A cell is a complex unit that performs several complex functions. An organelle is a specialized subunit within a cell that fulfills a specific role or function. Organelles are enclosed within their own lipid bilayers or are unbound by membranes. If a cell is viewed as an organism, the organelles are an equivalent of the cell’s internal organs. Cell organelles carry out various functions from maintaining the shape of the cell to reproduction, movement, protein synthesis Synthesis Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), energy production, and the transport of substances in and out of the cell.
Last updated: Mar 27, 2025
Organelles are specialized structures within the eukaryotic Eukaryotic Eukaryotes can be single-celled or multicellular organisms and include plants, animals, fungi, and protozoa. Eukaryotic cells contain a well-organized nucleus contained by a membrane, along with other membrane-bound organelles. Cell Types: Eukaryotic versus Prokaryotic cell that carry out specific functions (cell’s “internal organs”).
Membrane-bound organelles:
Non-membrane-bound organelles:
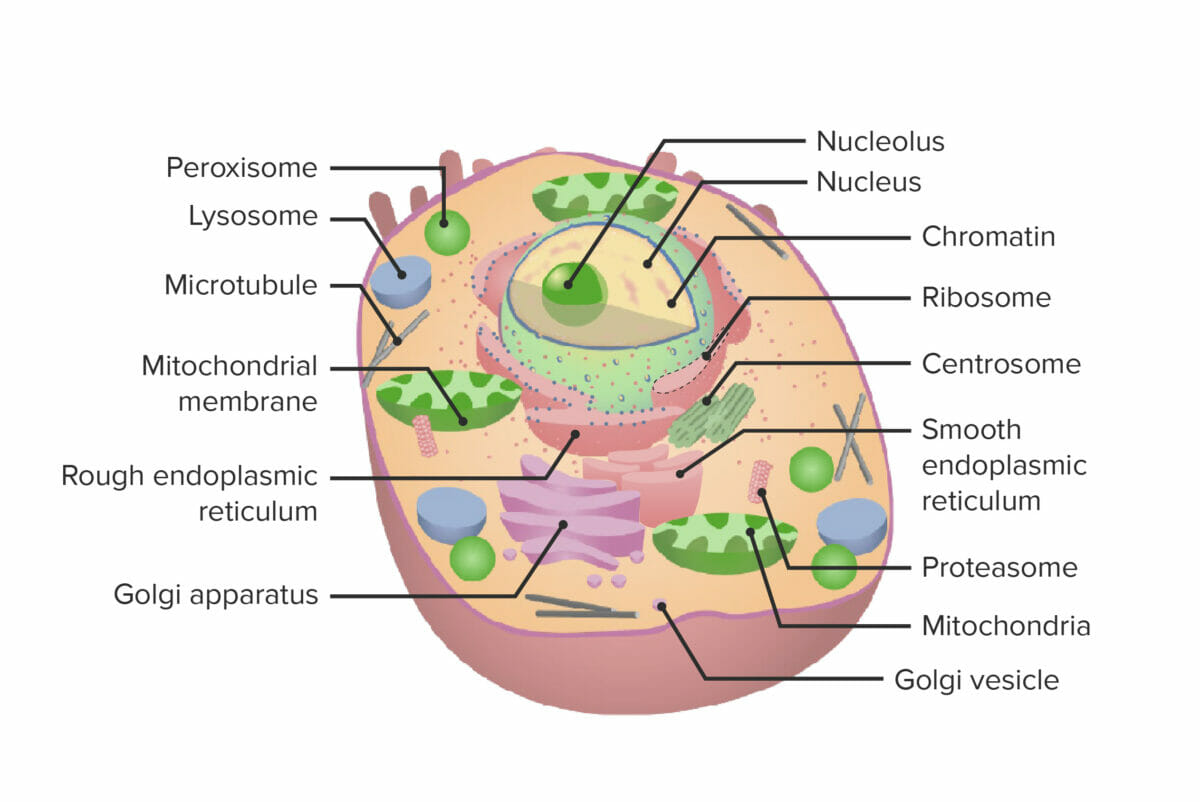
The cell and cellular organelles
ER: endoplasmic reticulum
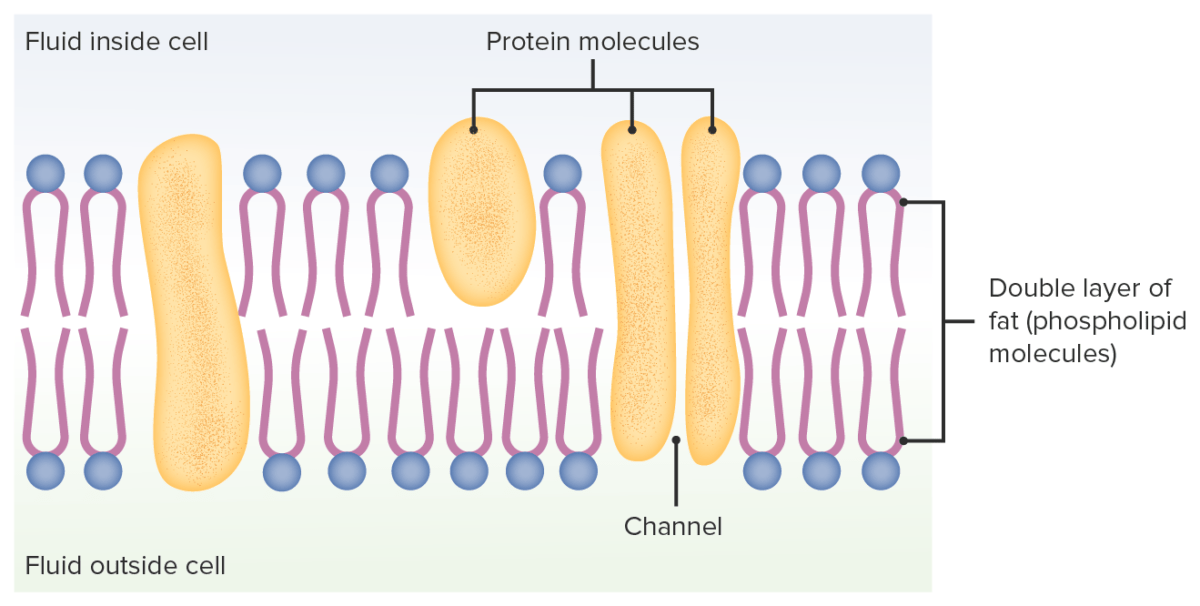
Illustration of the structure of plasma membrane
Image by Lecturio.Structure:
Functions:
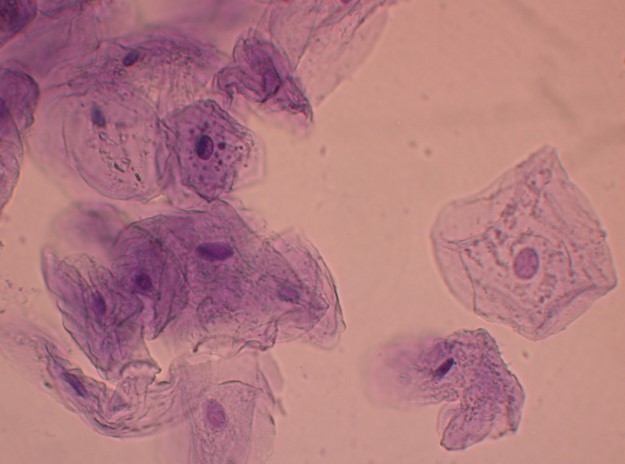
Eukaryotic cells containing nuclei (darker purple)
Image: “Eukayotic Cell” by Jlipuma1. License: CC BY 4.0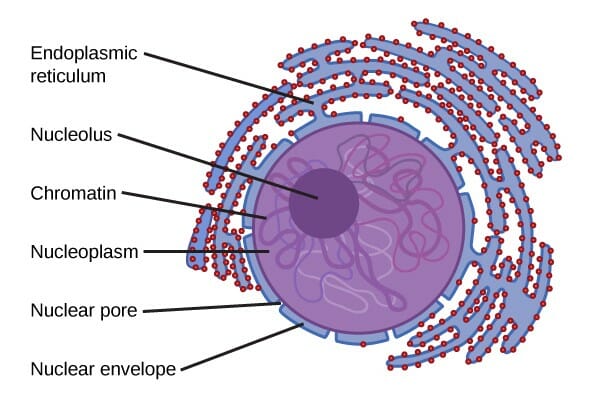
Illustration of the structure of the nucleus
Image: “Figure 4.11 – The nucleus” by OpenStax College. License: CC BY 4.0Structure:
Functions:
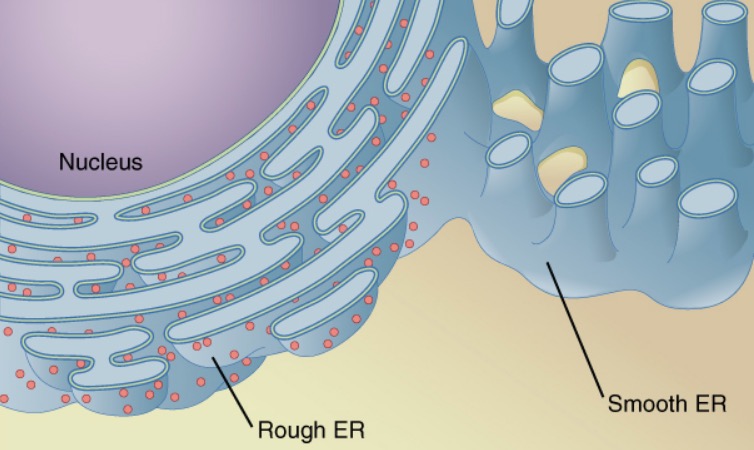
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER):
A winding network of thin membranous sacs found in close association with the cell nucleus
Structure:
Functions:
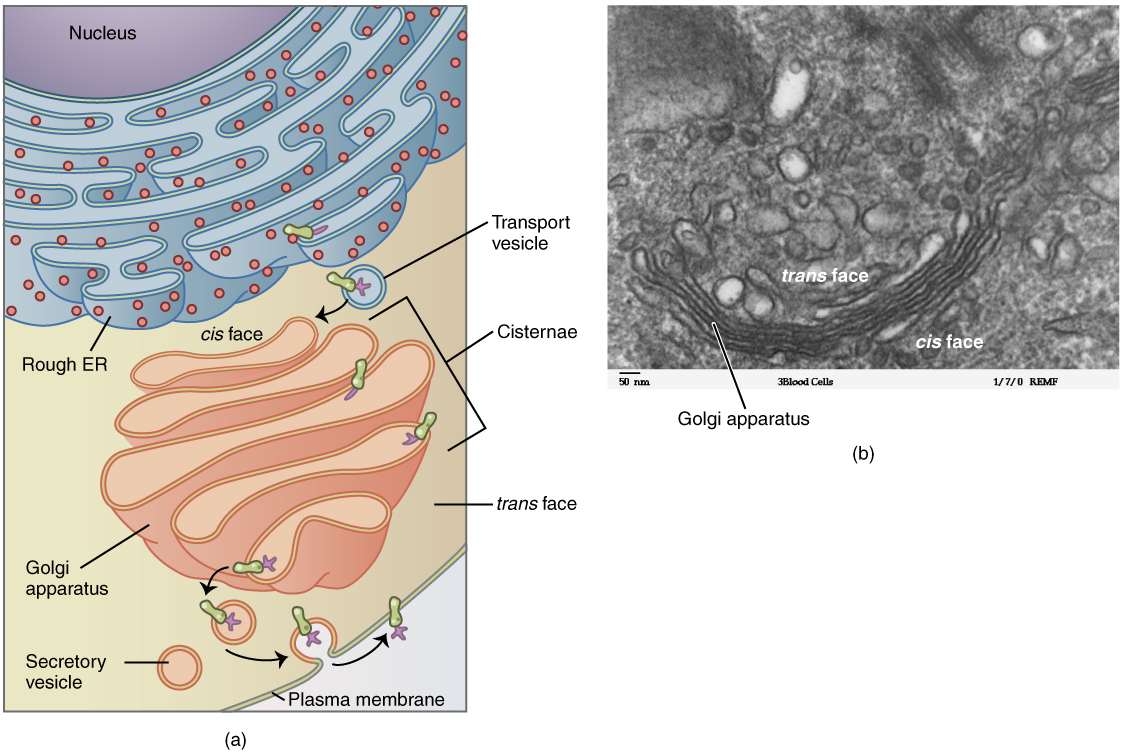
Golgi apparatus as part of the secretory pathway creating a plasma membrane-bound protein:
(a) Schematic diagram
(b) Electron microscope image
Structure:
Functions:
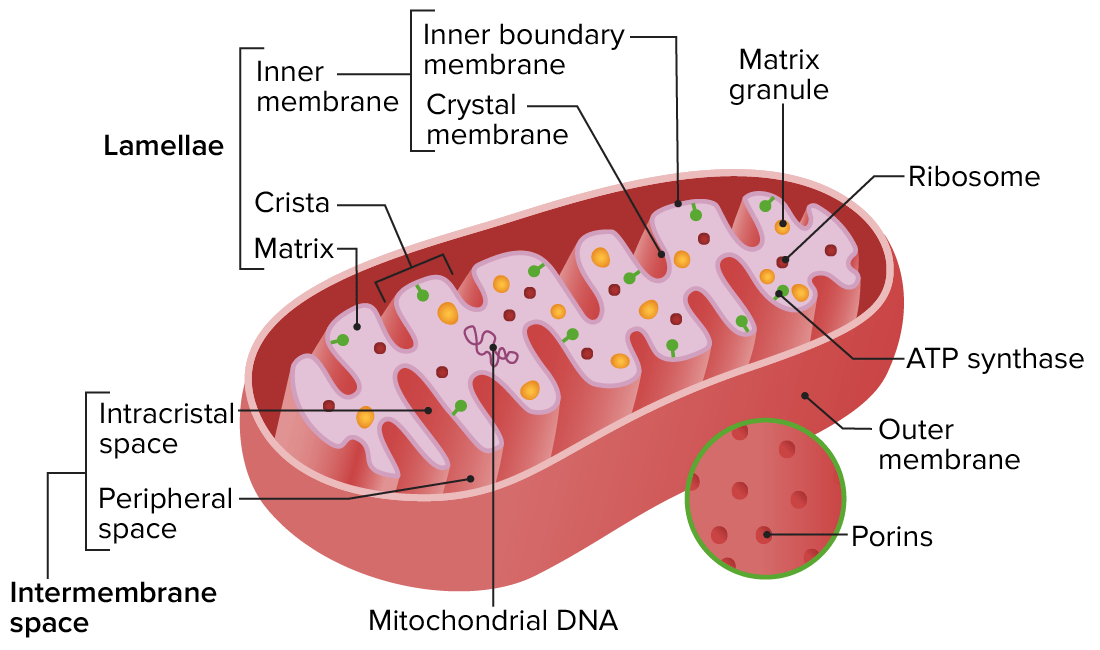
Structural features of mitochondria
Image by Lecturio.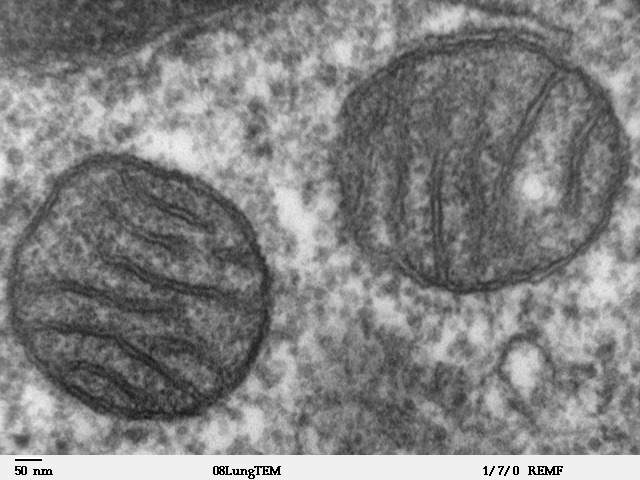
Mitochondria in mammalian lung: transmission electron microscope image
Image: “Mitochondria, mammalian lung” by Louisa Howard. License: Public DomainStructure:
Functions:
Structure:
Function:
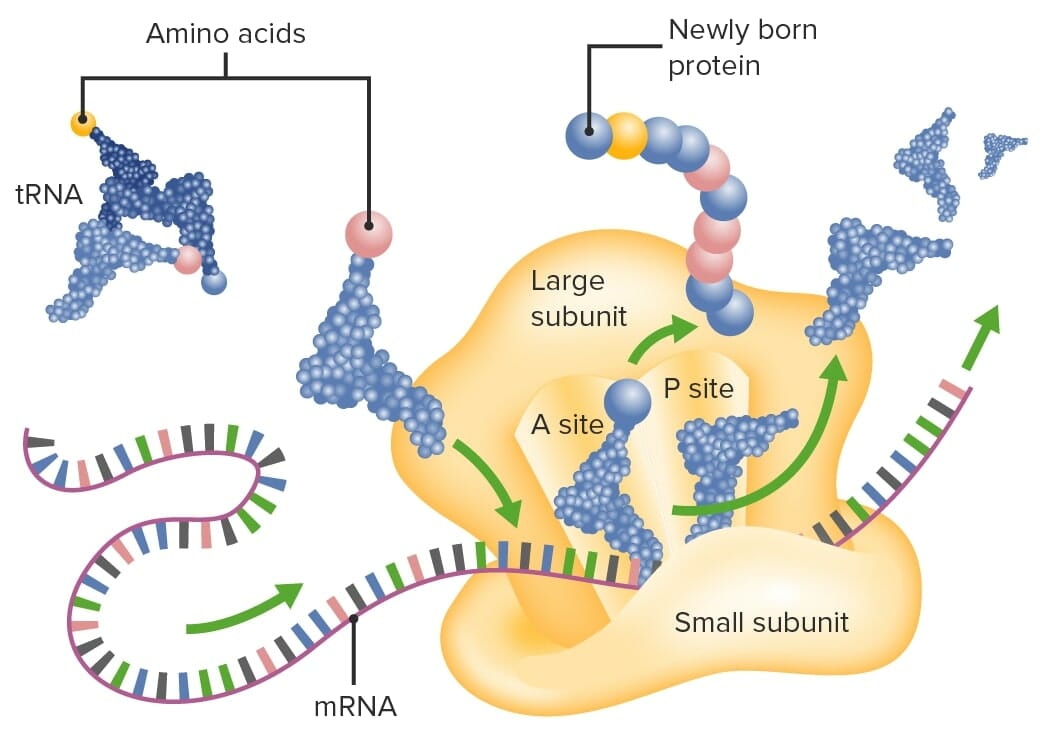
Ribosomes (composed of a small and large subunit) translate mRNA into a polypeptide chain by attracting tRNA (which are tethered to amino acids) with complementary anticodon sequences.
tRNA: transfer RNA
A site: aminoacyl site
P site: peptidyl site
mRNA: messenger RNA
Microphotography of the nucleus and nucleolus
Image: “Nucleus&Nucleolus”. License: Public DomainStructure:
Functions:
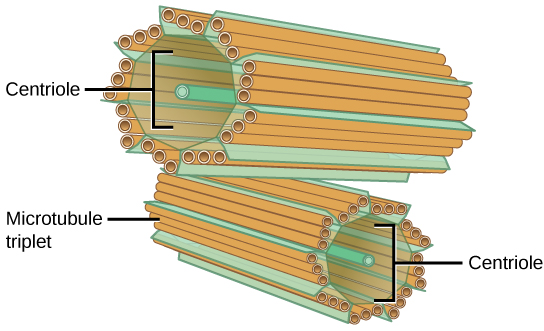
Schematic diagram of centrioles: cylindrical organelles comprising microtubule triplets
Image: “Figure 04 03 08” by CNX OpenStax. License: CC BY 4.0