Hemolytic anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature Premature Childbirth before 37 weeks of pregnancy (259 days from the first day of the mother's last menstrual period, or 245 days after fertilization). Necrotizing Enterocolitis destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells Red blood cells Erythrocytes, or red blood cells (RBCs), are the most abundant cells in the blood. While erythrocytes in the fetus are initially produced in the yolk sac then the liver, the bone marrow eventually becomes the main site of production. Erythrocytes: Histology ( RBCs RBCs Erythrocytes, or red blood cells (RBCs), are the most abundant cells in the blood. While erythrocytes in the fetus are initially produced in the yolk sac then the liver, the bone marrow eventually becomes the main site of production. Erythrocytes: Histology). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Extravascular destruction of RBCs RBCs Erythrocytes, or red blood cells (RBCs), are the most abundant cells in the blood. While erythrocytes in the fetus are initially produced in the yolk sac then the liver, the bone marrow eventually becomes the main site of production. Erythrocytes: Histology is affected by macrophages Macrophages The relatively long-lived phagocytic cell of mammalian tissues that are derived from blood monocytes. Main types are peritoneal macrophages; alveolar macrophages; histiocytes; kupffer cells of the liver; and osteoclasts. They may further differentiate within chronic inflammatory lesions to epithelioid cells or may fuse to form foreign body giant cells or langhans giant cells. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation of the liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy, spleen Spleen The spleen is the largest lymphoid organ in the body, located in the LUQ of the abdomen, superior to the left kidney and posterior to the stomach at the level of the 9th-11th ribs just below the diaphragm. The spleen is highly vascular and acts as an important blood filter, cleansing the blood of pathogens and damaged erythrocytes. Spleen: Anatomy, bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis, and lymph nodes Lymph Nodes They are oval or bean shaped bodies (1 - 30 mm in diameter) located along the lymphatic system. Lymphatic Drainage System: Anatomy. Other than the site of destruction, HA can also be classified according to the type of RBC defect that causes their destruction. If the RBC has an intrinsic and usually inherited defect such as a hemoglobinopathy, a membrane defect, or a metabolic defect, its destruction is called intracorpuscular hemolysis. If the RBC is normal but is damaged by an external force such as an antibody, mechanical trauma, or a pathogen, then its destruction is classified as extracorpuscular hemolysis, which is almost always an acquired disorder.
Last updated: Dec 3, 2024
Intravascular hemolysis
Extravascular hemolysis
Hemolytic anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types is a normocytic anemia Normocytic Anemia Anemia: Overview and Types.
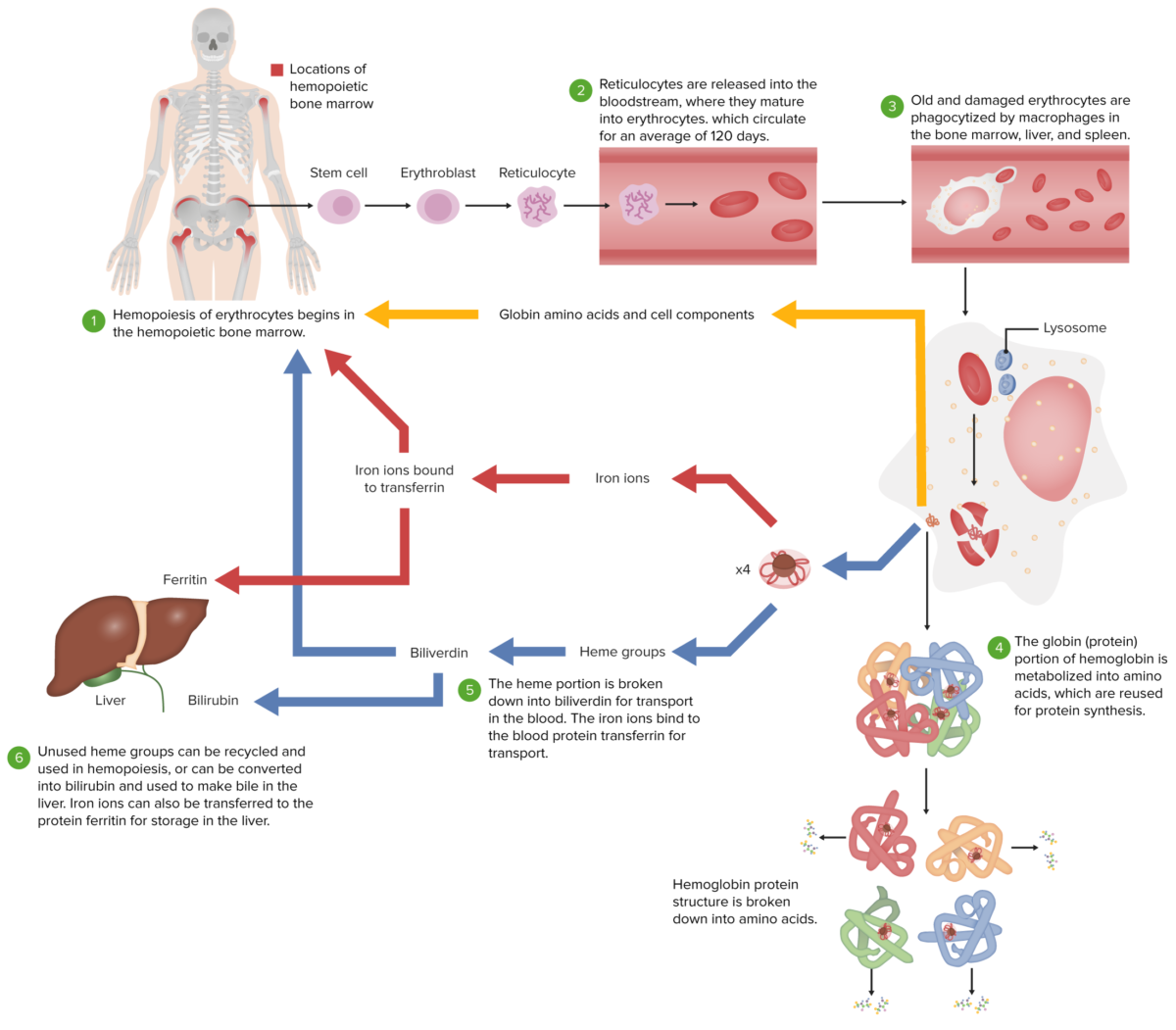
Normal erythrocyte life cycle
Image by Lecturio.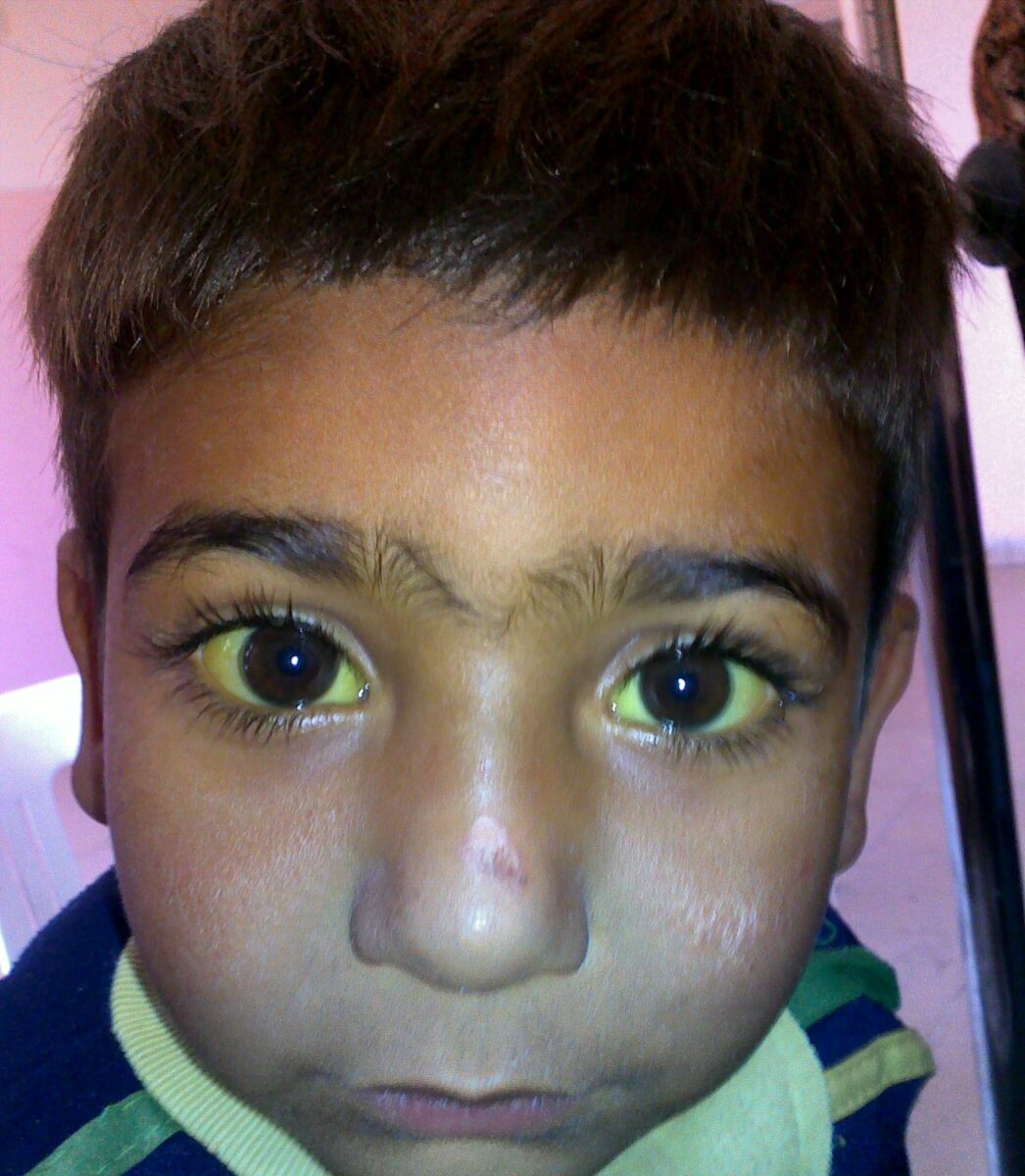
Jaundice in a child with G6PD deficiency
Image: “Jaundice” by Sab3el3eish. License: CC BY 3.0General
Intravascular hemolysis
Extravascular hemolysis
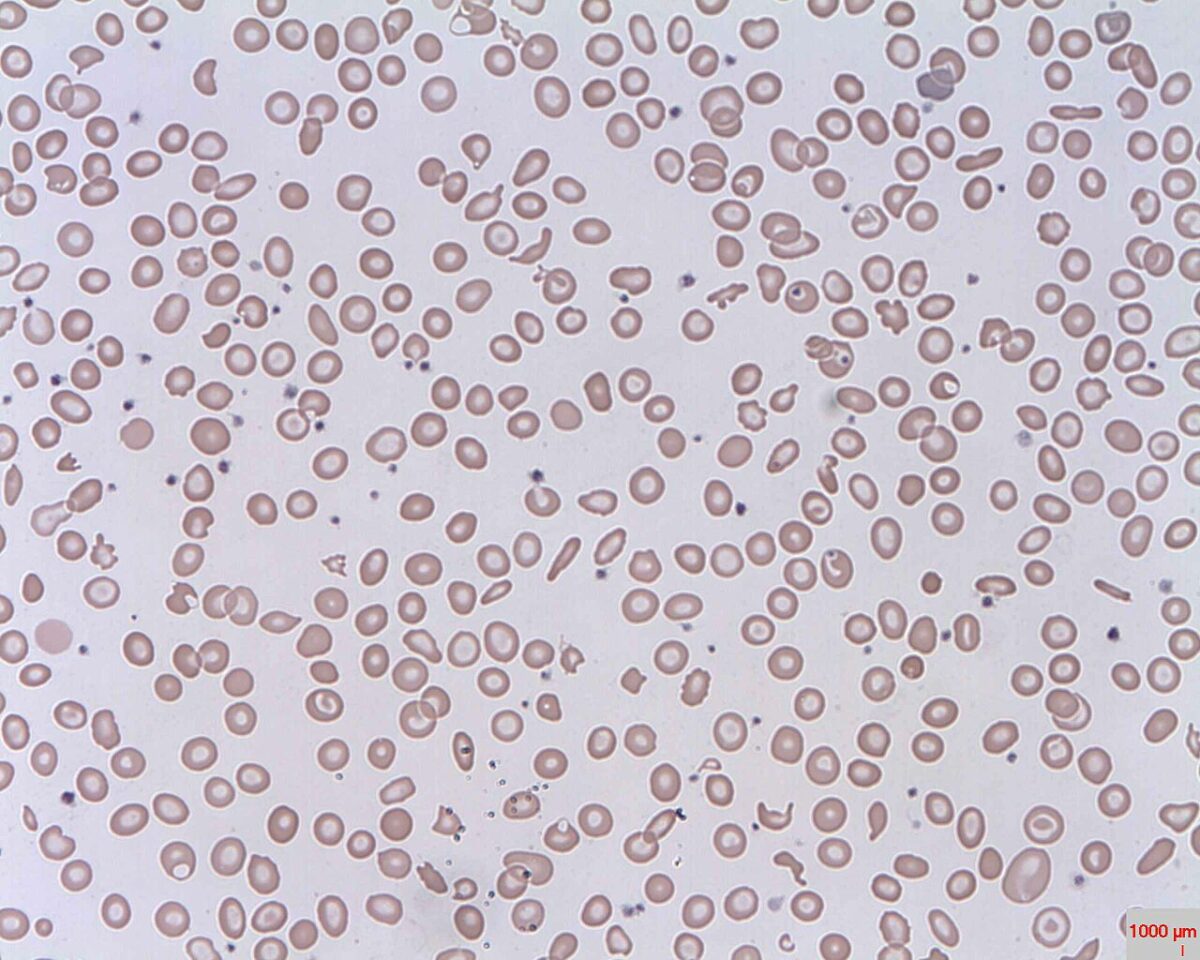
Schistocytes (fragmented RBCs) seen in intravascular hemolysis
Image: “Schistocytes” by Prof. Osaro Erhabor. License: Public Domain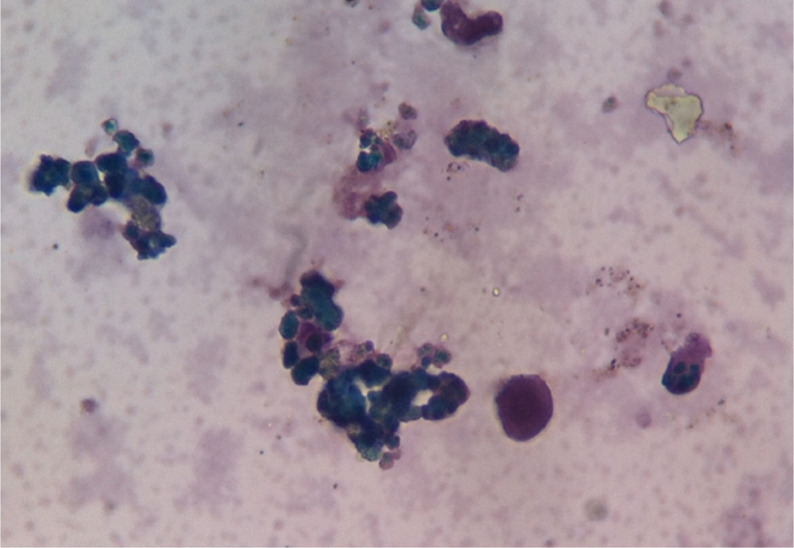
Hemosiderinuria in intravascular hemolysis
Image: “Hemosiderinuria. Perls’ reaction weakly positive in the urine.” by Salido, Eduardo & Cabañas, Valentín & Berenguer, Mercedes & Macizo, María & Candel, Faustino & Pérez-López, Raúl & Moraleda, Jose. (2014). Serological Findings in a Child with Paroxysmal Cold Haemoglobinuria. Case reports in medicine. 2014. Edited by Lecturio.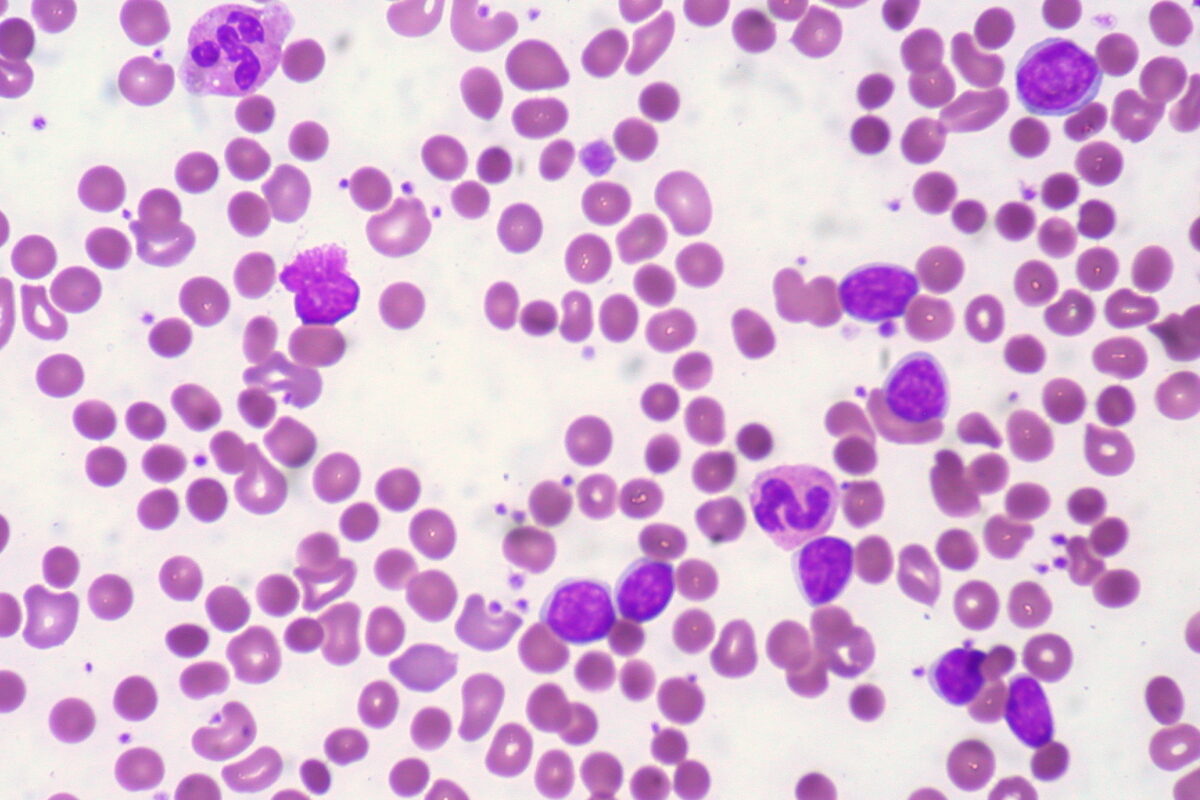
Patient with CLL presents with warm AIHA. Blood film shows spherocytes.
Image: “CLL with Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia” by Ed Uthman from Houston, TX, USA. License: CC BY 2.0