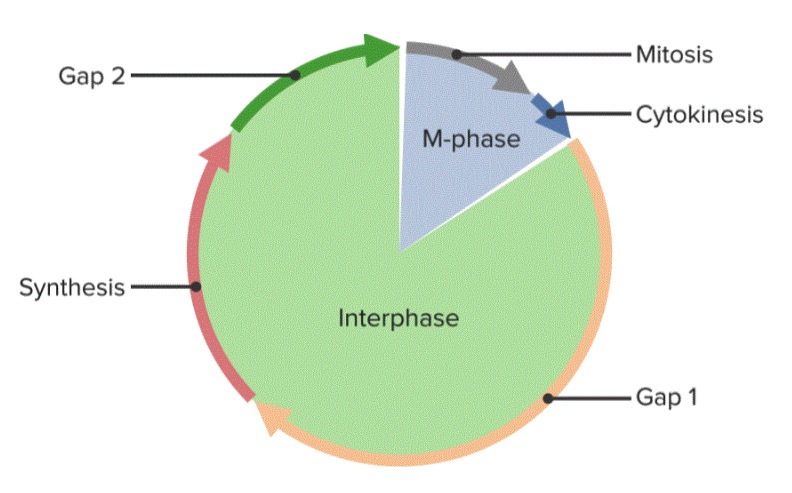
The cell cycle, divided into 5 phases
Image by Lecturio.During mitosis, the cell’s duplicated DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure is separated and distributed to 2 identical daughter cells. The process lasts approximately 1 hour.
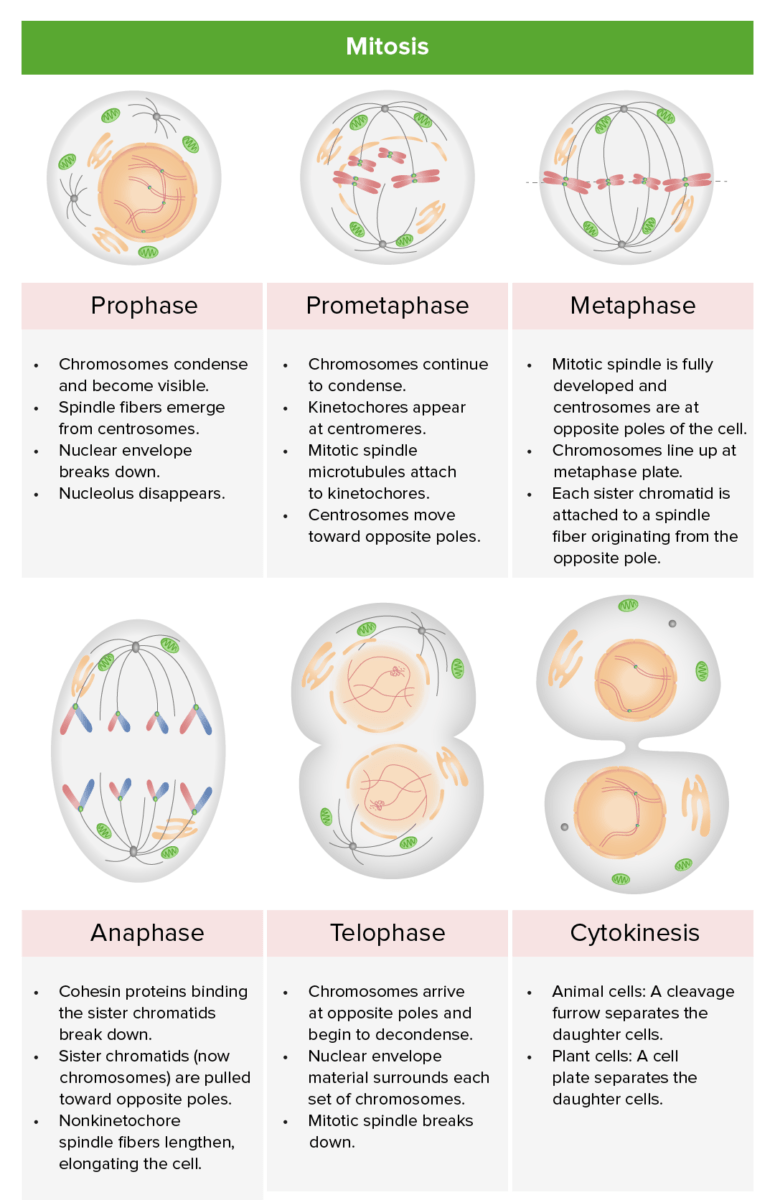
Review of the stages of mitosis: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase: During karyotyping, the cell cycle is halted in metaphase, usually by adding an agent like colchicine (inhibits microtubule polymerization to halt mitosis).
Image by Lecturio.The cell cycle is tightly regulated. Not passing a checkpoint should trigger Trigger The type of signal that initiates the inspiratory phase by the ventilator Invasive Mechanical Ventilation programmed cell death Cell death Injurious stimuli trigger the process of cellular adaptation, whereby cells respond to withstand the harmful changes in their environment. Overwhelmed adaptive mechanisms lead to cell injury. Mild stimuli produce reversible injury. If the stimulus is severe or persistent, injury becomes irreversible. Apoptosis is programmed cell death, a mechanism with both physiologic and pathologic effects. Cell Injury and Death ( apoptosis Apoptosis A regulated cell death mechanism characterized by distinctive morphologic changes in the nucleus and cytoplasm, including the endonucleolytic cleavage of genomic DNA, at regularly spaced, internucleosomal sites, I.e., DNA fragmentation. It is genetically-programmed and serves as a balance to mitosis in regulating the size of animal tissues and in mediating pathologic processes associated with tumor growth. Ischemic Cell Damage). Apoptosis Apoptosis A regulated cell death mechanism characterized by distinctive morphologic changes in the nucleus and cytoplasm, including the endonucleolytic cleavage of genomic DNA, at regularly spaced, internucleosomal sites, I.e., DNA fragmentation. It is genetically-programmed and serves as a balance to mitosis in regulating the size of animal tissues and in mediating pathologic processes associated with tumor growth. Ischemic Cell Damage failure results in mutation Mutation Genetic mutations are errors in DNA that can cause protein misfolding and dysfunction. There are various types of mutations, including chromosomal, point, frameshift, and expansion mutations. Types of Mutations accumulation, leading to disease.
The cell cycle begins when the cell has:
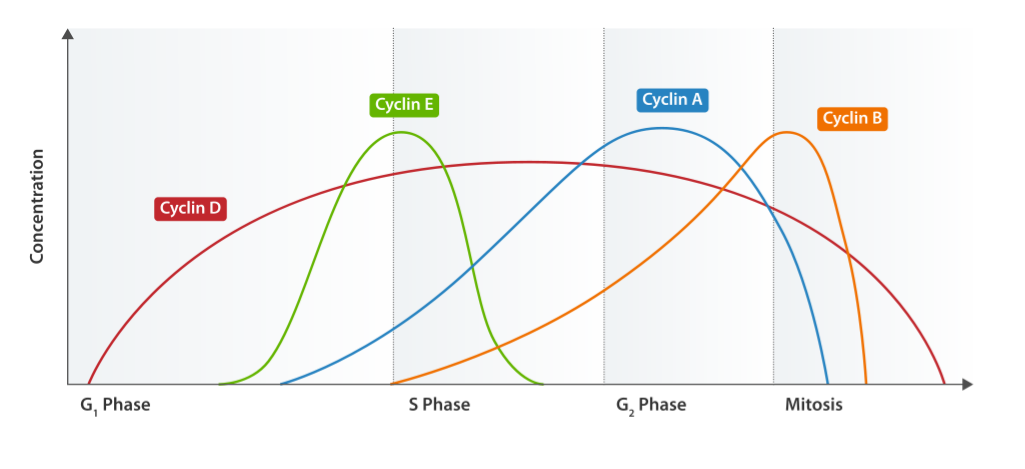
Cyclin expression cycle
Image: “Cyclin Expression” by T4taylor. License: Public Domain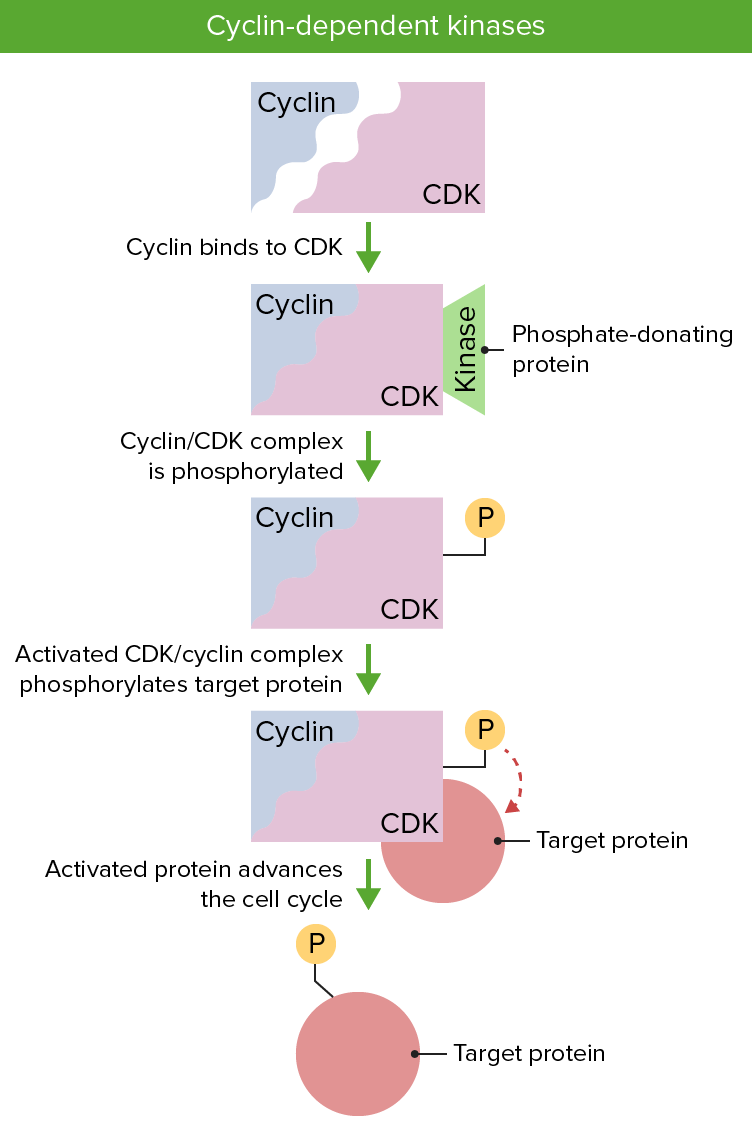
Cyclin and cyclin dependent kinases are essential to regulation of the cell cycle. Presence of both proteins is necessary and their activation via phosphorylation permits the progression of the cell cycle.
Image by Lecturio.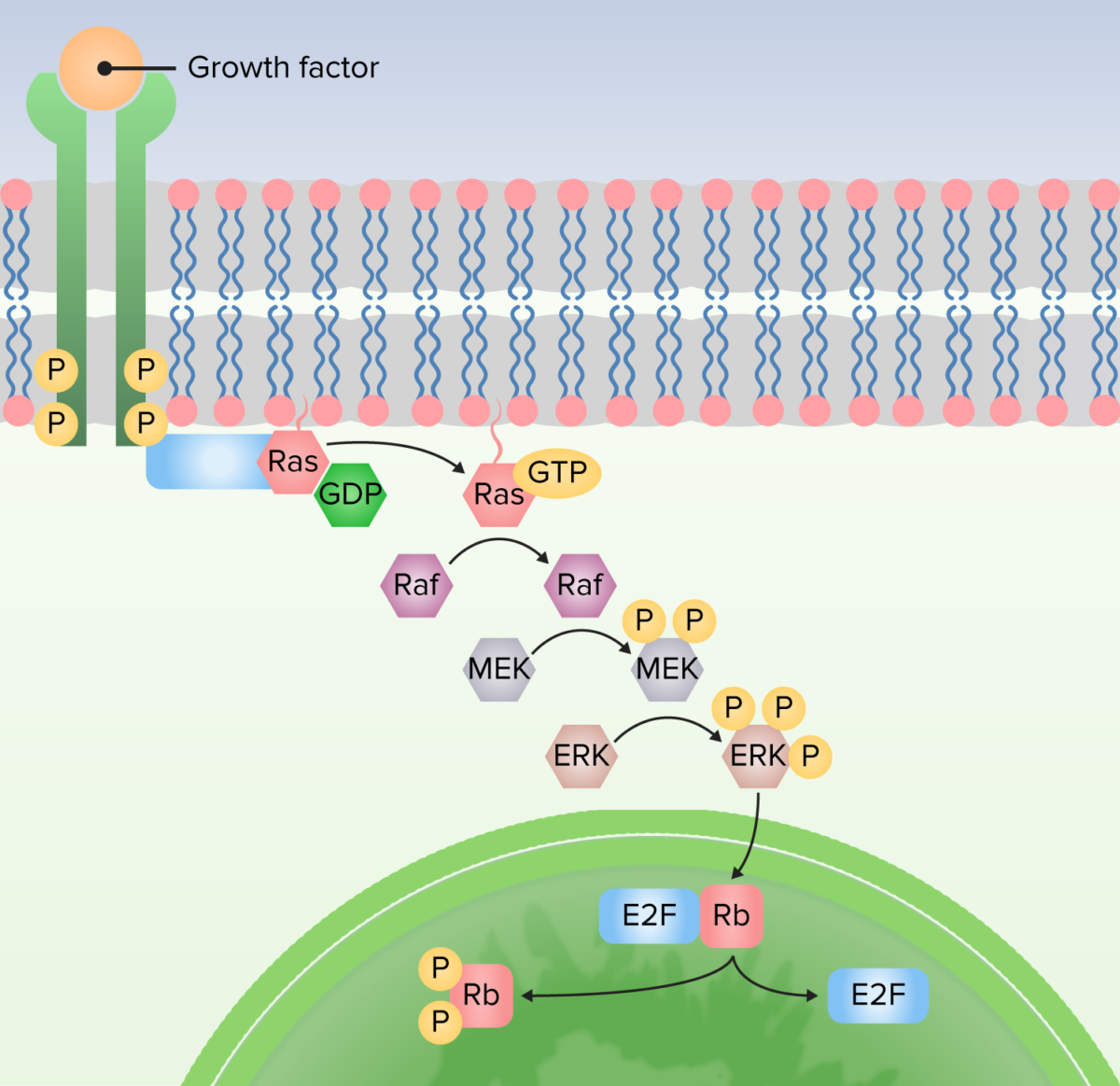
1. Protein bound to receptor to activate Ras by exchanging guanosine diphosphate (GDP) for guanosine triphosphate (GTP).
2. Ras activates the first kinase (Raf).
3. Raf activates the second kinase (MEK).
4. MEK activates MAP kinases (ERK).
5. MAP kinase (ERK) activates proteins to produce cellular responses, including transcription factors that alter gene expression.