Cellulitis is a common infection caused by bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology that affects the dermis Dermis A layer of vascularized connective tissue underneath the epidermis. The surface of the dermis contains innervated papillae. Embedded in or beneath the dermis are sweat glands; hair follicles; and sebaceous glands. Skin: Structure and Functions and subcutaneous tissue Subcutaneous tissue Loose connective tissue lying under the dermis, which binds skin loosely to subjacent tissues. It may contain a pad of adipocytes, which vary in number according to the area of the body and vary in size according to the nutritional state. Soft Tissue Abscess of the skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions. It is frequently caused by Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess and Streptococcus Streptococcus Streptococcus is one of the two medically important genera of gram-positive cocci, the other being Staphylococcus. Streptococci are identified as different species on blood agar on the basis of their hemolytic pattern and sensitivity to optochin and bacitracin. There are many pathogenic species of streptococci, including S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, S. pneumoniae, and the viridans streptococci. Streptococcus pyogenes. The skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions infection presents as an erythematous and edematous area with warmth and tenderness. The borders are not clearly delineated. The lower extremities are the most frequent site of infection, but cellulitis can occur anywhere on the body. Diagnosis is usually clinical, and management involves oral and/or parenteral antibiotics. Coverage for MRSA MRSA A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins. Staphylococcus may be added, depending on the presence of risk factors.
Last updated: May 17, 2024
Cellulitis is inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body’s defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation of the skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions and subcutaneous tissues. It is often due to infection.
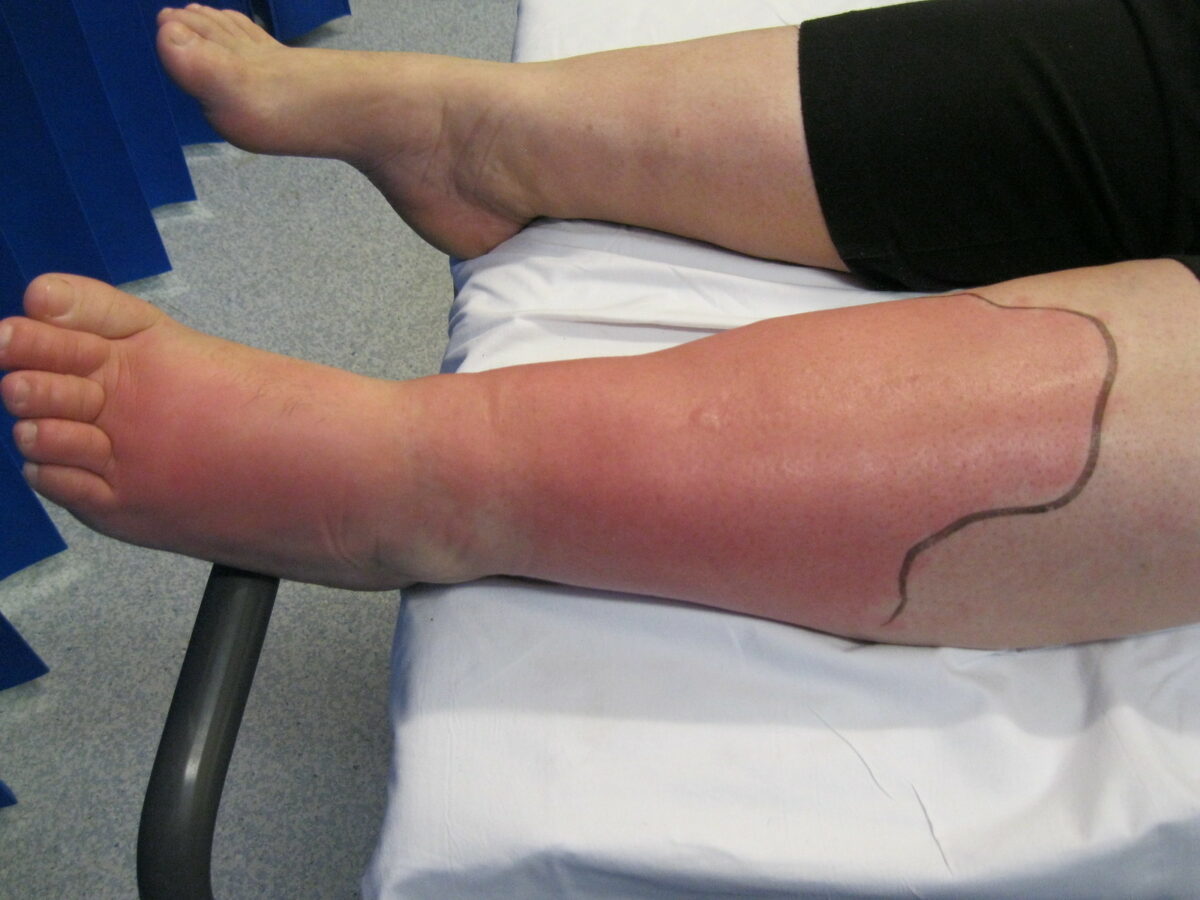
Left lower extremity cellulitis:
Edema and erythema of the skin are noted in the left leg and foot.
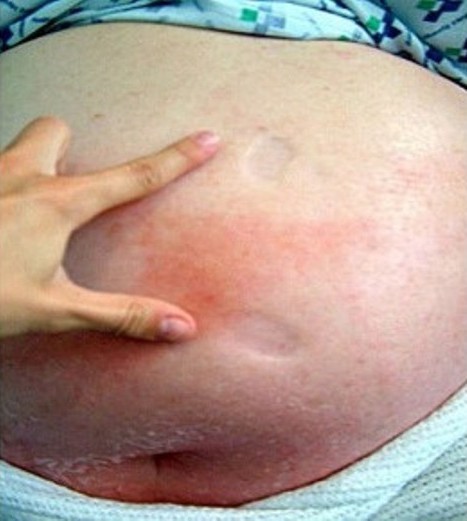
Abdominal wall cellulitis:
Image shows marked pitting edema and erythema with poorly demarcated borders due to cellulitis.
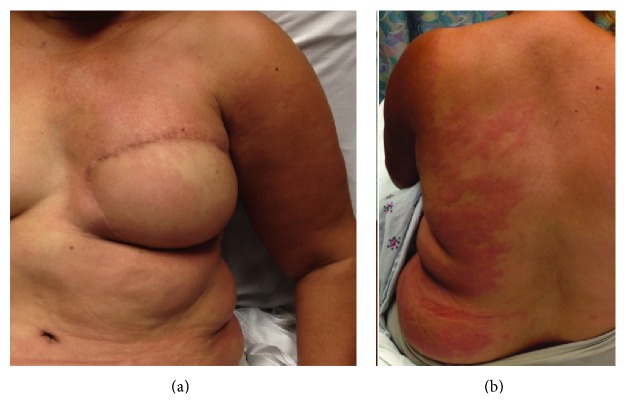
Lymphedema cellulitis:
Stagnant lymph is an ideal medium for bacterial growth, and progression can be rapid owing to a decreased ability to fight infection in the affected area. Infections are commonly caused by gram-positive cocci bacteria.
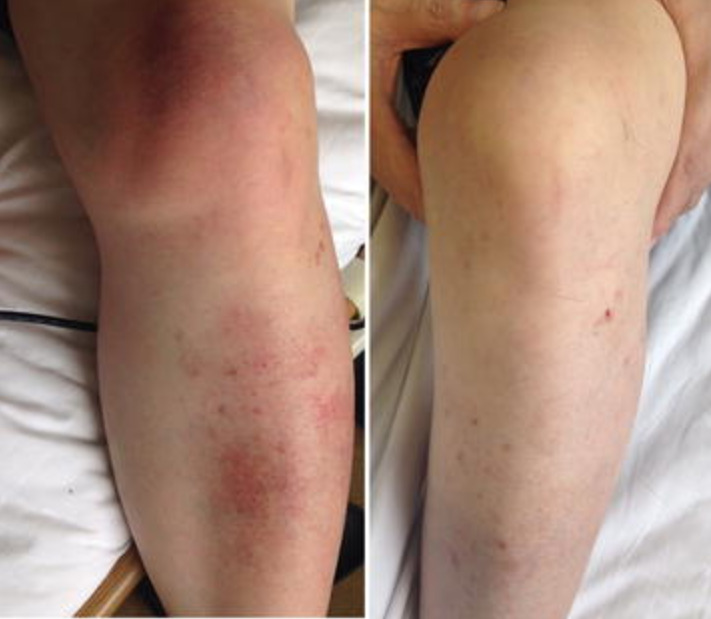
Cellulitis in the left lower leg and knee:
Left: Local swelling with salmon-pink skin discoloration and local warmth is evident.
Right: leg after 6 weeks of antibiotic therapy