Gluconeogenesis is the process of making glucose Glucose A primary source of energy for living organisms. It is naturally occurring and is found in fruits and other parts of plants in its free state. It is used therapeutically in fluid and nutrient replacement. Lactose Intolerance from noncarbohydrate precursors. This metabolic pathway is more than just a reversal of glycolysis Glycolysis Glycolysis is a central metabolic pathway responsible for the breakdown of glucose and plays a vital role in generating free energy for the cell and metabolites for further oxidative degradation. Glucose primarily becomes available in the blood as a result of glycogen breakdown or from its synthesis from noncarbohydrate precursors (gluconeogenesis) and is imported into cells by specific transport proteins. Glycolysis. Gluconeogenesis provides the body with glucose Glucose A primary source of energy for living organisms. It is naturally occurring and is found in fruits and other parts of plants in its free state. It is used therapeutically in fluid and nutrient replacement. Lactose Intolerance not obtained from food, such as during a fasting period. The production of glucose Glucose A primary source of energy for living organisms. It is naturally occurring and is found in fruits and other parts of plants in its free state. It is used therapeutically in fluid and nutrient replacement. Lactose Intolerance is critical for organs and cells that cannot use fat for fuel. Gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis Glycogenolysis The release of glucose from glycogen by glycogen phosphorylase (phosphorolysis). The released glucose-1-phosphate is then converted to glucose-6-phosphate by phosphoglucomutase before entering glycolysis. Glycogenolysis is stimulated by glucagon or epinephrine via the activation of phosphorylase kinase. Glycogen Metabolism are the 2 major ways the body produces glucose Glucose A primary source of energy for living organisms. It is naturally occurring and is found in fruits and other parts of plants in its free state. It is used therapeutically in fluid and nutrient replacement. Lactose Intolerance. Key enzymes Enzymes Enzymes are complex protein biocatalysts that accelerate chemical reactions without being consumed by them. Due to the body's constant metabolic needs, the absence of enzymes would make life unsustainable, as reactions would occur too slowly without these molecules. Basics of Enzymes for gluconeogenesis are pyruvate Pyruvate Derivatives of pyruvic acid, including its salts and esters. Glycolysis carboxylase, phosphoenolpyruvate Phosphoenolpyruvate A monocarboxylic acid anion derived from selective deprotonation of the carboxy group of phosphoenolpyruvic acid. It is a metabolic intermediate in glycolysis; gluconeogenesis; and other pathways. Glycolysis carboxykinase, fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase, and glucose-6-phosphatase. Thus, gluconeogenesis becomes the main source of glycemic maintenance after glycogen stores are depleted.
Last updated: May 18, 2025
Gluconeogenesis precursors include lactate, glycerol, alanine Alanine A non-essential amino acid that occurs in high levels in its free state in plasma. It is produced from pyruvate by transamination. It is involved in sugar and acid metabolism, increases immunity, and provides energy for muscle tissue, brain, and the central nervous system. Synthesis of Nonessential Amino Acids, and glutamine Glutamine A non-essential amino acid present abundantly throughout the body and is involved in many metabolic processes. It is synthesized from glutamic acid and ammonia. It is the principal carrier of nitrogen in the body and is an important energy source for many cells. Synthesis of Nonessential Amino Acids. This process occurs in multiple locations, beginning in the mitochondria Mitochondria Semiautonomous, self-reproducing organelles that occur in the cytoplasm of all cells of most, but not all, eukaryotes. Each mitochondrion is surrounded by a double limiting membrane. The inner membrane is highly invaginated, and its projections are called cristae. Mitochondria are the sites of the reactions of oxidative phosphorylation, which result in the formation of ATP. They contain distinctive ribosomes, transfer RNAs; amino Acyl tRNA synthetases; and elongation and termination factors. Mitochondria depend upon genes within the nucleus of the cells in which they reside for many essential messenger RNAs. Mitochondria are believed to have arisen from aerobic bacteria that established a symbiotic relationship with primitive protoeukaryotes. The Cell: Organelles but finishing with the shuttling of glucose Glucose A primary source of energy for living organisms. It is naturally occurring and is found in fruits and other parts of plants in its free state. It is used therapeutically in fluid and nutrient replacement. Lactose Intolerance into the cytoplasm via glucose Glucose A primary source of energy for living organisms. It is naturally occurring and is found in fruits and other parts of plants in its free state. It is used therapeutically in fluid and nutrient replacement. Lactose Intolerance transporters.
Gluconeogenesis is the opposite of glycolysis Glycolysis Glycolysis is a central metabolic pathway responsible for the breakdown of glucose and plays a vital role in generating free energy for the cell and metabolites for further oxidative degradation. Glucose primarily becomes available in the blood as a result of glycogen breakdown or from its synthesis from noncarbohydrate precursors (gluconeogenesis) and is imported into cells by specific transport proteins. Glycolysis. There are 11 enzymes Enzymes Enzymes are complex protein biocatalysts that accelerate chemical reactions without being consumed by them. Due to the body’s constant metabolic needs, the absence of enzymes would make life unsustainable, as reactions would occur too slowly without these molecules. Basics of Enzymes, or steps, required for the complete process of gluconeogenesis.
There are 4 irreversible steps that need to happen in gluconeogenesis. These steps are catalyzed by:
11 steps:
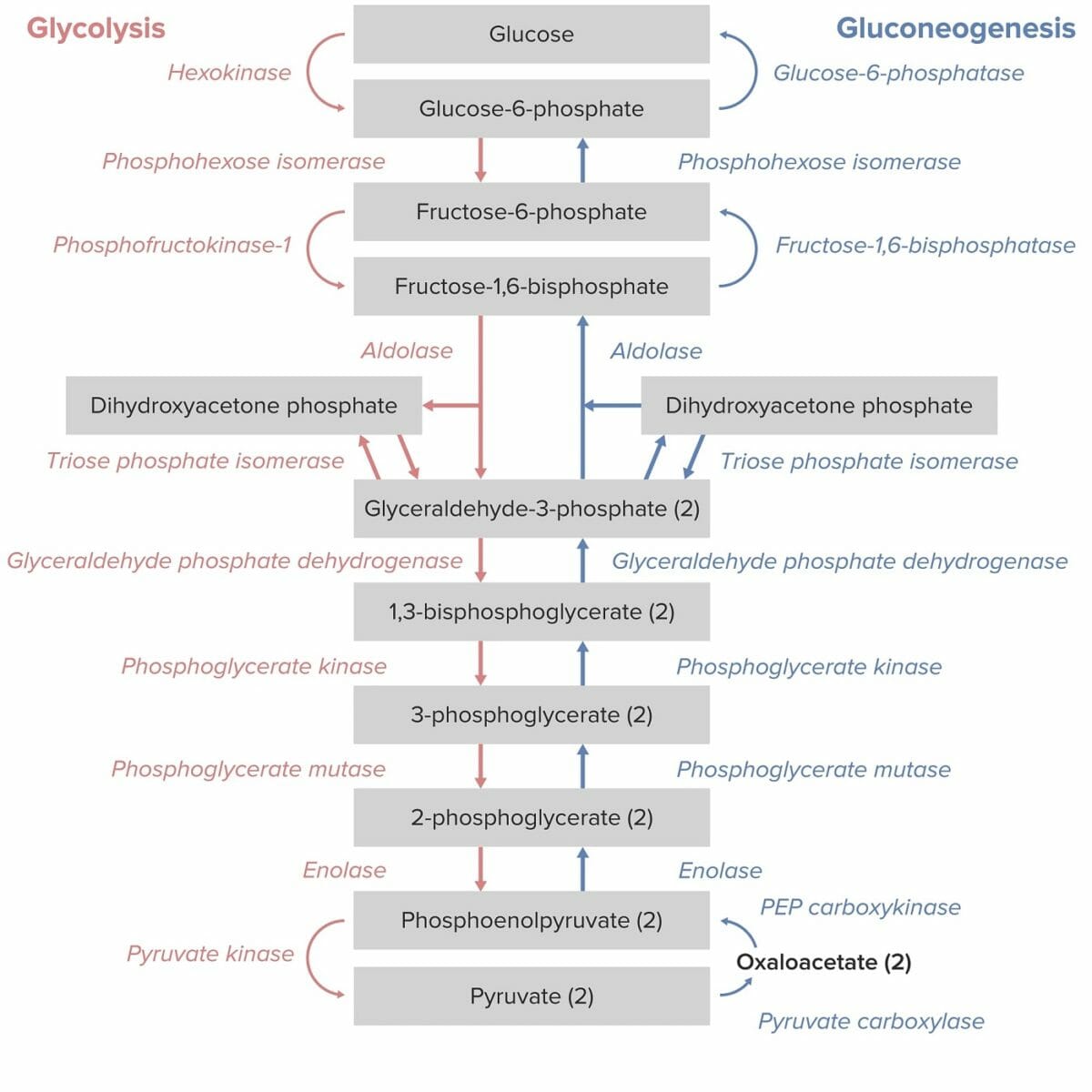
Gluconeogenesis as the reverse of glycolysis:
Note the key enzymes that are unique to gluconeogenesis: PEP carboxykinase, fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase, and glucose 6-phosphatase.
Gluconeogenesis occurs in organs that have high energy requirements.
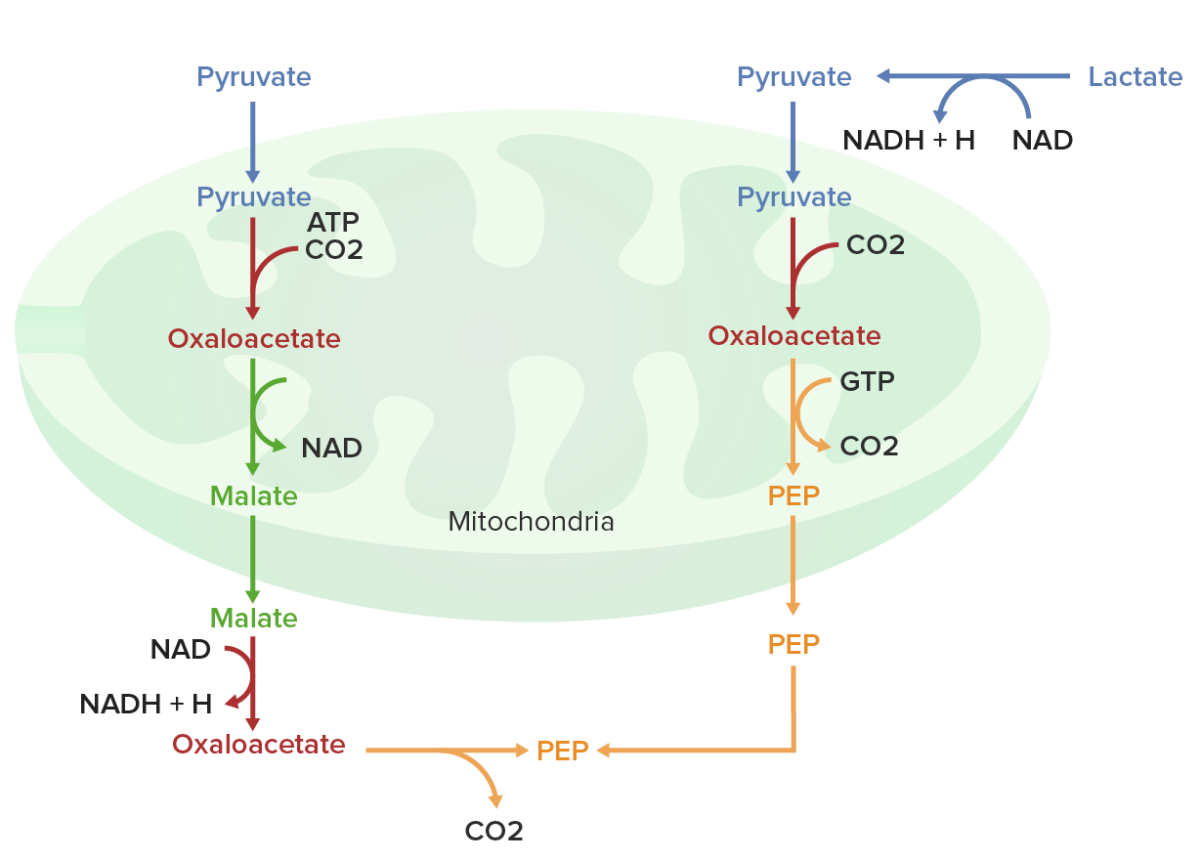
Oxaloacetate must be converted into malate before transit from the mitochondrion into the cytoplasm
ATP: adenosine triphosphate
CO2: carbon dioxide
GTP: guanosine triphosphate
NAD/NADH: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
PEP: phosphoenolpyruvate
There are several points of regulation for gluconeogenesis.