Fat necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage of the breast is an inflammatory, benign Benign Fibroadenoma condition resulting from injury to the breast tissue. Forms of injury include blunt traumatic injury as well as trauma from surgical procedures, biopsies, and radiation Radiation Emission or propagation of acoustic waves (sound), electromagnetic energy waves (such as light; radio waves; gamma rays; or x-rays), or a stream of subatomic particles (such as electrons; neutrons; protons; or alpha particles). Osteosarcoma therapy. Fat necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage of the breast is characterized by the presence of an ill-defined breast mass Mass Three-dimensional lesion that occupies a space within the breast Imaging of the Breast that is usually accompanied by overlying skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions changes. Oil cysts Cysts Any fluid-filled closed cavity or sac that is lined by an epithelium. Cysts can be of normal, abnormal, non-neoplastic, or neoplastic tissues. Fibrocystic Change may also form as fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans and calcification trap oil from degenerating fat cells. Fat necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage of the breast may be clinically and radiographically difficult to distinguish from a malignant mass Mass Three-dimensional lesion that occupies a space within the breast Imaging of the Breast. Diagnosis relies on a history consistent with trauma, breast imaging Breast Imaging Female breasts, made of glandular, adipose, and connective tissue, are hormone-sensitive organs that undergo changes along with the menstrual cycle and during pregnancy. Breasts may be affected by various diseases, in which different imaging methods are important to arrive at the correct diagnosis and management. Mammography is used for breast cancer screening and diagnostic evaluation of various breast-related symptoms. Imaging of the Breast, and, less commonly, a core needle biopsy Core Needle Biopsy Fibrocystic Change for definitive diagnosis. Treatment is usually not required. The primary clinical significance of this condition is its possible confusion with breast cancer Breast cancer Breast cancer is a disease characterized by malignant transformation of the epithelial cells of the breast. Breast cancer is the most common form of cancer and 2nd most common cause of cancer-related death among women. Breast Cancer on exam and imaging.
Last updated: Mar 13, 2025
Fat necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage is a benign Benign Fibroadenoma breast lesion that results from injury to the breast tissue.
Mechanisms of injury:
Tissue response:

Fat necrosis of the breast with an area of skin necrosis secondary to injection of methylene blue dye
Image: “Skin and fat necrosis of the right breast” by St Georges Hospital, London, UK. License: CC BY 2.0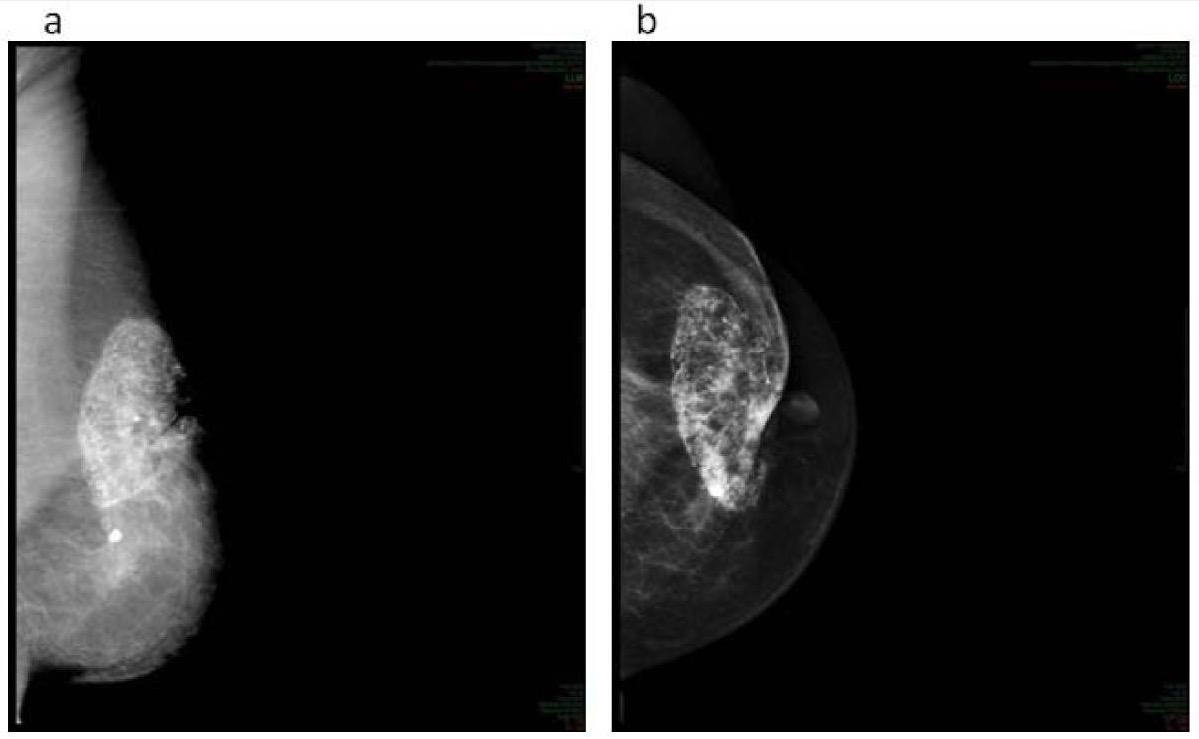
Mammography demonstrating fat necrosis
Image: “G3 fat necrosis” by Department of Radiation Oncology, Laboratory of Medical Physics and Expert Systems, Regina Elena National Cancer Institute, Rome, Italy. License: CC BY 2.0