Cowden syndrome, also known as multiple hamartoma Hamartoma A focal malformation resembling a neoplasm, composed of an overgrowth of mature cells and tissues that normally occur in the affected area. Colorectal Cancer syndrome, is an autosomal dominant Autosomal dominant Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal dominant diseases are expressed when only 1 copy of the dominant allele is inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance inherited condition that presents with multiple, noncancerous Noncancerous Benign Bone Tumors growths on various parts of the body. The syndrome is classified as a phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) hamartoma Hamartoma A focal malformation resembling a neoplasm, composed of an overgrowth of mature cells and tissues that normally occur in the affected area. Colorectal Cancer tumor Tumor Inflammation syndrome that is caused by mutations in the PTEN gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship usually have macrocephaly, trichilemmomas (hair follicle tumors), and papillomatous papules in the mouth. Cowden syndrome is associated with an increased risk of developing breast, thyroid Thyroid The thyroid gland is one of the largest endocrine glands in the human body. The thyroid gland is a highly vascular, brownish-red gland located in the visceral compartment of the anterior region of the neck. Thyroid Gland: Anatomy, colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy, and endometrial cancer Endometrial Cancer Endometrial carcinoma (EC) is the most common gynecologic malignancy in the developed world, and it has several histologic types. Endometrioid carcinoma (known as type 1 EC) typically develops from atypical endometrial hyperplasia, is hormonally responsive, and carries a favorable prognosis. Endometrial Hyperplasia and Endometrial Cancer. Management includes surveillance Surveillance Developmental Milestones and Normal Growth for associated tumors and prophylactic surgeries.
Last updated: Apr 15, 2025
Cowden syndrome is an autosomal dominant Autosomal dominant Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal dominant diseases are expressed when only 1 copy of the dominant allele is inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance genodermatosis caused by a mutation Mutation Genetic mutations are errors in DNA that can cause protein misfolding and dysfunction. There are various types of mutations, including chromosomal, point, frameshift, and expansion mutations. Types of Mutations in the PTEN gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics and characterized by multiple benign Benign Fibroadenoma hamartomas in any location of the body, mucocutaneous lesions, and macrocephaly.
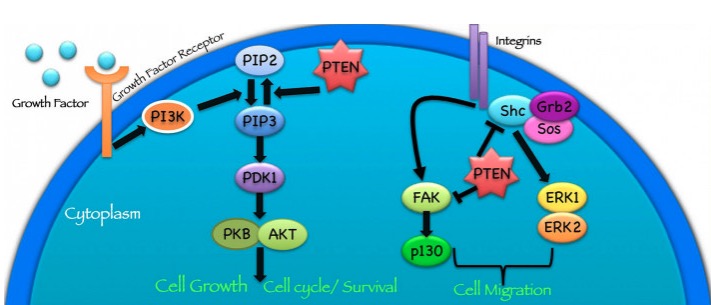
PTEN protein function:
The PTEN protein works in different ways to suppress the formation and spread of tumors.
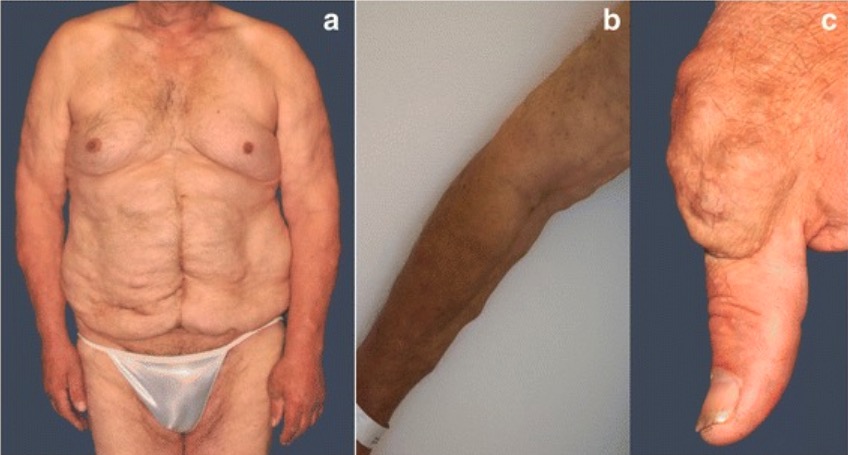
Multiple soft tissue tumors on the torso (a), limbs (b), and the left thumb basal joint (c)
Image: “Fig. 2” by Steffen Pistorius et al. License: CC BY 4.0
Macrocephaly and diffusely enlarged thyroid gland in a pediatric patient with Cowden syndrome
Image: “Diffusely enlarged thyroid gland” by Cláudia Patraquim et al. License: CC BY 2.0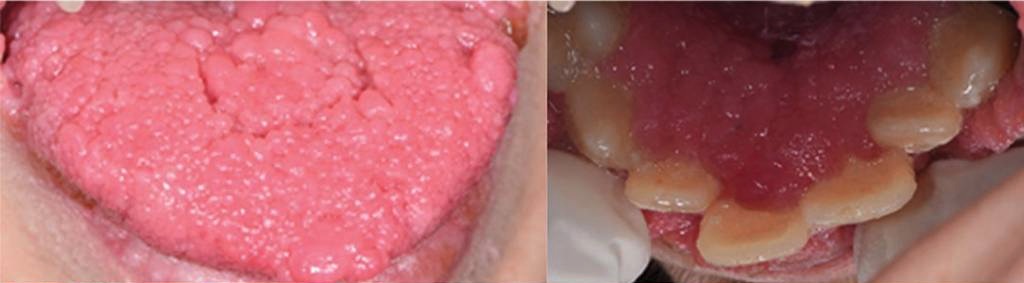
Left: multiple papillomatous lesions on the tongue
Right: multiple coalescent papillomatous lesions covering the cervical area of teeth
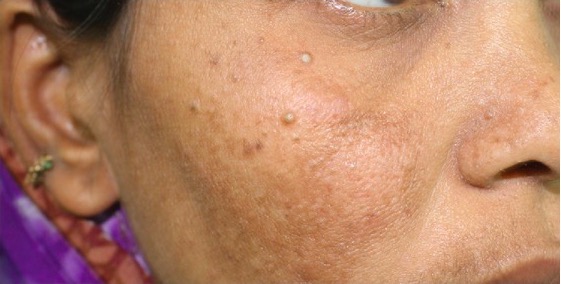
Trichilemmomas on the right malar bone of a patient with multiple hamartoma disease
Image: “Trichilemmomas on the right malar bone” by Prashanthi Chippagiri et al. License: CC BY 3.0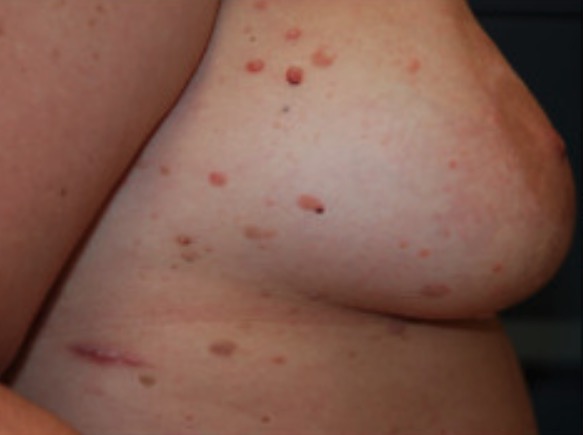
Multiple seborrheic keratoses in a patient with early-onset bilateral breast cancer
Image: “Cutaneous findings of our case” by Laura Maria Pradella et al. License: CC BY 2.0, cropped by Lecturio.Lab work-up is directed by the clinical presentation. Cowden syndrome can present with anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types (from GI blood loss), renal disease, thyroid Thyroid The thyroid gland is one of the largest endocrine glands in the human body. The thyroid gland is a highly vascular, brownish-red gland located in the visceral compartment of the anterior region of the neck. Thyroid Gland: Anatomy disease, and skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions lesions.
Imaging for Cowden syndrome is based on the presenting complaint, and can include:
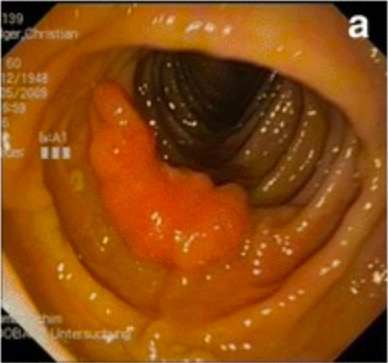
Hamartoma of the descending colon in a patient with Cowden syndrome
Image: “Preoperative colonoscopic views” by Pistorius et al. License: CC BY 4.0, cropped by Lecturio.