Lactose intolerance (LI) is a clinical condition presenting with gut symptoms after the ingestion of lactose. Malabsorption is not always present, but when it is, the most common cause is lactase deficiency due to enzyme nonpersistence. Lactose is a disaccharide in milk that requires lactase to break it down into its 2 absorbable constituents, glucose and galactose. LI typically presents with bloating, abdominal cramping, diarrhea, and flatulence. The diagnosis is suspected clinically based on symptoms after a lactose-containing meal and confirmed by a lactose hydrogen breath test. The treatment goal is to eliminate symptoms while maintaining sufficient calcium and vitamin D intake.
Last updated: Mar 10, 2023
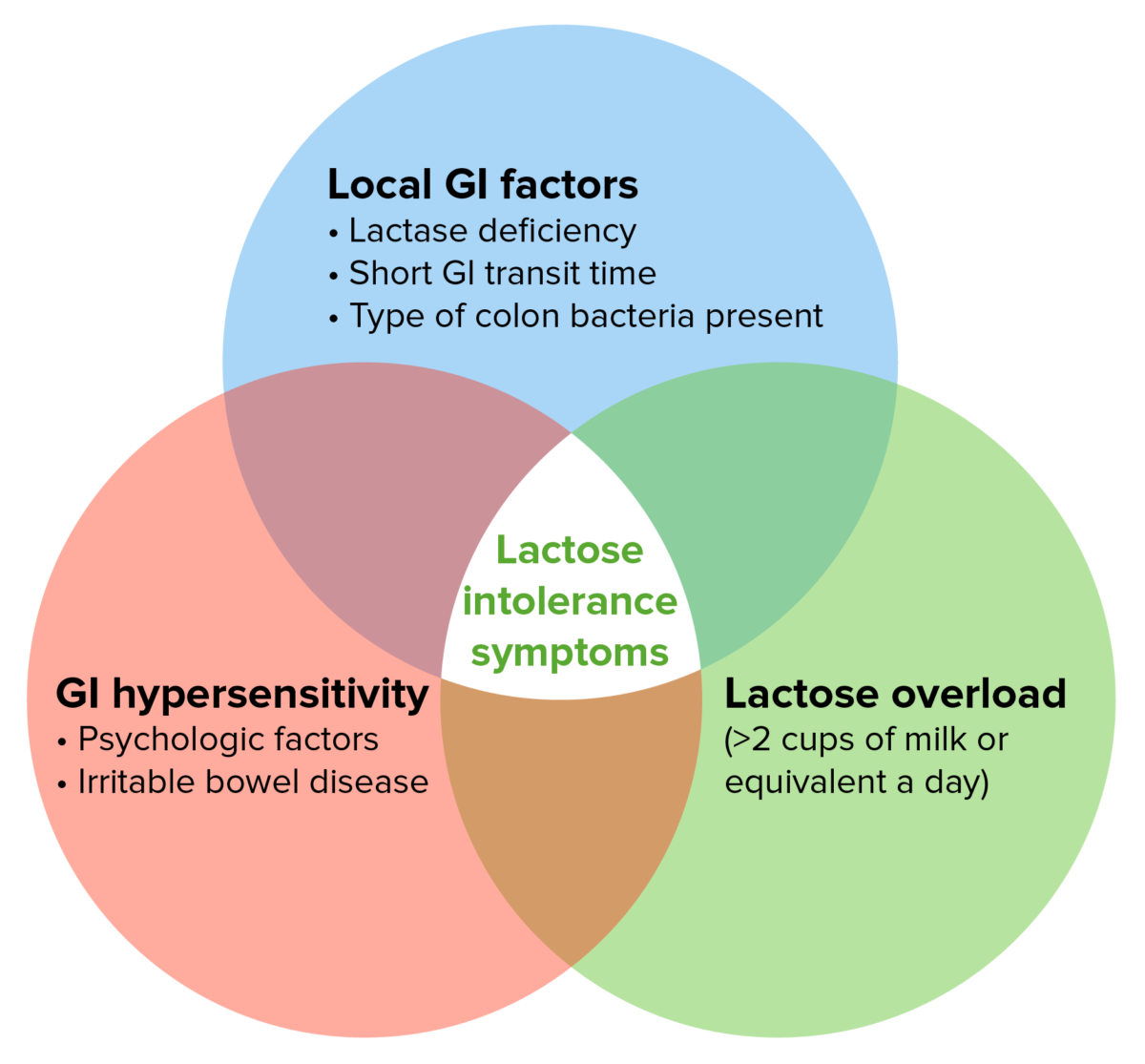
Pathogenesis of LI symptoms:
The likelihood of a person with primary LD developing symptoms after lactose ingestion depends on a number of factors.
Consider a diagnosis of LI if typical symptoms occur within a few hours after ingestion of a lactose-containing meal and resolve after 5–7 days.
Note: Tests for LD alone do not confirm LI unless symptoms are also provoked by lactose loading.
Always consider potential secondary causes of LD when making the diagnosis:
Treat the primary disorder. It may take months for normal lactase Lactase An enzyme which catalyzes the hydrolysis of lactose to d-galactose and d-glucose. Defects in the enzyme cause lactose intolerance. Digestion and Absorption of Carbohydrates activity to return to normal.