There are 2 primary portions of the adrenal glands Adrenal Glands The adrenal glands are a pair of retroperitoneal endocrine glands located above the kidneys. The outer parenchyma is called the adrenal cortex and has 3 distinct zones, each with its own secretory products. Beneath the cortex lies the adrenal medulla, which secretes catecholamines involved in the fight-or-flight response. Adrenal Glands: Anatomy, the adrenal medulla Adrenal Medulla The inner portion of the adrenal gland. Derived from ectoderm, adrenal medulla consists mainly of chromaffin cells that produces and stores a number of neurotransmitters, mainly adrenaline (epinephrine) and norepinephrine. The activity of the adrenal medulla is regulated by the sympathetic nervous system. Adrenal Glands: Anatomy and the adrenal cortex Adrenal Cortex The outer layer of the adrenal gland. It is derived from mesoderm and comprised of three zones (outer zona glomerulosa, middle zona fasciculata, and inner zona reticularis) with each producing various steroids preferentially, such as aldosterone; hydrocortisone; dehydroepiandrosterone; and androstenedione. Adrenal cortex function is regulated by pituitary adrenocorticotropin. Adrenal Glands: Anatomy. Each of these areas secretes different hormones Hormones Hormones are messenger molecules that are synthesized in one part of the body and move through the bloodstream to exert specific regulatory effects on another part of the body. Hormones play critical roles in coordinating cellular activities throughout the body in response to the constant changes in both the internal and external environments. Hormones: Overview and Types and has different regulatory mechanisms. The adrenal medulla Adrenal Medulla The inner portion of the adrenal gland. Derived from ectoderm, adrenal medulla consists mainly of chromaffin cells that produces and stores a number of neurotransmitters, mainly adrenaline (epinephrine) and norepinephrine. The activity of the adrenal medulla is regulated by the sympathetic nervous system. Adrenal Glands: Anatomy is the inner portion of the gland, secreting epinephrine Epinephrine The active sympathomimetic hormone from the adrenal medulla. It stimulates both the alpha- and beta- adrenergic systems, causes systemic vasoconstriction and gastrointestinal relaxation, stimulates the heart, and dilates bronchi and cerebral vessels. Sympathomimetic Drugs and, to a lesser degree, norepinephrine Norepinephrine Precursor of epinephrine that is secreted by the adrenal medulla and is a widespread central and autonomic neurotransmitter. Norepinephrine is the principal transmitter of most postganglionic sympathetic fibers, and of the diffuse projection system in the brain that arises from the locus ceruleus. Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNS. These hormones Hormones Hormones are messenger molecules that are synthesized in one part of the body and move through the bloodstream to exert specific regulatory effects on another part of the body. Hormones play critical roles in coordinating cellular activities throughout the body in response to the constant changes in both the internal and external environments. Hormones: Overview and Types function in conjunction with the sympathetic nervous system Nervous system The nervous system is a small and complex system that consists of an intricate network of neural cells (or neurons) and even more glial cells (for support and insulation). It is divided according to its anatomical components as well as its functional characteristics. The brain and spinal cord are referred to as the central nervous system, and the branches of nerves from these structures are referred to as the peripheral nervous system. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification and contribute to the fight-or-flight response. The adrenal cortex Adrenal Cortex The outer layer of the adrenal gland. It is derived from mesoderm and comprised of three zones (outer zona glomerulosa, middle zona fasciculata, and inner zona reticularis) with each producing various steroids preferentially, such as aldosterone; hydrocortisone; dehydroepiandrosterone; and androstenedione. Adrenal cortex function is regulated by pituitary adrenocorticotropin. Adrenal Glands: Anatomy is the outer portion of the gland and is part of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. The cortex secretes mineralocorticoids Mineralocorticoids Mineralocorticoids are a drug class within the corticosteroid family and fludrocortisone is the primary medication within this class. Fludrocortisone is a fluorinated analog of cortisone. The fluorine moiety protects the drug from isoenzyme inactivation in the kidney, allowing it to exert its mineralocorticoid effect. Mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids Glucocorticoids Glucocorticoids are a class within the corticosteroid family. Glucocorticoids are chemically and functionally similar to endogenous cortisol. There are a wide array of indications, which primarily benefit from the antiinflammatory and immunosuppressive effects of this class of drugs. Glucocorticoids, and androgens Androgens Androgens are naturally occurring steroid hormones responsible for development and maintenance of the male sex characteristics, including penile, scrotal, and clitoral growth, development of sexual hair, deepening of the voice, and musculoskeletal growth. Androgens and Antiandrogens. The mineralocorticoid aldosterone Aldosterone A hormone secreted by the adrenal cortex that regulates electrolyte and water balance by increasing the renal retention of sodium and the excretion of potassium. Hyperkalemia is primarily involved in fluid volume and potassium Potassium An element in the alkali group of metals with an atomic symbol k, atomic number 19, and atomic weight 39. 10. It is the chief cation in the intracellular fluid of muscle and other cells. Potassium ion is a strong electrolyte that plays a significant role in the regulation of fluid volume and maintenance of the water-electrolyte balance. Hyperkalemia regulation. The glucocorticoids Glucocorticoids Glucocorticoids are a class within the corticosteroid family. Glucocorticoids are chemically and functionally similar to endogenous cortisol. There are a wide array of indications, which primarily benefit from the antiinflammatory and immunosuppressive effects of this class of drugs. Glucocorticoids (e.g., cortisol Cortisol Glucocorticoids) provide the body with immediate energy and have antiinflammatory properties. The androgens Androgens Androgens are naturally occurring steroid hormones responsible for development and maintenance of the male sex characteristics, including penile, scrotal, and clitoral growth, development of sexual hair, deepening of the voice, and musculoskeletal growth. Androgens and Antiandrogens stimulate secondary sex characteristics Secondary sex characteristics Gonadal Hormones.
Last updated: May 17, 2024
The adrenal glands Adrenal Glands The adrenal glands are a pair of retroperitoneal endocrine glands located above the kidneys. The outer parenchyma is called the adrenal cortex and has 3 distinct zones, each with its own secretory products. Beneath the cortex lies the adrenal medulla, which secretes catecholamines involved in the fight-or-flight response. Adrenal Glands: Anatomy have 2 primary areas with separate functions and regulatory mechanisms.
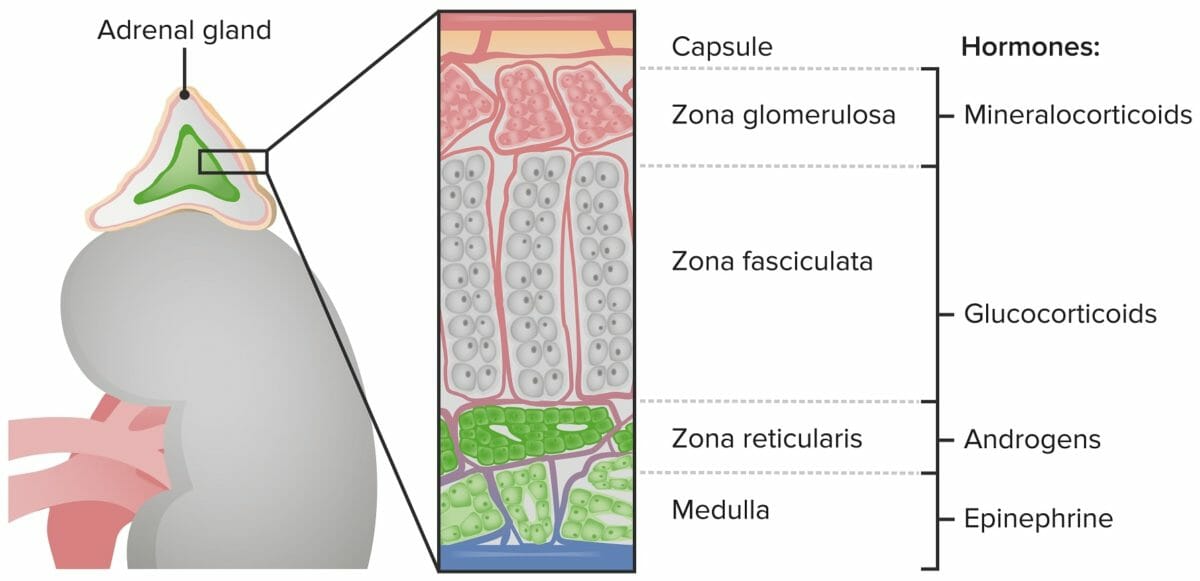
Zones of the adrenal cortex and medulla and their hormonal products
Image by Lecturio.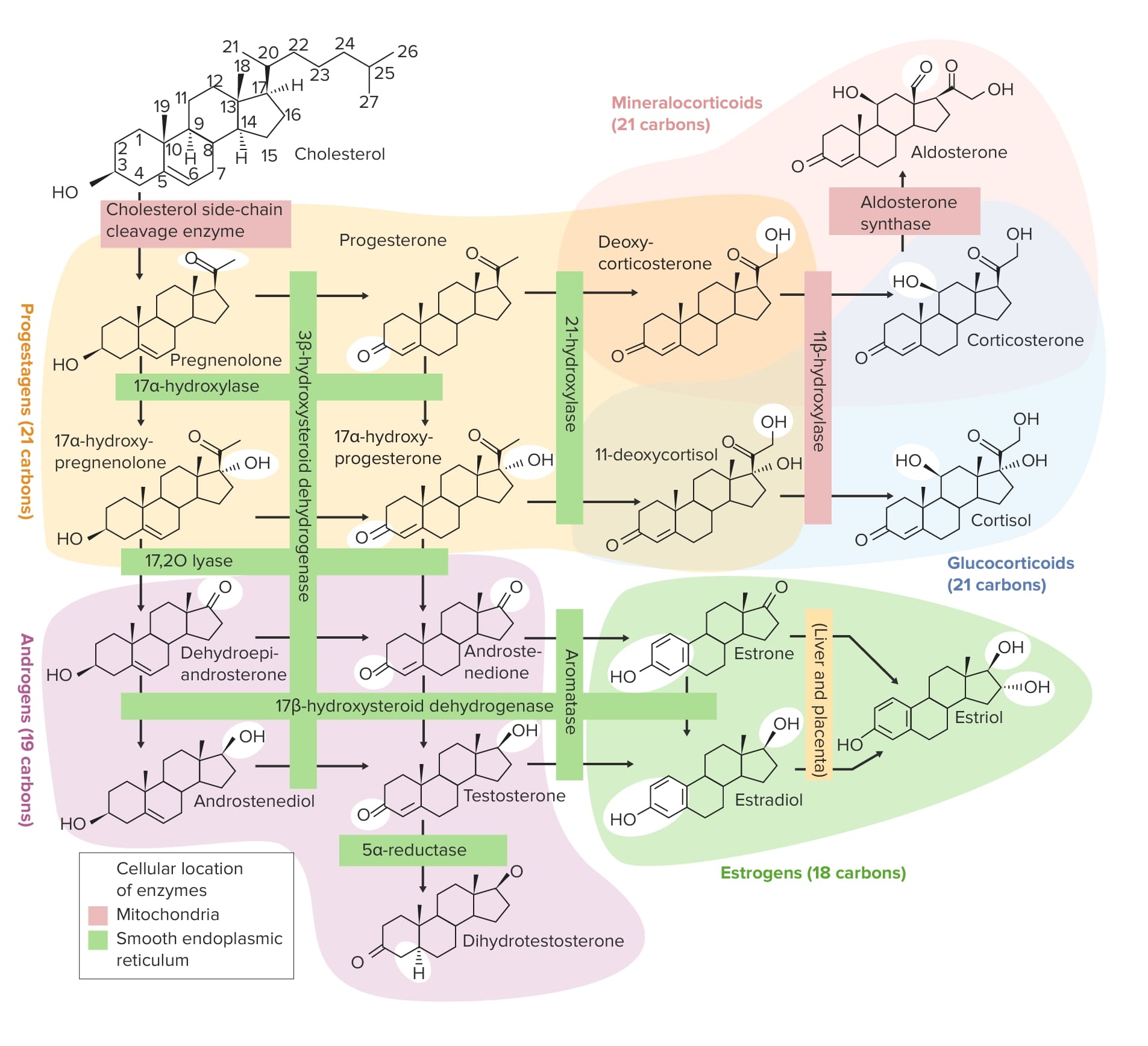
Overview of the steroidogenesis pathways
Image by Lecturio.Hormones Hormones Hormones are messenger molecules that are synthesized in one part of the body and move through the bloodstream to exert specific regulatory effects on another part of the body. Hormones play critical roles in coordinating cellular activities throughout the body in response to the constant changes in both the internal and external environments. Hormones: Overview and Types secreted by the adrenal cortex Adrenal Cortex The outer layer of the adrenal gland. It is derived from mesoderm and comprised of three zones (outer zona glomerulosa, middle zona fasciculata, and inner zona reticularis) with each producing various steroids preferentially, such as aldosterone; hydrocortisone; dehydroepiandrosterone; and androstenedione. Adrenal cortex function is regulated by pituitary adrenocorticotropin. Adrenal Glands: Anatomy (not the medulla) are controlled by, and help regulate, the HPA axis.
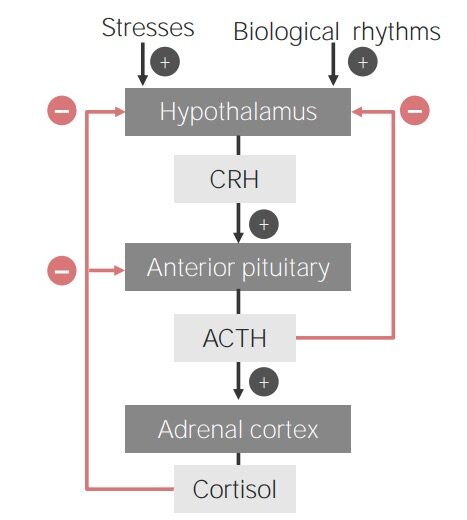
Flowchart showing the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal cortex axis
ACTH: adrenocorticotropic hormone
CRH: corticotropin-releasing hormone
The RAAS is one of the primary regulators of blood pressure, total body water Total body water Body Fluid Compartments, serum sodium Sodium A member of the alkali group of metals. It has the atomic symbol na, atomic number 11, and atomic weight 23. Hyponatremia levels, and pH pH The quantitative measurement of the acidity or basicity of a solution. Acid-Base Balance balance in the body.
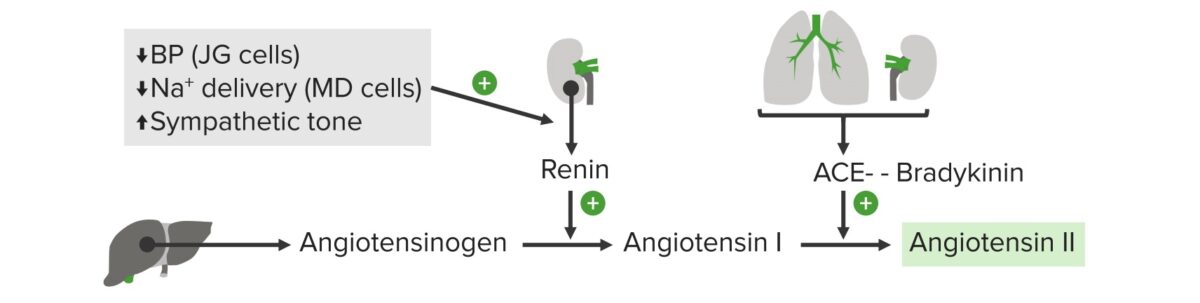
Diagram of the
RAAS:
Angiotensinogen is secreted by hepatocytes. Renin is secreted by juxtaglomerular (JG) cells in the kidney, and converts the angiotensinogen to angiotensin I. Renin secretion is stimulated by a decrease in blood pressure (BP) which is sensed by the JG cells in the kidney, decreased sodium delivery to the kidney which is sensed by the macula densa (MD) cells, and an increase in sympathetic tone. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) is secreted by the lungs, and converts the angiotensin I to angiotensin II.
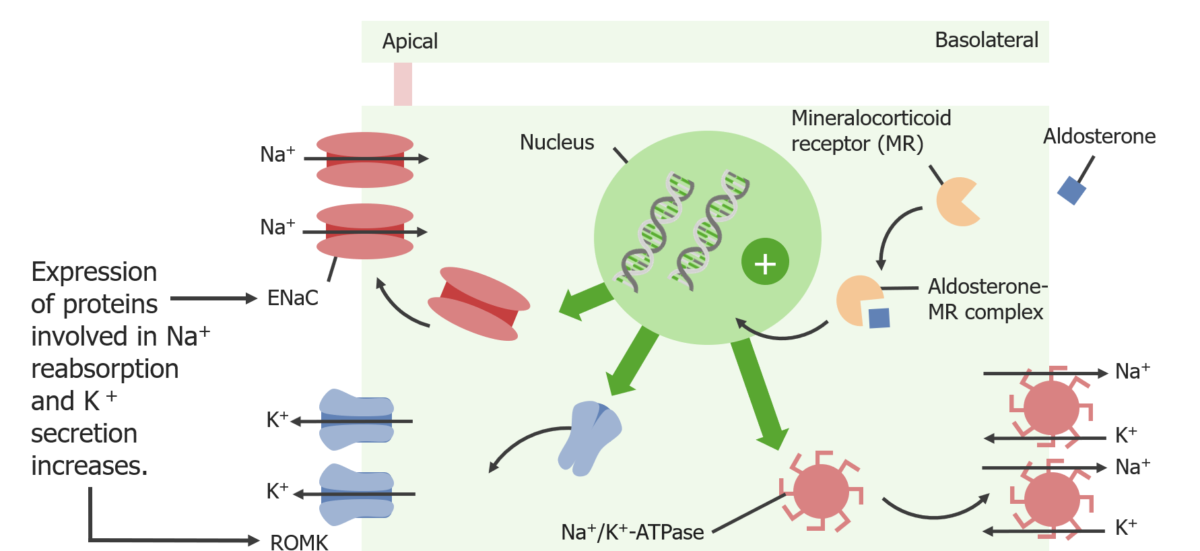
Actions of aldosterone at the principal cell:
Aldosterone stimulates the production of epithelial sodium channels (ENaC), renal outer medullary potassium (ROMK) channels, and Na+/K+ ATPases. The Na+K+ ATPase creates a chemical gradient for Na+ (allowing for increased reabsorption of Na+ through the ENaCs) and a chemical gradient for K+ (allowing for increased K+ secretion through the ROMK channels).
ROMK: renal outer medullary potassium channel
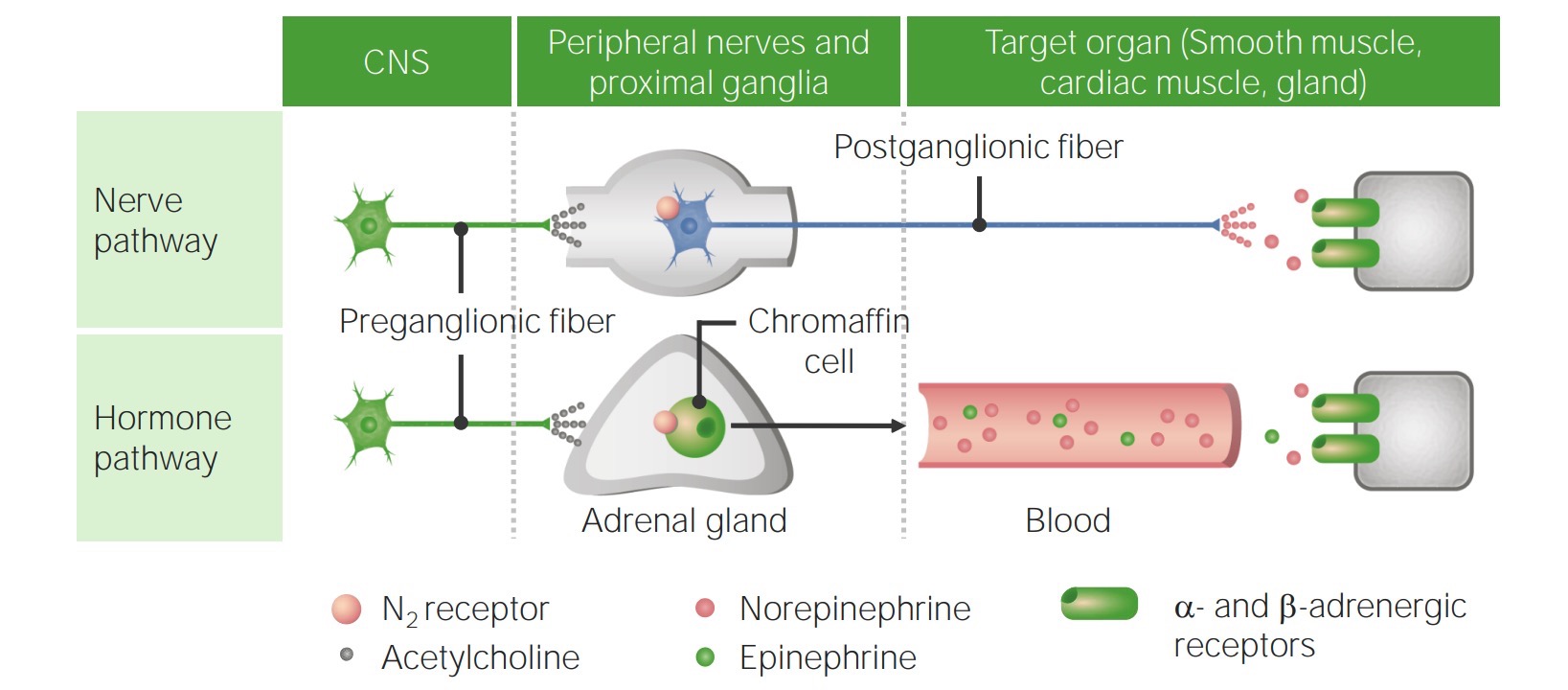
Differences between the nerve and hormone pathways used for sympathetic signaling:
The adrenal medulla is considered a modified sympathetic ganglion because it secretes catecholamines just like postganglionic nerves of the sympathetic nervous system. The chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla are unique due to their ability to convert nerve stimuli into endocrine signals.
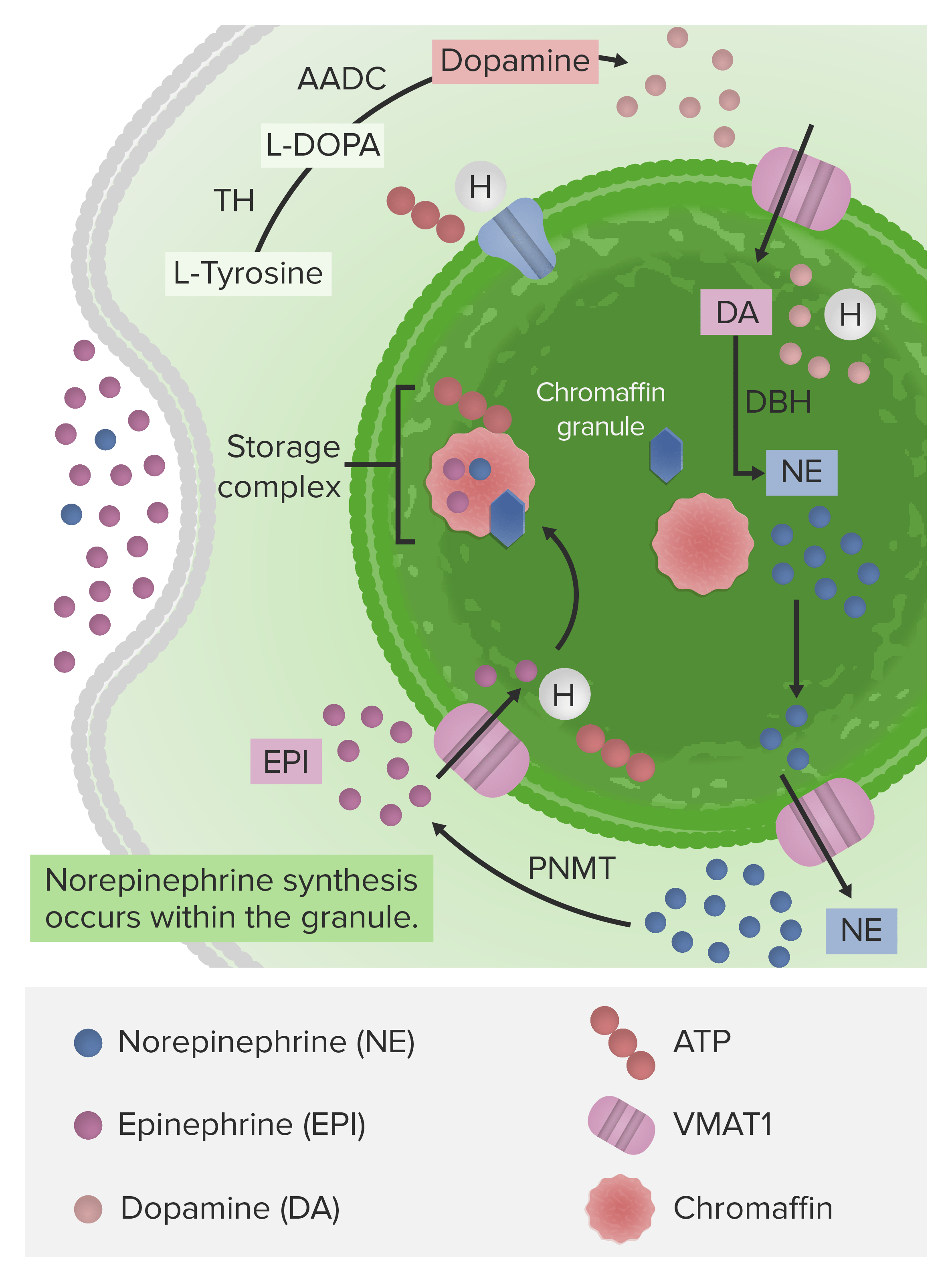
The synthetic pathway of norepinephrine and epinephrine from dopamine (synthesized from the amino acid L-Tyrosine):
Notice dopamine is converted into norepinephrine within the chromaffin granule (where the synthetic enzyme is located). The enzyme that converts norepinephrine to epinephrine is located in the cytosol. Epinephrine is then moved back into the chromaffin granule and stored until a signal is received from the sympathetic nervous system, which triggers its release.
TH: tyrosine hydroxylase
L-DOPA: levo-dihydroxyphenylalanine
AADC: aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase
DBH: dopamine β-hydroxylase
PNMT: phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase
VMAT1: vesicular monoamine transporter 1
The primary purpose of the medullary catecholamines is to supplement the effects of the sympathetic nervous system Nervous system The nervous system is a small and complex system that consists of an intricate network of neural cells (or neurons) and even more glial cells (for support and insulation). It is divided according to its anatomical components as well as its functional characteristics. The brain and spinal cord are referred to as the central nervous system, and the branches of nerves from these structures are referred to as the peripheral nervous system. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification. Because these substances are released directly into the bloodstream as hormones Hormones Hormones are messenger molecules that are synthesized in one part of the body and move through the bloodstream to exert specific regulatory effects on another part of the body. Hormones play critical roles in coordinating cellular activities throughout the body in response to the constant changes in both the internal and external environments. Hormones: Overview and Types, their effects last longer than when catecholamines are released as neurotransmitters. These effects include characteristics of the fight-or-flight response:
There are a number of clinical conditions that result from abnormalities of the adrenal hormones Hormones Hormones are messenger molecules that are synthesized in one part of the body and move through the bloodstream to exert specific regulatory effects on another part of the body. Hormones play critical roles in coordinating cellular activities throughout the body in response to the constant changes in both the internal and external environments. Hormones: Overview and Types. Some of the most clinically important include: