Orbital and preseptal cellulitis Cellulitis Cellulitis is a common infection caused by bacteria that affects the dermis and subcutaneous tissue of the skin. It is frequently caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. The skin infection presents as an erythematous and edematous area with warmth and tenderness. Cellulitis are infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease differentiated by the anatomic sites affected in the orbit. Infection anterior to the orbital septum is preseptal cellulitis Cellulitis Cellulitis is a common infection caused by bacteria that affects the dermis and subcutaneous tissue of the skin. It is frequently caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. The skin infection presents as an erythematous and edematous area with warmth and tenderness. Cellulitis; infection posterior to the septum is orbital cellulitis Cellulitis Cellulitis is a common infection caused by bacteria that affects the dermis and subcutaneous tissue of the skin. It is frequently caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. The skin infection presents as an erythematous and edematous area with warmth and tenderness. Cellulitis. Inoculation with the pathogen can occur through trauma or surgery. Cellulitis Cellulitis Cellulitis is a common infection caused by bacteria that affects the dermis and subcutaneous tissue of the skin. It is frequently caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. The skin infection presents as an erythematous and edematous area with warmth and tenderness. Cellulitis also occurs via extension Extension Examination of the Upper Limbs from a nearby structure (such as from sinus infection or sinusitis Sinusitis Sinusitis refers to inflammation of the mucosal lining of the paranasal sinuses. The condition usually occurs concurrently with inflammation of the nasal mucosa (rhinitis), a condition known as rhinosinusitis. Acute sinusitis is due to an upper respiratory infection caused by a viral, bacterial, or fungal agent. Sinusitis). Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship will have eyelid erythema Erythema Redness of the skin produced by congestion of the capillaries. This condition may result from a variety of disease processes. Chalazion, pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, and swelling Swelling Inflammation. Distinguishing characteristics of orbital cellulitis Cellulitis Cellulitis is a common infection caused by bacteria that affects the dermis and subcutaneous tissue of the skin. It is frequently caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. The skin infection presents as an erythematous and edematous area with warmth and tenderness. Cellulitis include ophthalmoplegia, proptosis Proptosis Retinoblastoma, painful eye movement, and possible vision Vision Ophthalmic Exam impairment. Complications are rare with preseptal cellulitis Cellulitis Cellulitis is a common infection caused by bacteria that affects the dermis and subcutaneous tissue of the skin. It is frequently caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. The skin infection presents as an erythematous and edematous area with warmth and tenderness. Cellulitis, and treatment can be initiated with oral antibiotics. Orbital cellulitis Cellulitis Cellulitis is a common infection caused by bacteria that affects the dermis and subcutaneous tissue of the skin. It is frequently caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. The skin infection presents as an erythematous and edematous area with warmth and tenderness. Cellulitis, however, requires intravenous broad-spectrum Broad-Spectrum Fluoroquinolones antibiotics and in severe cases, surgical drainage.
Last updated: Mar 6, 2023
Orbit:
Orbital septum:
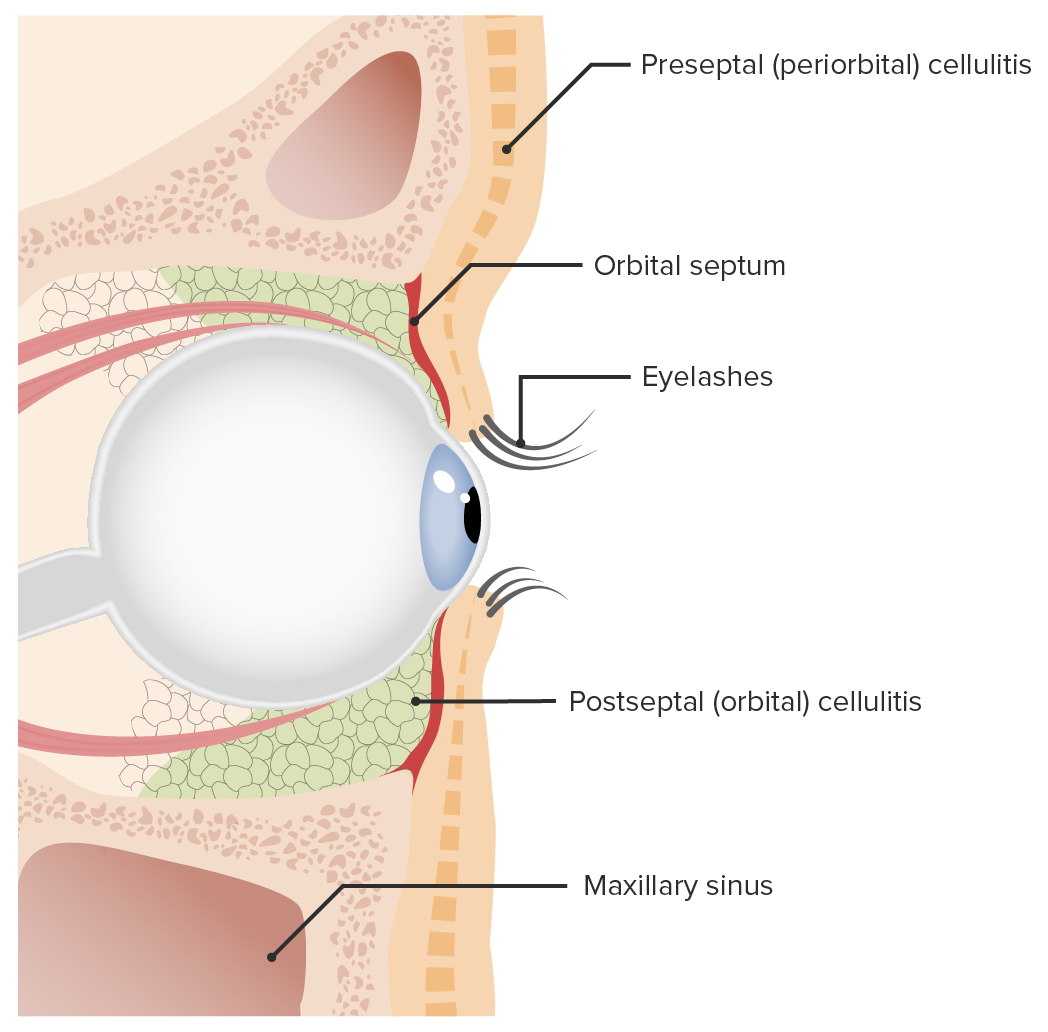
Preseptal and orbital cellulitis:
Preseptal cellulitis is differentiated from orbital cellulitis according to where the infection is in relation to the orbital septum. Preseptal infection occurs anterior to the orbital septum, while orbital cellulitis affects the area posterior to the septum.
Microbiology:
Preseptal and orbital cellulitis Cellulitis Cellulitis is a common infection caused by bacteria that affects the dermis and subcutaneous tissue of the skin. It is frequently caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. The skin infection presents as an erythematous and edematous area with warmth and tenderness. Cellulitis have common findings:
However, orbital cellulitis Cellulitis Cellulitis is a common infection caused by bacteria that affects the dermis and subcutaneous tissue of the skin. It is frequently caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. The skin infection presents as an erythematous and edematous area with warmth and tenderness. Cellulitis involves inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body’s defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation and swelling Swelling Inflammation of the extraocular muscles and fatty tissues, which is not found in preseptal cellulitis Cellulitis Cellulitis is a common infection caused by bacteria that affects the dermis and subcutaneous tissue of the skin. It is frequently caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. The skin infection presents as an erythematous and edematous area with warmth and tenderness. Cellulitis.
Red flags that raise suspicion for orbital cellulitis Cellulitis Cellulitis is a common infection caused by bacteria that affects the dermis and subcutaneous tissue of the skin. It is frequently caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. The skin infection presents as an erythematous and edematous area with warmth and tenderness. Cellulitis:
| Clinical presentation | Orbital | Preseptal |
|---|---|---|
| Eyelid swelling Swelling Inflammation and redness Redness Inflammation, eye discharge | Yes | Yes |
| Normal pupillary response | Usually | Yes |
| Pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways with eye movement | Yes | No |
| Diplopia Diplopia A visual symptom in which a single object is perceived by the visual cortex as two objects rather than one. Disorders associated with this condition include refractive errors; strabismus; oculomotor nerve diseases; trochlear nerve diseases; abducens nerve diseases; and diseases of the brain stem and occipital lobe. Myasthenia Gravis | May be present | No |
| Ophthalmoplegia | May be present | No |
| Proptosis Proptosis Retinoblastoma | May be present | No |
| Vision Vision Ophthalmic Exam impairment | May be present | No |
| Chemosis Chemosis Conjunctivitis (conjunctival swelling Swelling Inflammation) | May be present | Rare |
| Fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever | Usually | Rare |
| Complications |
|
Rare |
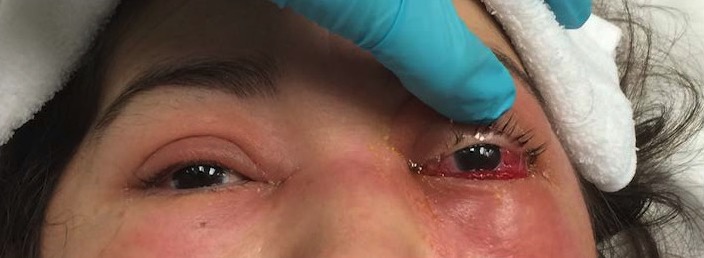
Left orbital cellulitis: The photograph shows left upper and lower eyelid edema and erythema, with conjunctival chemosis.
Image: “External photograph” by Ruiz Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Science, The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, Houston, TX, USA. License: CC BY 4.0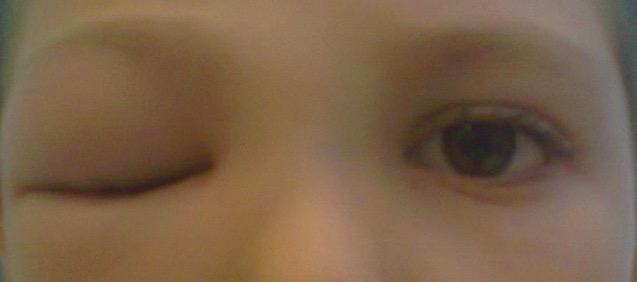
Right preseptal cellulitis:
The photograph shows marked, isolated, and unilateral periocular inflammation. The patient presented with painless eye movement.
Both conditions are usually diagnosed clinically.
Imaging studies:
CT scan with contrast:
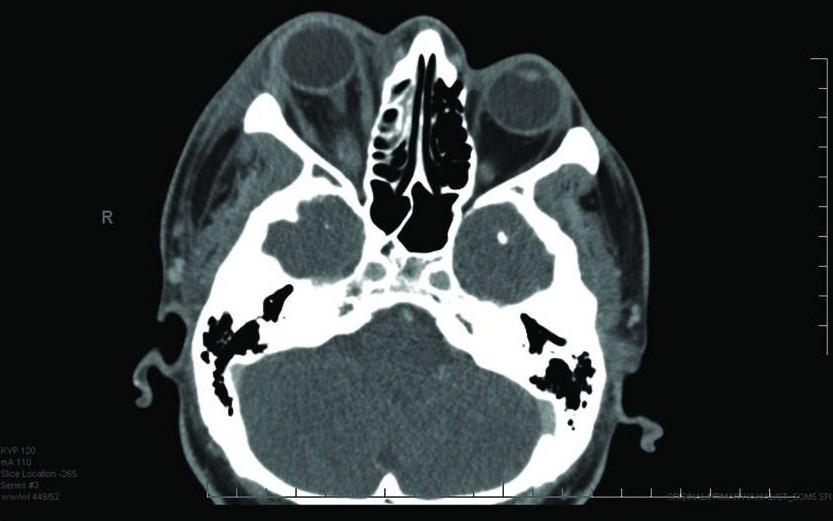
Orbital cellulitis:
CT scan shows right proptosis and facial soft tissue swelling.
Lab tests are generally of low diagnostic value.
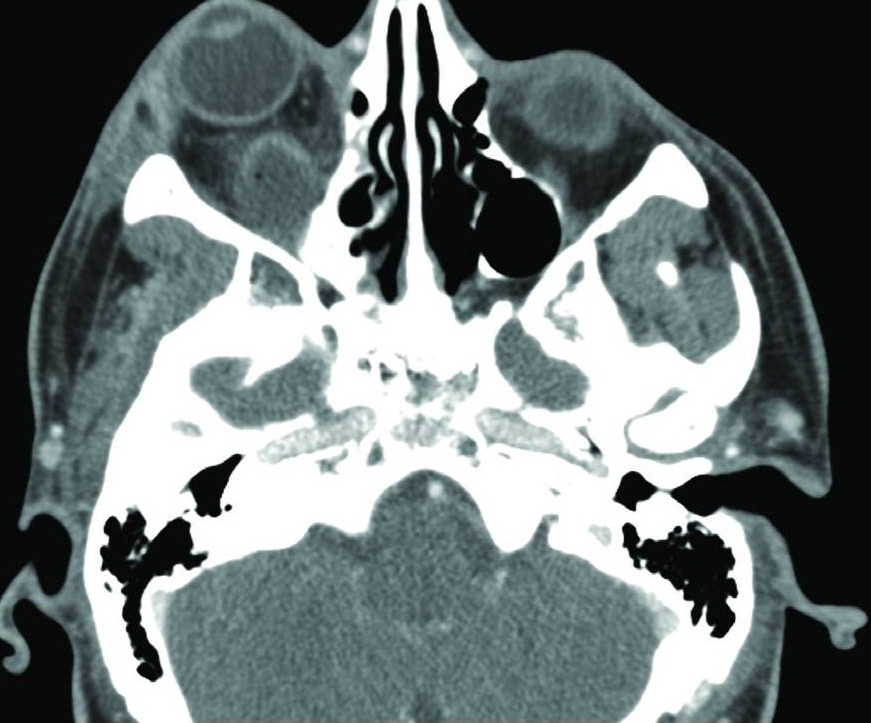
Orbital abscess:
CT scan shows development of an abscess (collection) posterior to the right eye.