Electrolytes are mineral salts that dissolve in water and dissociate into charged particles called ions, which can be either be positively (cations) or negatively (anions) charged. Electrolytes are distributed in the extracellular and intracellular compartments in different concentrations. Electrolytes are essential for various basic life-sustaining functions such as maintaining electrical neutrality in cells, generating action potentials in nerves and muscles, and maintaining normal blood pH pH The quantitative measurement of the acidity or basicity of a solution. Acid-Base Balance. The most important electrolytes are sodium Sodium A member of the alkali group of metals. It has the atomic symbol na, atomic number 11, and atomic weight 23. Hyponatremia, potassium Potassium An element in the alkali group of metals with an atomic symbol k, atomic number 19, and atomic weight 39. 10. It is the chief cation in the intracellular fluid of muscle and other cells. Potassium ion is a strong electrolyte that plays a significant role in the regulation of fluid volume and maintenance of the water-electrolyte balance. Hyperkalemia, chloride, magnesium, calcium, phosphate, and bicarbonate. In order for these electrolytes to participate in biochemical reactions and cellular processes, regulatory mechanisms are in place, which help maintain homeostasis Homeostasis The processes whereby the internal environment of an organism tends to remain balanced and stable. Cell Injury and Death.
Last updated: May 17, 2024
The ICF ICF The fluid inside cells. Body Fluid Compartments and ECF compartments have different and unequal electrolyte distribution to maintain physiological function.
Intracellular fluid Intracellular fluid The fluid inside cells. Body Fluid Compartments:
Extracellular fluid Extracellular fluid The fluid of the body that is outside of cells. It is the external environment for the cells. Body Fluid Compartments:
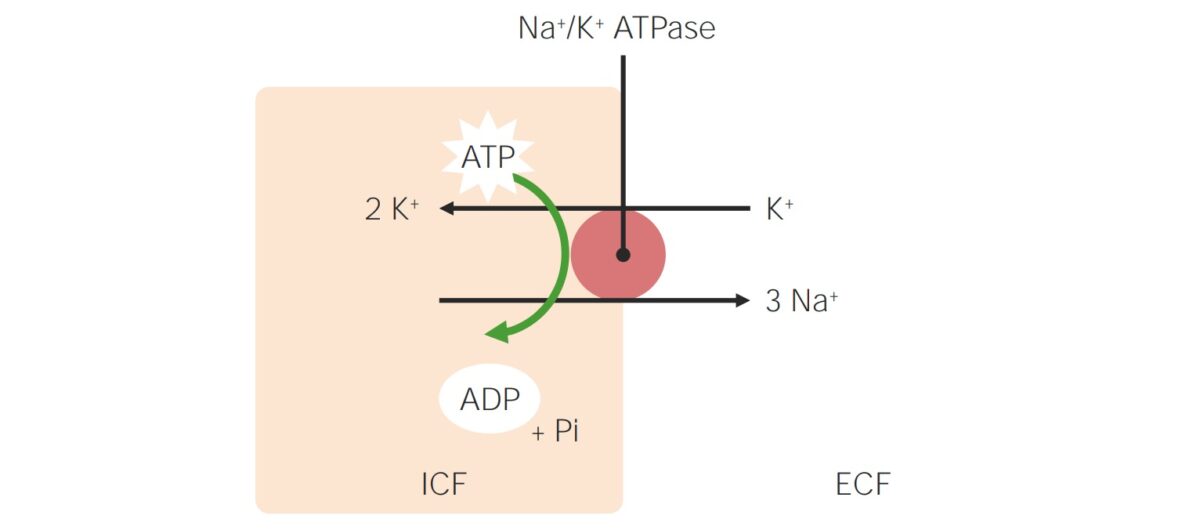
Sodium-potassium pump:
Transmembrane ATPase maintains a gradient of higher Na+ concentration in the ECF and a higher K+ concentration in the ICF. For every ATP consumed, the ATPase pumps 3 Na+ out of the cell and 2 K+ into the cell, which stabilizes the cellular resting membrane potential and cell volume.
Pi: inorganic phosphate
ECF: extracellular fluid
ICF: intracellular fluid
Chloride homeostasis Homeostasis The processes whereby the internal environment of an organism tends to remain balanced and stable. Cell Injury and Death:
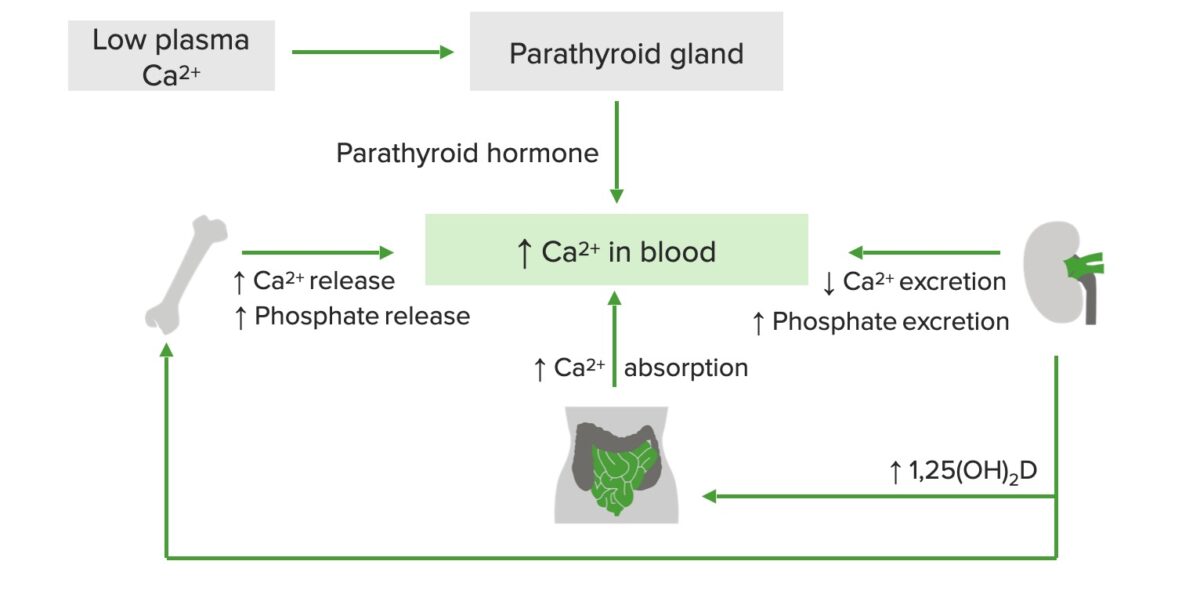
Schematic diagram of calcium (Ca²⁺) regulation:
Low plasma Ca²⁺ stimulates the release of parathyroid hormone (PTH), which increases Ca²⁺ and phosphate release from the bone, Ca²⁺ absorption in the GI tract, and vitamin D production in the kidneys. Active vitamin D, in turn, increases Ca²⁺ release from the bones and Ca²⁺ absorption in the small intestine.
CO2 + H2O ⇆ H2CO3 ⇆ H+ + HCO3–
To maintain homeostasis Homeostasis The processes whereby the internal environment of an organism tends to remain balanced and stable. Cell Injury and Death, the following mechanisms are triggered to keep the pH pH The quantitative measurement of the acidity or basicity of a solution. Acid-Base Balance in the physiological range (7.35–7.45):