Leprosy, also known as Hansen's disease, is a chronic bacterial infection caused by Mycobacterium leprae Mycobacterium leprae A species of gram-positive, aerobic bacteria that causes leprosy in man. Its organisms are generally arranged in clumps, rounded masses, or in groups of bacilli side by side. Mycobacterium complex bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology. Symptoms primarily affect the skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions and peripheral nerves Peripheral Nerves The nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord, including the autonomic, cranial, and spinal nerves. Peripheral nerves contain non-neuronal cells and connective tissue as well as axons. The connective tissue layers include, from the outside to the inside, the epineurium, the perineurium, and the endoneurium. Nervous System: Histology, resulting in cutaneous manifestations (e.g., hypopigmented macules) and neurologic manifestations (e.g., loss of sensation). Leprosy is known for its historical stigma and psychosocial effects on infected persons, prompting the World Health Organization (WHO) to pursue a disease elimination Elimination The initial damage and destruction of tumor cells by innate and adaptive immunity. Completion of the phase means no cancer growth. Cancer Immunotherapy plan that led to significant reduction in the prevalence Prevalence The total number of cases of a given disease in a specified population at a designated time. It is differentiated from incidence, which refers to the number of new cases in the population at a given time. Measures of Disease Frequency of leprosy. The diagnosis of leprosy is established clinically and supported with skin biopsy Skin Biopsy Secondary Skin Lesions. It is treated with long-term multidrug antibiotic combinations. Untreated leprosy leads to disability Disability Determination of the degree of a physical, mental, or emotional handicap. The diagnosis is applied to legal qualification for benefits and income under disability insurance and to eligibility for social security and workman's compensation benefits. ABCDE Assessment and permanent damage to the skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions, nerves, limbs, and eyes.
Last updated: Jun 1, 2025
Leprosy (also known as Hansen’s disease) is an infectious disease affecting skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions and peripheral nerves Peripheral Nerves The nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord, including the autonomic, cranial, and spinal nerves. Peripheral nerves contain non-neuronal cells and connective tissue as well as axons. The connective tissue layers include, from the outside to the inside, the epineurium, the perineurium, and the endoneurium. Nervous System: Histology.
Leprosy is caused by Mycobacterium leprae Mycobacterium leprae A species of gram-positive, aerobic bacteria that causes leprosy in man. Its organisms are generally arranged in clumps, rounded masses, or in groups of bacilli side by side. Mycobacterium complex bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology:
Risk factors for acquisition:
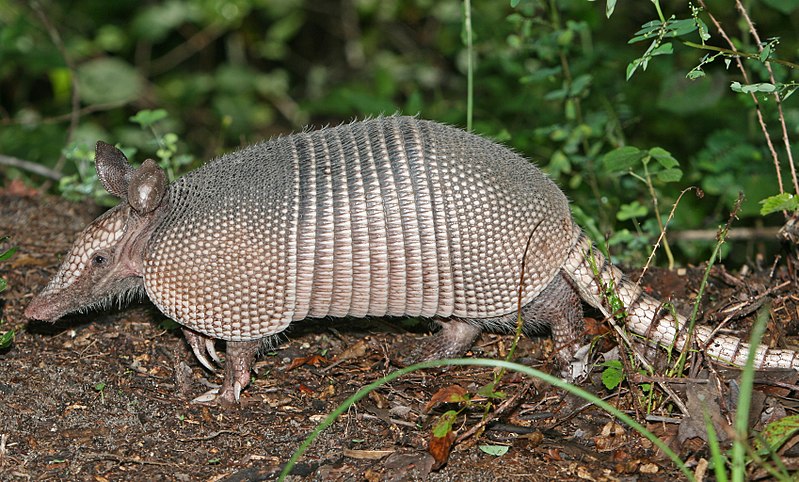

A nine-banded armadillo in the Green Swamp in central Florida
Image: “Armadillo” by http://www.birdphotos.com. License: CC BY 3.0
Map of the range of the nine-banded armadillo in the United States
Image: “Map of the range of the Nine-banded Armadillo in the United States” by Caliga10. License: Public DomainSkin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions lesions:
Other manifestations:
| Tuberculoid | Lepromatous | |
|---|---|---|
| Presentation | Immunocompetent individuals | Immunocompromised immunocompromised A human or animal whose immunologic mechanism is deficient because of an immunodeficiency disorder or other disease or as the result of the administration of immunosuppressive drugs or radiation. Gastroenteritis individuals |
| Location | Skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions and nerves | Skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions and nerves |
| Symptoms |
|
|
Late findings may include:
Possible immunologic reactions:
Lucio’s phenomenon:
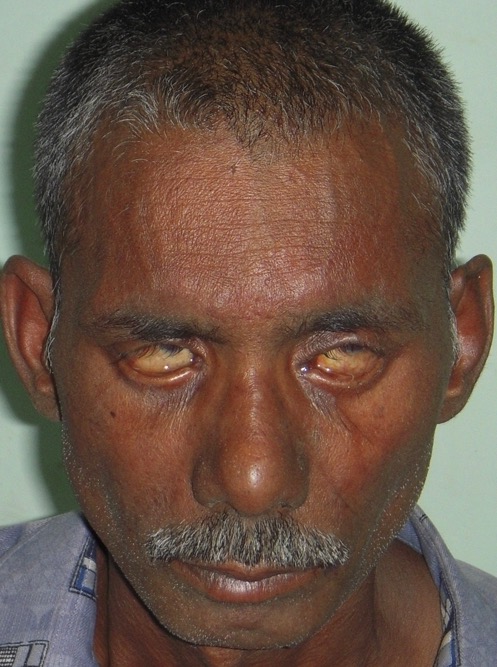
Lagophthalmos in a patient with lepromatous leprosy:
Patient is attempting to close his eyelids, but he is unable to do so.
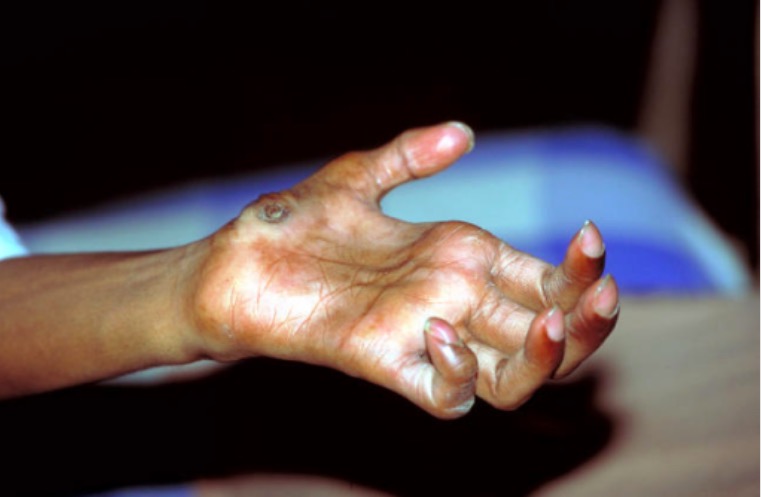
Clawed fingers: Typical deformity in a patient with advanced leprosy
Image: “Typical Deformity in a Patient with Leprosy” by Andrea Rinaldi. License: CC BY 4.0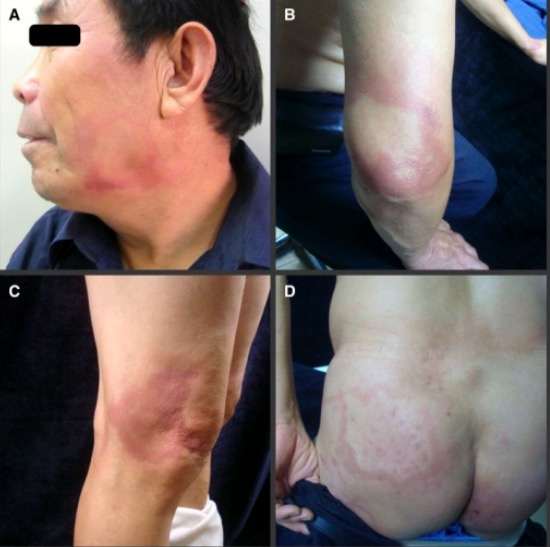
Cutaneous manifestations of leprosy:
Photographs show reddish patches and plaques on the patient’s face (A), elbow (B), knee (C), and buttock (D)
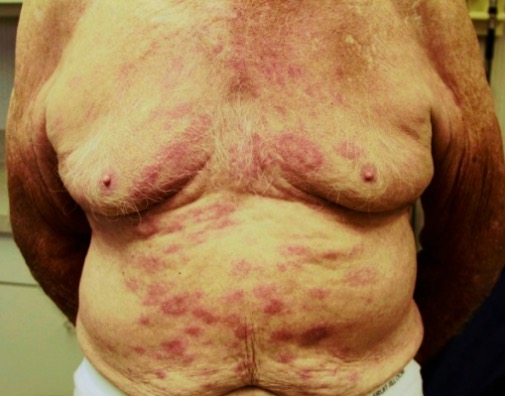
Leprosy: erythematous skin patches
Image: “Erythematous rash in trunk” by Infectious Diseases, Hattiesburg Clinic, Hattiesburg, Mississippi; Dermatology, Hattiesburg Clinic, Hattiesburg, Mississippi. License: CC BY 4.0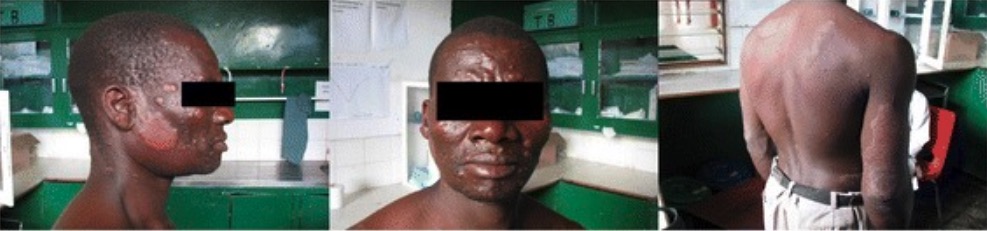
Widespread skin lesions consistent with lepromatous leprosy:
The patient is beginning to develop leonine facies, with a large number of papules and nodules afflicting the face, chest, back, legs, and groin. Large well-circumscribed plaques appear on the triceps aspect of the right arm and over his left shoulder and right flank.
The WHO defines leprosy as appearing in an individual who has not completed a course of treatment and has one or more of the following:
The WHO bases Bases Usually a hydroxide of lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium or cesium, but also the carbonates of these metals, ammonia, and the amines. Acid-Base Balance diagnosis on the above clinical presentation combined with a confirmatory laboratory test.
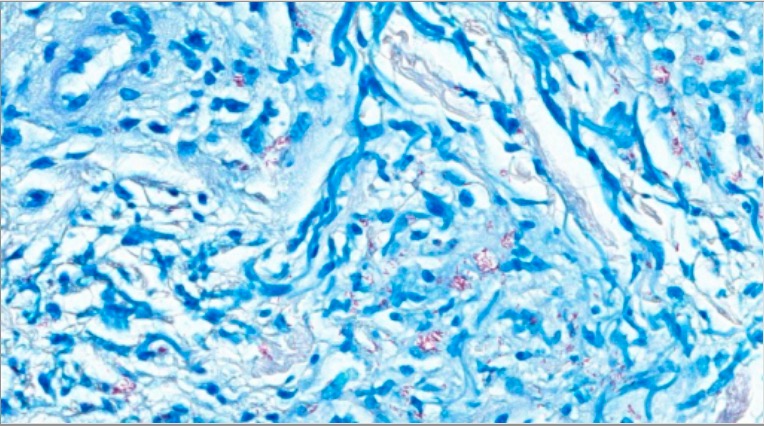
Fite stain for M. leprae
Image: “Fite stain-positive for Mycobacterium spp” by Infectious Diseases, Hattiesburg Clinic, Hattiesburg, Mississippi; Dermatology, Hattiesburg Clinic, Hattiesburg, Mississippi. License: CC BY 4.0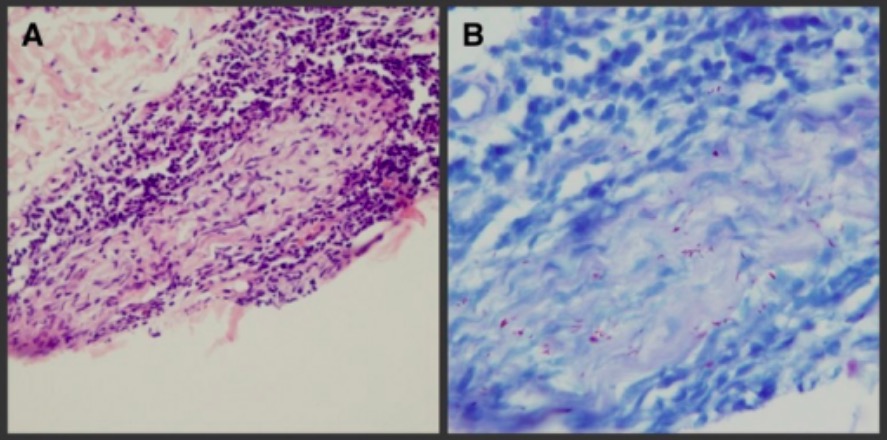
Leprosy diagnosis:
A: Plasmacytic and lymphocytic infiltration surrounding dermal nerve and Schwann cells and inflammatory cells infiltrated into nerve tract
B: Positive acid-fast bacilli stain for M. leprae bacilli
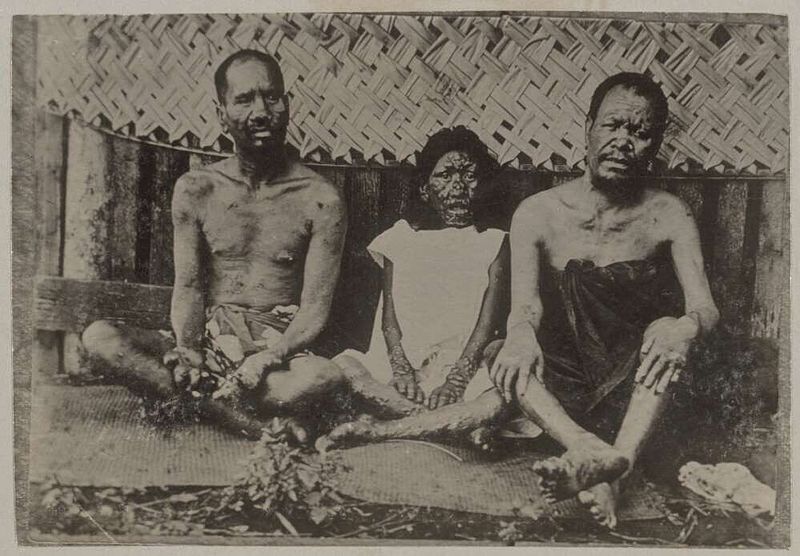

Three patients suffering from leprosy:
Note the nose disfigurement and digit amputations.