Hypoaldosteronism is a hormonal disorder characterized by low levels of aldosterone Aldosterone A hormone secreted by the adrenal cortex that regulates electrolyte and water balance by increasing the renal retention of sodium and the excretion of potassium. Hyperkalemia. These low levels can be caused by decreased aldosterone Aldosterone A hormone secreted by the adrenal cortex that regulates electrolyte and water balance by increasing the renal retention of sodium and the excretion of potassium. Hyperkalemia production or a peripheral resistance Resistance Physiologically, the opposition to flow of air caused by the forces of friction. As a part of pulmonary function testing, it is the ratio of driving pressure to the rate of air flow. Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing to aldosterone Aldosterone A hormone secreted by the adrenal cortex that regulates electrolyte and water balance by increasing the renal retention of sodium and the excretion of potassium. Hyperkalemia. When hypoaldosteronism occurs as a result of an acquired decrease in renin Renin A highly specific (leu-leu) endopeptidase that generates angiotensin I from its precursor angiotensinogen, leading to a cascade of reactions which elevate blood pressure and increase sodium retention by the kidney in the renin-angiotensin system. Renal Sodium and Water Regulation production, the condition is more commonly referred to as renal tubular acidosis Acidosis A pathologic condition of acid accumulation or depletion of base in the body. The two main types are respiratory acidosis and metabolic acidosis, due to metabolic acid build up. Respiratory Acidosis ( RTA RTA Renal tubular acidosis (RTA) is an imbalance in physiologic pH caused by the kidney's inability to acidify urine to maintain blood pH at physiologic levels. Renal tubular acidosis exist in multiple types, including distal RTA (type 1), proximal RTA (type 2), and hyperkalemic RTA (type 4). Renal Tubular Acidosis) type 4 Type 4 Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship are usually older, with underlying renal disease (e.g., diabetic nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy Kidney injuries associated with diabetes mellitus and affecting kidney glomerulus; arterioles; kidney tubules; and the interstitium. Clinical signs include persistent proteinuria, from microalbuminuria progressing to albuminuria of greater than 300 mg/24 h, leading to reduced glomerular filtration rate and end-stage renal disease. Chronic Diabetic Complications). Hypoaldosteronism usually presents as hyperkalemia Hyperkalemia Hyperkalemia is defined as a serum potassium (K+) concentration >5.2 mEq/L. Homeostatic mechanisms maintain the serum K+ concentration between 3.5 and 5.2 mEq/L, despite marked variation in dietary intake. Hyperkalemia can be due to a variety of causes, which include transcellular shifts, tissue breakdown, inadequate renal excretion, and drugs. Hyperkalemia with a mild hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis Hyperchloremic Metabolic Acidosis Potassium-sparing Diuretics (normal anion gap Anion gap Metabolic Acidosis). Most patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship are asymptomatic and routine lab evaluation demonstrates hyperkalemia Hyperkalemia Hyperkalemia is defined as a serum potassium (K+) concentration >5.2 mEq/L. Homeostatic mechanisms maintain the serum K+ concentration between 3.5 and 5.2 mEq/L, despite marked variation in dietary intake. Hyperkalemia can be due to a variety of causes, which include transcellular shifts, tissue breakdown, inadequate renal excretion, and drugs. Hyperkalemia, prompting a further workup. The condition is diagnosed using serum and urine tests that demonstrate reduced aldosterone Aldosterone A hormone secreted by the adrenal cortex that regulates electrolyte and water balance by increasing the renal retention of sodium and the excretion of potassium. Hyperkalemia levels and a reduced transtubular potassium Potassium An element in the alkali group of metals with an atomic symbol k, atomic number 19, and atomic weight 39. 10. It is the chief cation in the intracellular fluid of muscle and other cells. Potassium ion is a strong electrolyte that plays a significant role in the regulation of fluid volume and maintenance of the water-electrolyte balance. Hyperkalemia gradient, among other characteristic findings. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship are managed based on their underlying etiology.
Last updated: May 17, 2024
Hypoaldosteronism is defined as decreased secretion Secretion Coagulation Studies of aldosterone Aldosterone A hormone secreted by the adrenal cortex that regulates electrolyte and water balance by increasing the renal retention of sodium and the excretion of potassium. Hyperkalemia from the zona glomerulosa Zona Glomerulosa The narrow subcapsular outer zone of the adrenal cortex. This zone produces a series of enzymes that convert pregnenolone to aldosterone. The final steps involve three successive oxidations by cytochrome p-450 cyp11b2. Adrenal Glands: Anatomy of the adrenal cortex Adrenal Cortex The outer layer of the adrenal gland. It is derived from mesoderm and comprised of three zones (outer zona glomerulosa, middle zona fasciculata, and inner zona reticularis) with each producing various steroids preferentially, such as aldosterone; hydrocortisone; dehydroepiandrosterone; and androstenedione. Adrenal cortex function is regulated by pituitary adrenocorticotropin. Adrenal Glands: Anatomy, which may be primary or secondary in nature.
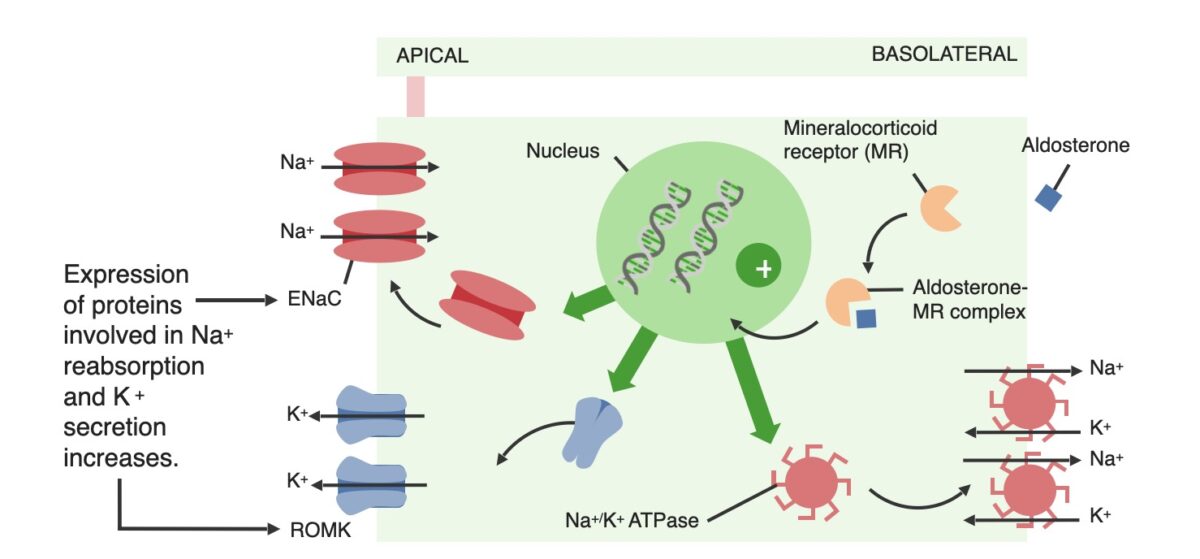
Effects of aldosterone on the principal cells within the distal renal tubules. Mineralocorticoids work similarly.
ENaC: epithelial Na+ channel
ROMK: renal outer medullary potassium
The 2 primary mechanisms that cause hypoaldosteronism are reduced aldosterone Aldosterone A hormone secreted by the adrenal cortex that regulates electrolyte and water balance by increasing the renal retention of sodium and the excretion of potassium. Hyperkalemia production (which can be hyporeninemic or hyperreninemic) and aldosterone Aldosterone A hormone secreted by the adrenal cortex that regulates electrolyte and water balance by increasing the renal retention of sodium and the excretion of potassium. Hyperkalemia resistance Resistance Physiologically, the opposition to flow of air caused by the forces of friction. As a part of pulmonary function testing, it is the ratio of driving pressure to the rate of air flow. Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing. Medications are often the cause of both mechanisms.
| Mechanism | Etiology |
|---|---|
| Reduced
aldosterone
Aldosterone
A hormone secreted by the adrenal cortex that regulates electrolyte and water balance by increasing the renal retention of sodium and the excretion of potassium.
Hyperkalemia
synthesis
Synthesis
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) due to ↓ stimulation of
RAAS
RAAS
A blood pressure regulating system of interacting components that include renin; angiotensinogen; angiotensin converting enzyme; angiotensin i; angiotensin ii; and angiotensinase. Renin, an enzyme produced in the kidney, acts on angiotensinogen, an alpha-2 globulin produced by the liver, forming angiotensin I. Angiotensin-converting enzyme, contained in the lung, acts on angiotensin I in the plasma converting it to angiotensin II, an extremely powerful vasoconstrictor. Angiotensin II causes contraction of the arteriolar and renal vascular smooth muscle, leading to retention of salt and water in the kidney and increased arterial blood pressure. In addition, angiotensin II stimulates the release of aldosterone from the adrenal cortex, which in turn also increases salt and water retention in the kidney. Angiotensin-converting enzyme also breaks down bradykinin, a powerful vasodilator and component of the kallikrein-kinin system.
Adrenal Hormones: Hyporeninemic hypoaldosteronism (also referred to as type 4 Type 4 Spinal Muscular Atrophy renal tubular acidosis Acidosis A pathologic condition of acid accumulation or depletion of base in the body. The two main types are respiratory acidosis and metabolic acidosis, due to metabolic acid build up. Respiratory Acidosis ( RTA RTA Renal tubular acidosis (RTA) is an imbalance in physiologic pH caused by the kidney’s inability to acidify urine to maintain blood pH at physiologic levels. Renal tubular acidosis exist in multiple types, including distal RTA (type 1), proximal RTA (type 2), and hyperkalemic RTA (type 4). Renal Tubular Acidosis)) |
|
| Reduced
aldosterone
Aldosterone
A hormone secreted by the adrenal cortex that regulates electrolyte and water balance by increasing the renal retention of sodium and the excretion of potassium.
Hyperkalemia
synthesis
Synthesis
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) due to direct adrenal issues: Hyperreninemic hypoaldosteronism |
|
| Aldosterone Aldosterone A hormone secreted by the adrenal cortex that regulates electrolyte and water balance by increasing the renal retention of sodium and the excretion of potassium. Hyperkalemia resistance Resistance Physiologically, the opposition to flow of air caused by the forces of friction. As a part of pulmonary function testing, it is the ratio of driving pressure to the rate of air flow. Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing (psudohypoaldosteronism) |
|
The diagnosis of hypoaldosteronism should be considered in any patient with persistent hyperkalemia Hyperkalemia Hyperkalemia is defined as a serum potassium (K+) concentration >5.2 mEq/L. Homeostatic mechanisms maintain the serum K+ concentration between 3.5 and 5.2 mEq/L, despite marked variation in dietary intake. Hyperkalemia can be due to a variety of causes, which include transcellular shifts, tissue breakdown, inadequate renal excretion, and drugs. Hyperkalemia without an obvious cause, such as renal failure Renal failure Conditions in which the kidneys perform below the normal level in the ability to remove wastes, concentrate urine, and maintain electrolyte balance; blood pressure; and calcium metabolism. Renal insufficiency can be classified by the degree of kidney damage (as measured by the level of proteinuria) and reduction in glomerular filtration rate. Crush Syndrome or potassium-sparing diuretics Diuretics Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. Heart Failure and Angina Medication.
The management depends on the underlying etiology.