Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) is a condition seen in premature infants of low birth weight that is characterized by progressive and excessive neovascularization. In this condition, the inappropriate proliferation of blood vessels and fibrovascular tissue behind the lens prevents retinal development. The end result is severe visual deficits or even blindness of the infant afflicted. Treatment with laser photocoagulation prevents vision loss in 95% of cases.
Last updated: May 17, 2024
Premature infants Premature infants A human infant born before 37 weeks of gestation. Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS) of low birth weight are at risk of developing hyperoxia during their care; this can lead to:
International classification of retinopathy Retinopathy Degenerative changes to the retina due to hypertension. Alport Syndrome uses a number of parameters to describe the disease:
| Stages | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| 1 | A demarcation line between the vascular and avascular Avascular Corneal Abrasions, Erosion, and Ulcers retina Retina The ten-layered nervous tissue membrane of the eye. It is continuous with the optic nerve and receives images of external objects and transmits visual impulses to the brain. Its outer surface is in contact with the choroid and the inner surface with the vitreous body. The outermost layer is pigmented, whereas the inner nine layers are transparent. Eye: Anatomy |
| 2 | A demarcation line grows to occupy a volume and a ridge is formed above the plane of the retina Retina The ten-layered nervous tissue membrane of the eye. It is continuous with the optic nerve and receives images of external objects and transmits visual impulses to the brain. Its outer surface is in contact with the choroid and the inner surface with the vitreous body. The outermost layer is pigmented, whereas the inner nine layers are transparent. Eye: Anatomy, protruding into the vitreous. |
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
Retinal detachment
Retinal detachment
Retinal detachment is the separation of the neurosensory retina from the retinal pigmented epithelium and choroid. Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment, the most common type, stems from a break in the retina, allowing fluid to accumulate in the subretinal space.
Retinal Detachment (partial or subtotal)
|
| 5 |
|
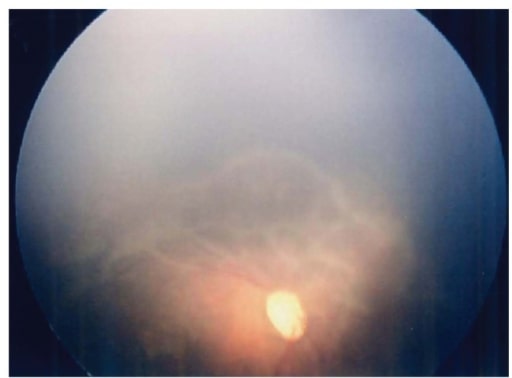
Fundus image of the right eye at 57 days after birth. Note the wide avascular retina with markedly progressed tractional changes.
Image: “Fundus image of the right eye” by Department of Pediatrics, Hamamatsu University School of Medicine. License: CC BY 3.0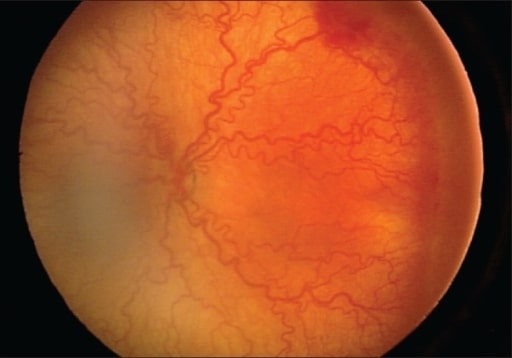
Presence of severe, aggressive posterior retinopathy with intense plus and minimum changes in the periphery
Image: “Presence of severe aggressive posterior ROP” by Division of Pediatric Ophthalmology, King Khaled Eye Specialist Hospital, Riyadh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. License: CC BY 2.0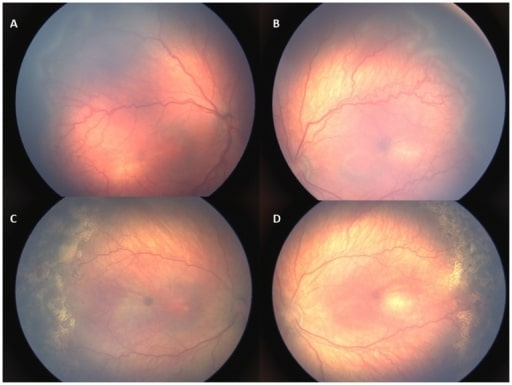
Retinal images of an infant with type 1 retinopathy. A, B: Zone II stage 3 retinopathy with plus disease before treatment. C, D: Plus disease and retinopathy regressed 1 week following laser treatment.
Image: “Retinal images of an infant with type 1 ROP” by US National Library of Medicine. License: CC BY 4.0The following conditions are differential diagnoses for blindness in infancy: