Normal intracranial pressure Intracranial Pressure Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (ICP) is defined as < 15 mm Hg, whereas pathologically increased ICP Increased ICP Excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid within the cranium which may be associated with dilation of cerebral ventricles, intracranial. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage is any pressure ≥ 20 mm Hg. Increased ICP Increased ICP Excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid within the cranium which may be associated with dilation of cerebral ventricles, intracranial. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage may result from several etiologies, including trauma, intracranial hemorrhage Intracranial hemorrhage Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is a type of cerebrovascular accident (stroke) resulting from intracranial hemorrhage into the subarachnoid space between the arachnoid and the pia mater layers of the meninges surrounding the brain. Most sahs originate from a saccular aneurysm in the circle of willis but may also occur as a result of trauma, uncontrolled hypertension, vasculitis, anticoagulant use, or stimulant use. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage, mass Mass Three-dimensional lesion that occupies a space within the breast Imaging of the Breast lesions, cerebral edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema, increased CSF production, and decreased CSF absorption Absorption Absorption involves the uptake of nutrient molecules and their transfer from the lumen of the GI tract across the enterocytes and into the interstitial space, where they can be taken up in the venous or lymphatic circulation. Digestion and Absorption. Increased ICP Increased ICP Excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid within the cranium which may be associated with dilation of cerebral ventricles, intracranial. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage can lead to brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification herniation Herniation Omphalocele and death if not treated promptly. Clinical presentation includes headache Headache The symptom of pain in the cranial region. It may be an isolated benign occurrence or manifestation of a wide variety of headache disorders. Brain Abscess, drowsiness or altered level of consciousness Altered Level of Consciousness Intracerebral Hemorrhage, and papilledema Papilledema Swelling of the optic disk, usually in association with increased intracranial pressure, characterized by hyperemia, blurring of the disk margins, microhemorrhages, blind spot enlargement, and engorgement of retinal veins. Chronic papilledema may cause optic atrophy and visual loss. Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension. Diagnosis is suspected based on the clinical presentation and confirmed with urgent brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification imaging. Immediate management includes measures to decrease ICP, medications including diuretics Diuretics Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. Heart Failure and Angina Medication, and surgery.
Last updated: May 16, 2024
Pathologically increased ICP Increased ICP Excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid within the cranium which may be associated with dilation of cerebral ventricles, intracranial. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage is a pressure ≥ 20 mm Hg.
Increased ICP Increased ICP Excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid within the cranium which may be associated with dilation of cerebral ventricles, intracranial. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage may be due to various clinical conditions. Brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema or obstruction of CSF outflow may result in herniation Herniation Omphalocele and death.
Extracellular:
Intracellular:
Clinical suspicion of increased ICP Increased ICP Excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid within the cranium which may be associated with dilation of cerebral ventricles, intracranial. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage should be aroused in any patient with headaches and papilledema Papilledema Swelling of the optic disk, usually in association with increased intracranial pressure, characterized by hyperemia, blurring of the disk margins, microhemorrhages, blind spot enlargement, and engorgement of retinal veins. Chronic papilledema may cause optic atrophy and visual loss. Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension.
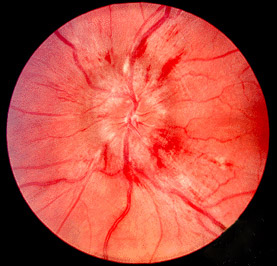
Photo demonstrating papilledema (swollen optic disc with blurred disk margins)
Image: “Papilledema” by Jonathan Trobe, M.D. License: CC BY 3.0Subfalcine herniation Herniation Omphalocele:
Central transtentorial herniation Herniation Omphalocele:
Uncal herniation Herniation Omphalocele:
Cerebellotonsillar herniation Herniation Omphalocele:
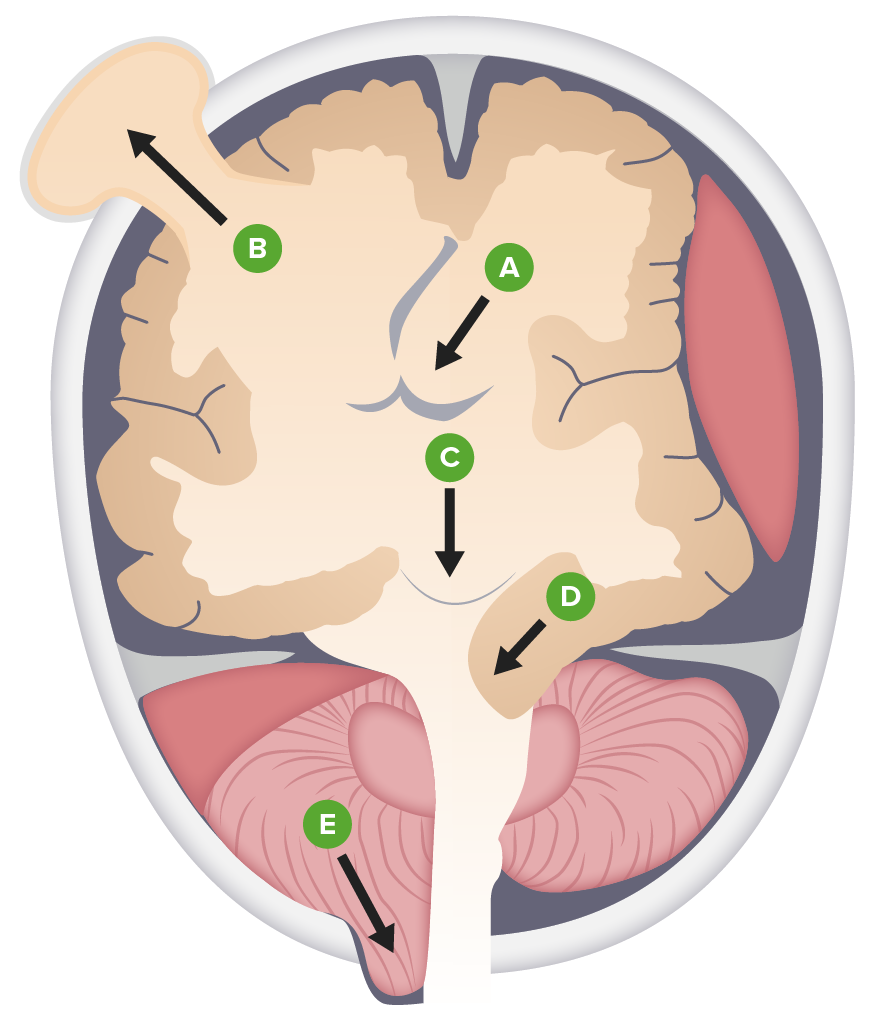
Types of brain herniation:
A. Subfalcine
B. External
C. Central (transtentorial)
D. Uncal
E. Downward cerebellotonsillar
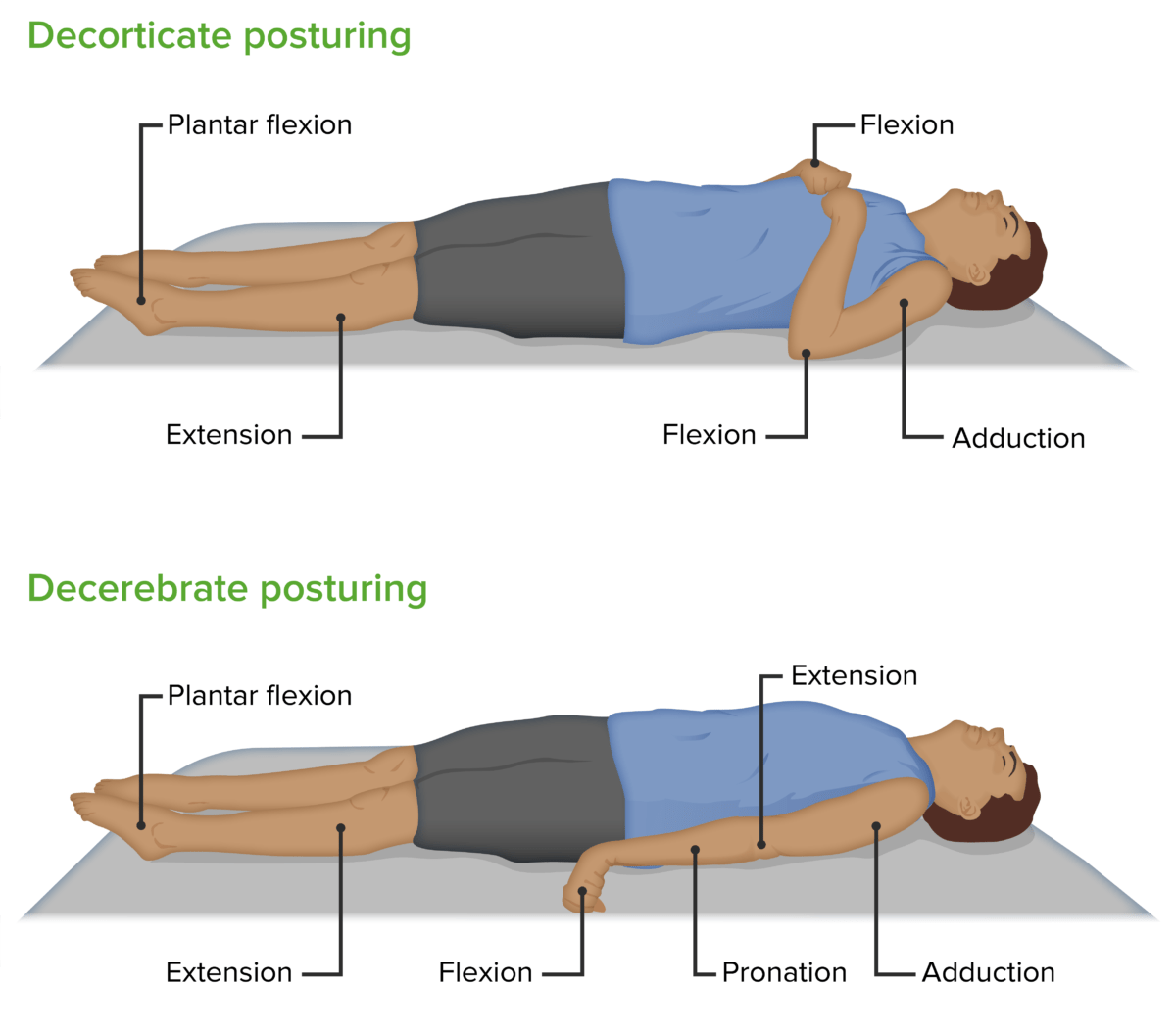
Decorticate and decerebrate posturing
Image by Lecturio.Diagnosis is urgent for a patient presenting with symptoms and signs of increased ICP Increased ICP Excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid within the cranium which may be associated with dilation of cerebral ventricles, intracranial. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Increased ICP Increased ICP Excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid within the cranium which may be associated with dilation of cerebral ventricles, intracranial. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage is a medical emergency regardless of the cause, and immediate measures to reduce ICP acutely should be started until definitive management can be accomplished.
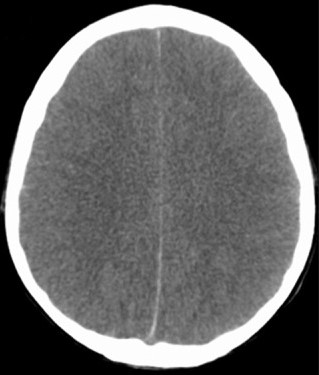
Brain edema on CT:
CT scan of a patient with cerebral edema secondary to viral meningoencephalitis showing lack of differentiation between white and gray matter and the obliteration of sulci spaces
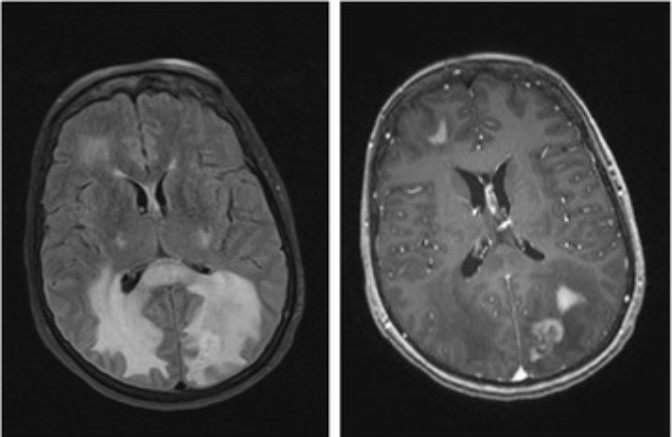
Brain edema and midline shift on MRI:
Fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) (left) and axial T1 postcontrast (right) MRIs of a patient with lymphoma. See the increased intensity around the lesions, indicating vasogenic cerebral edema, and the midline shift, indicating subfalcine herniation.
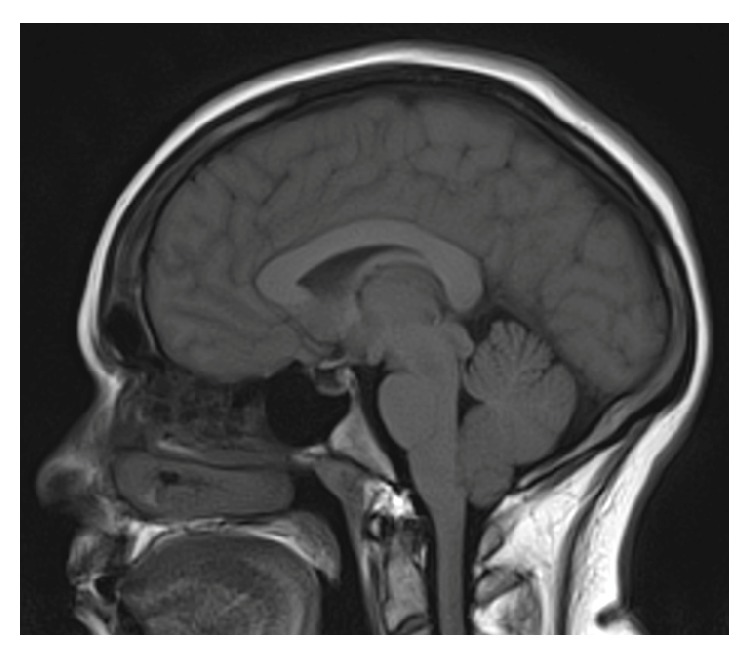
Cerebellar tonsillar herniation:
Sagittal MRI of a patient with cerebellar tonsillar herniation following lumbar puncture in idiopathic intracranial hypertension