Diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus ( DM DM Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus) is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by persistent hyperglycemia Hyperglycemia Abnormally high blood glucose level. Diabetes Mellitus due to impaired insulin Insulin Insulin is a peptide hormone that is produced by the beta cells of the pancreas. Insulin plays a role in metabolic functions such as glucose uptake, glycolysis, glycogenesis, lipogenesis, and protein synthesis. Exogenous insulin may be needed for individuals with diabetes mellitus, in whom there is a deficiency in endogenous insulin or increased insulin resistance. Insulin secretion Secretion Coagulation Studies ( type 1 Type 1 Spinal Muscular Atrophy DM DM Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus), insulin resistance Insulin resistance Diminished effectiveness of insulin in lowering blood sugar levels: requiring the use of 200 units or more of insulin per day to prevent hyperglycemia or ketosis. Diabetes Mellitus (type 2 DM DM Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus), or both (latent autoimmune diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus in adults ( LADA LADA Autoimmune diabetes in adults with slowly progressive pancreatic beta cell failure and the presence of circulating autoantibodies to pancreatic islets cell antigens. Diabetes Mellitus)). The goal of diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus management is to prevent chronic serious and potentially disabling complications due to damage to various organs. Adequate long-term control of blood glucose Glucose A primary source of energy for living organisms. It is naturally occurring and is found in fruits and other parts of plants in its free state. It is used therapeutically in fluid and nutrient replacement. Lactose Intolerance is crucial in the prevention of complications. Macrovascular complications include heart disease, stroke, and peripheral vascular disease. Microvascular disease can cause retinopathy Retinopathy Degenerative changes to the retina due to hypertension. Alport Syndrome, neuropathy Neuropathy Leprosy, nephropathy, or symptomatic cardiac disease, which are not seen during stress testing or angiogram that are used to diagnose large vessel diseases.
Last updated: Jul 10, 2023
Diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus ( DM DM Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus) is a common disease that can lead to multiple serious complications. Long-term glycemic control is imperative to prevent these complications.
Chronic complications of diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus have unique pathophysiological processes and are dependent on the organ system involved.
There are various forms of kidney disease in diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus, including nonclassical glomerular lesions and tubulointerstitial disease.
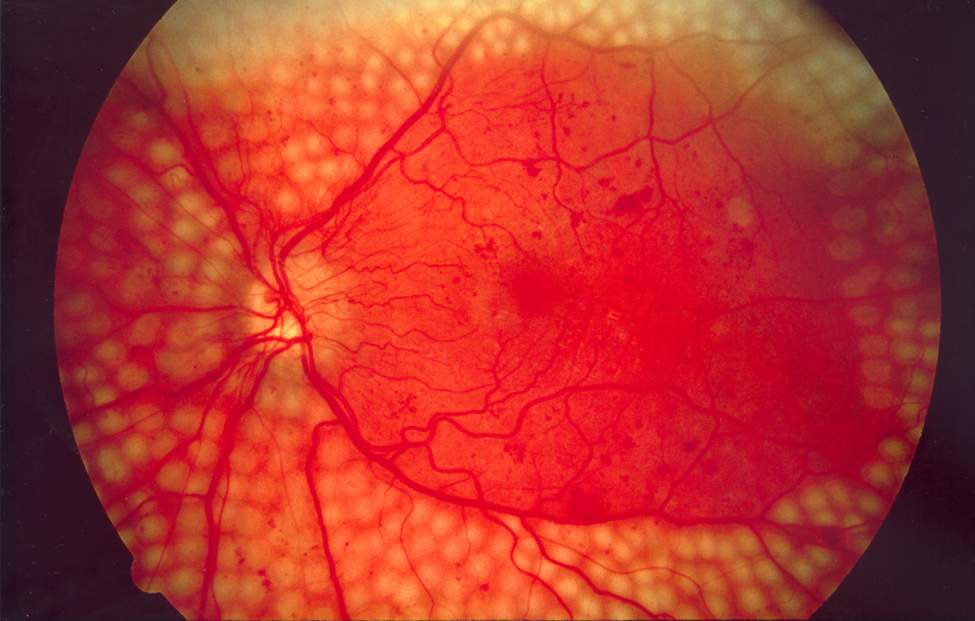
Image of the fundus showing scatter laser surgery for diabetic retinopathy
Image: “Fundus photo showing scatter laser surgery for diabetic retinopathy” by National Eye Institute, National Institutes of Health. License: Public Domain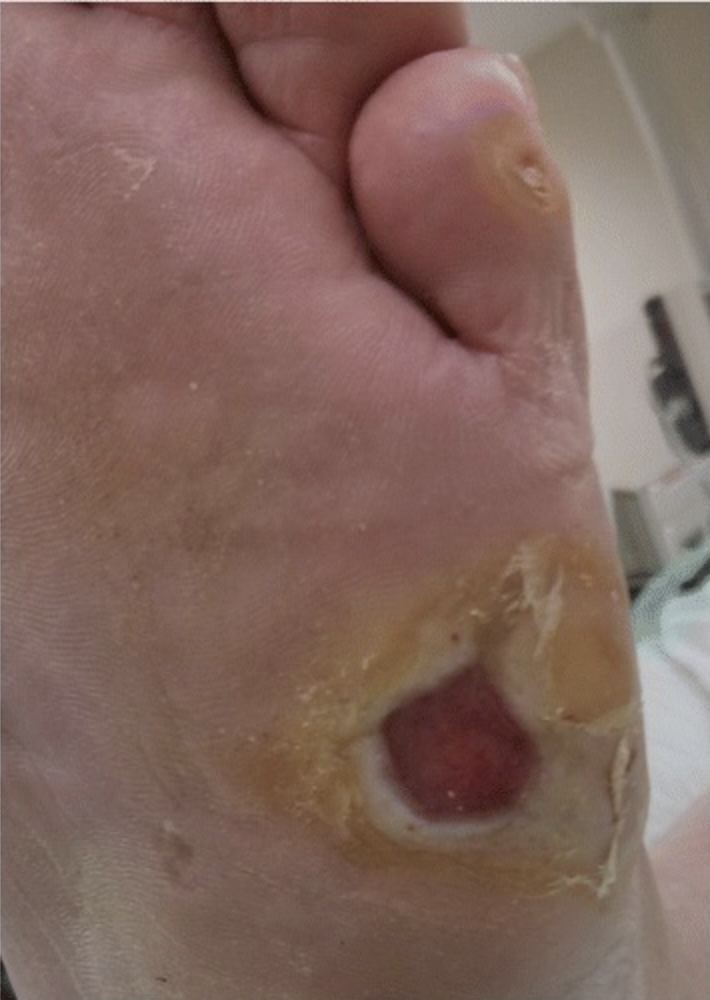
Foot injury in an individual with peripheral neuropathy:
Peripheral neuropathy causes affected individuals to not feel small injuries to the extremities, which are often then untended. Combined with reduced blood flow to extremities, these injuries can lead to chronic foot ulcers that may even require surgical debridement in individuals with diabetes.
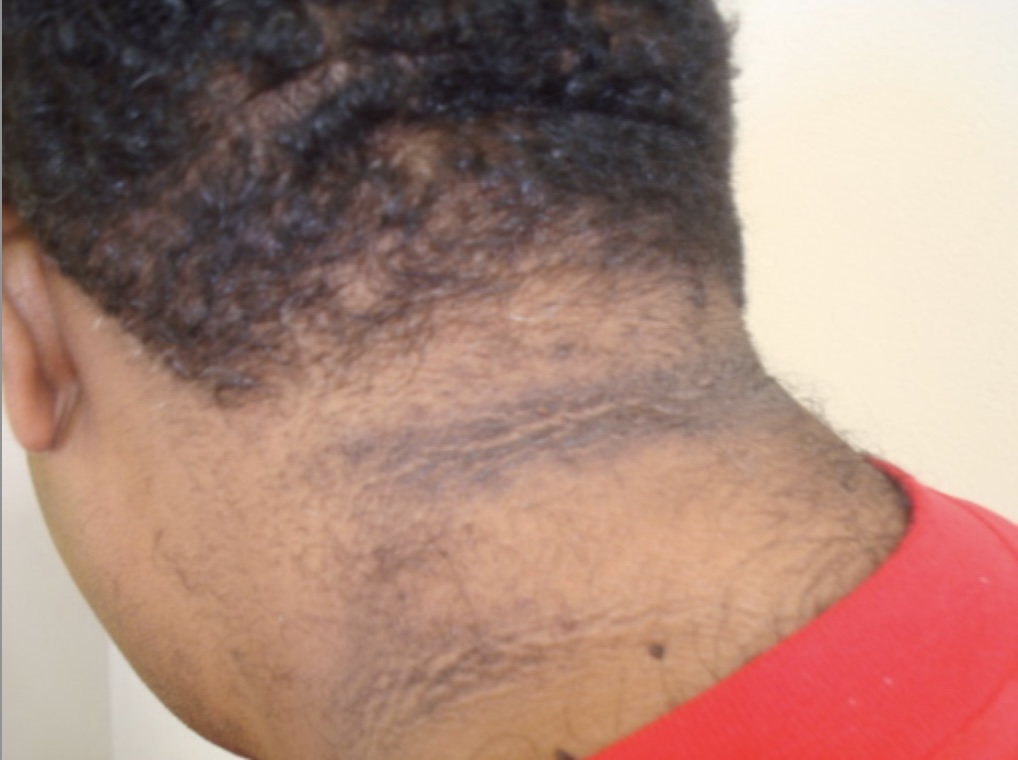
Acanthosis nigricans: a common finding in individuals with insulin resistance (such as in diabetes). Acanthosis nigricans is described as velvety, thickened, and darkened areas of the skin, often seen on the nape of the neck.
Image: “Acanthosis nigricans Grade 1” by Department of Clinical Medical Sciences, The University of West Indies, St Augustine, Trinidad & Tobago, WI. License: CC BY 2.0Coronary artery Coronary Artery Truncus Arteriosus disease:
Peripheral arterial disease:
Carotid stenosis Stenosis Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS): ultrasound to evaluate the extent of occlusive disease
Diabetic nephropathy is usually diagnosed during an annual screening Screening Preoperative Care urine test for microalbuminuria.
Diagnosed during annual screening Screening Preoperative Care eye examinations with an eye specialist (ophthalmologist or optometrist)
With all diabetic complications, prevention is key, and glycemic control is the top priority.