Down syndrome, or trisomy Trisomy The possession of a third chromosome of any one type in an otherwise diploid cell. Types of Mutations 21, is the most common chromosomal aberration and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental delay. Both boys and girls are affected and have characteristic craniofacial and musculoskeletal features, as well as multiple medical anomalies involving the cardiac, gastrointestinal, ocular, and auditory systems. Characteristic traits include upslanting, almond-shaped eyes with skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions covering the inner aspects, broad flattened nasal bridge, small rounded ears, and small mouth with large tongue Tongue The tongue, on the other hand, is a complex muscular structure that permits tasting and facilitates the process of mastication and communication. The blood supply of the tongue originates from the external carotid artery, and the innervation is through cranial nerves. Lips and Tongue: Anatomy. Screening Screening Preoperative Care for Down syndrome occurs during the 1st and 2nd trimesters of pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care and includes both blood tests and prenatal ultrasonography. Ultimately, karyotyping Karyotyping Mapping of the karyotype of a cell. Chromosome Testing confirms diagnosis in the prenatal or postnatal period Postnatal period Prenatal and Postnatal Physiology of the Neonate. There is no cure for Down syndrome. Treatment is based on the clinical manifestations present; it includes a strong support system and early intervention programs to help with education and development.
Last updated: Mar 18, 2025
There are 3 genotypes that result in Down syndrome.
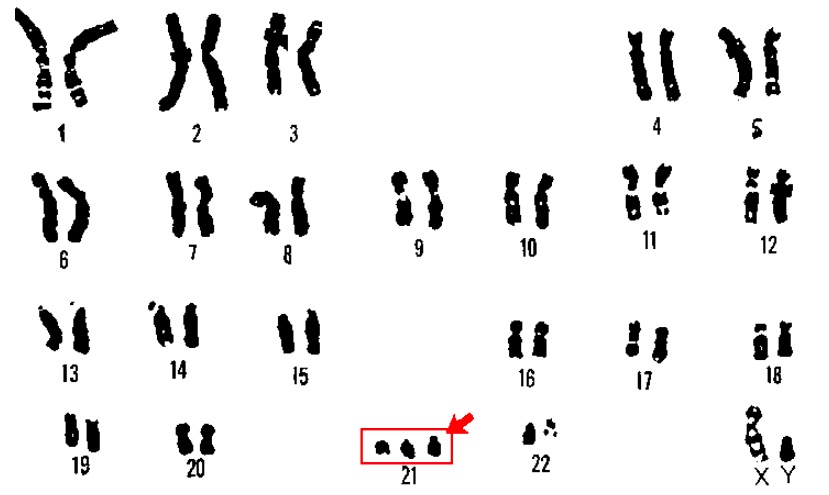
Karyotype of trisomy 21 (Down syndrome):
A karyotype is a laboratory technique in which an individual’s chromosomes are paired and photographed. In a patient with Down syndrome, 3 copies of chromosome 21 are usually visible.
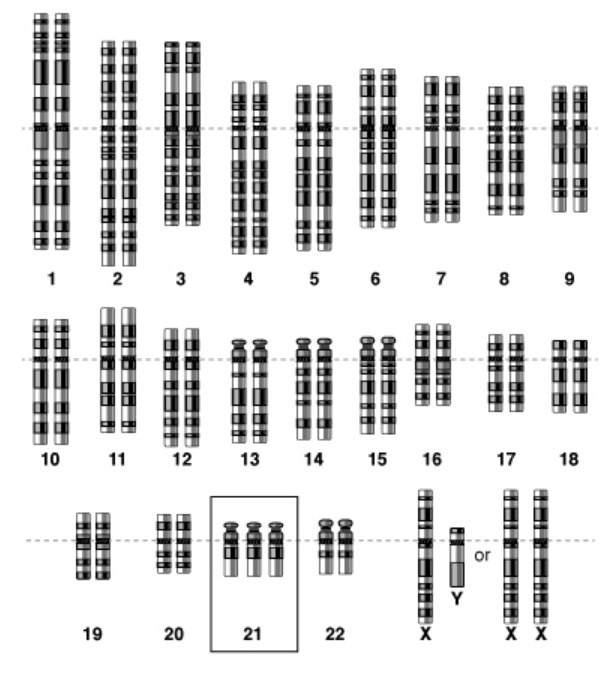
Scheme of a genetic mutation, in this case of trisomy 21
Image: “Genome scheme of trisomy 21” by National Human Genome Research Institute. License: Public Domain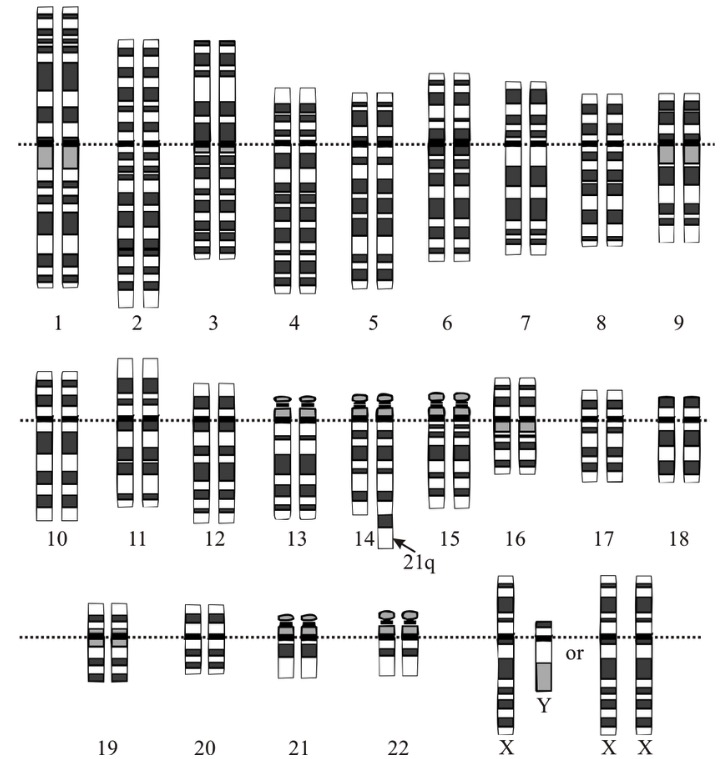
Down syndrome translocation
Image: “Down syndrome translocation” by National Human Genome Research Institute. License: Public Domain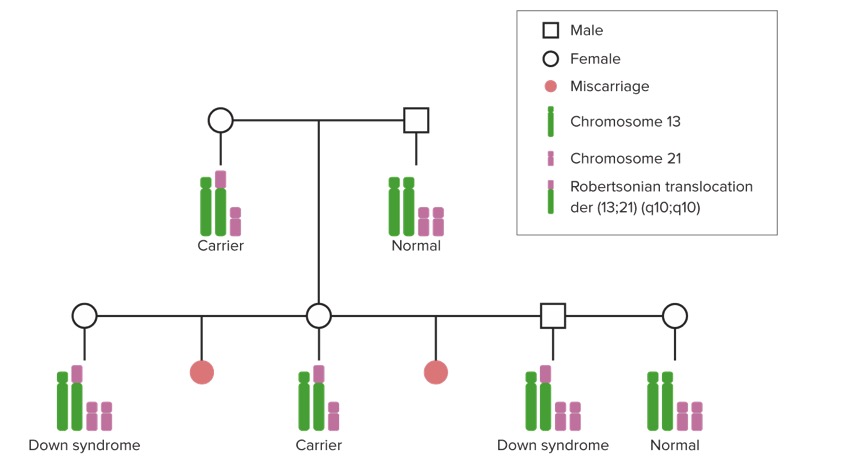
Robertsonian translocation of Down syndrome in families:
In a Robertsonian translocation causing Down syndrome, part of an extra or a whole extra chromosome 21 is attached (translocated) to another chromosome. Individuals who inherit this chromosome have 3 copies of the genetic material found on chromosome 21, and thus have Down syndrome.
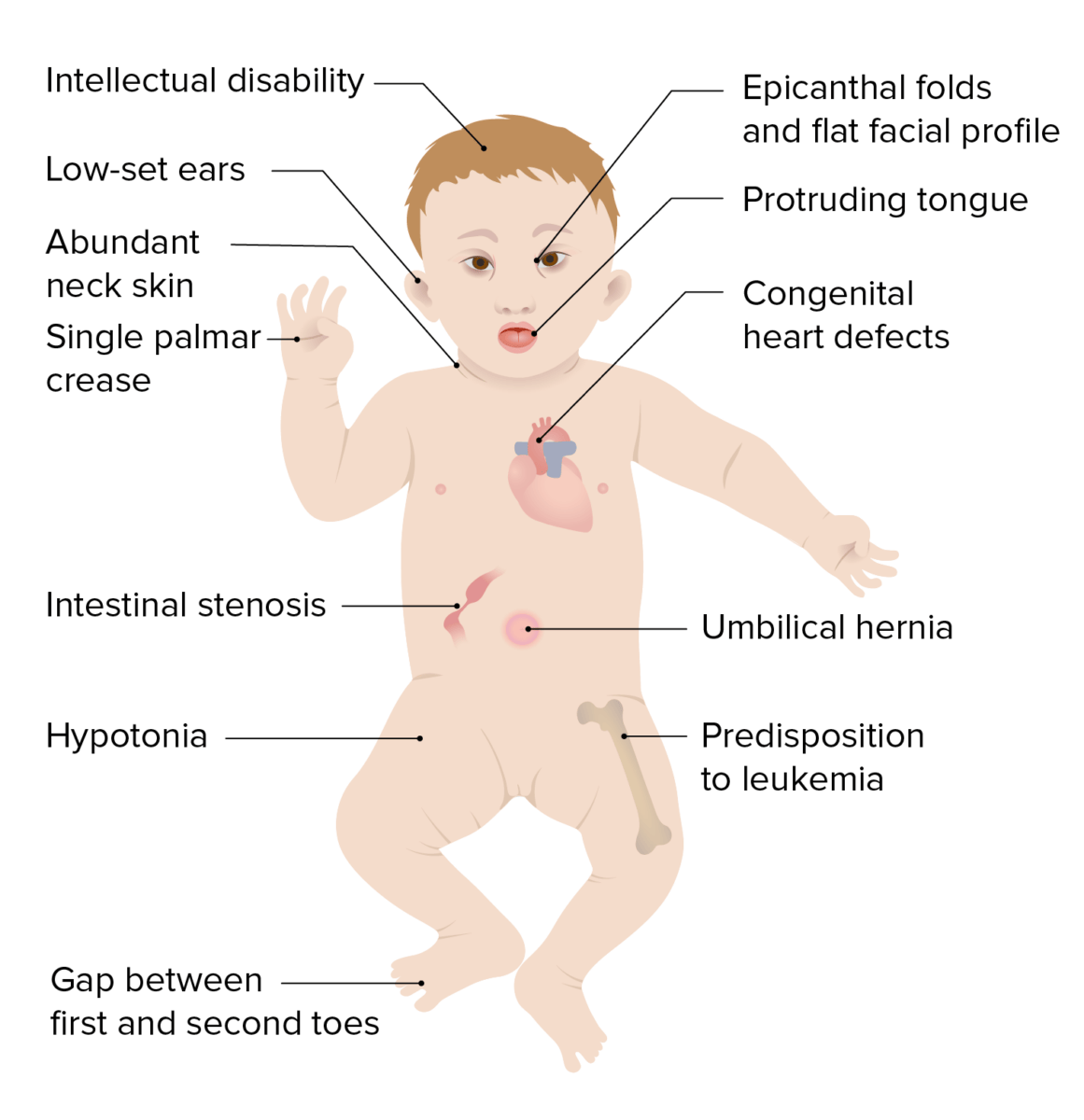
Clinical presentation of Down syndrome
Image by Lecturio.
The eyes of a baby with Down syndrome:
Brushfield spots are visible between the inner and outer circles of the iris.
High prevalence Prevalence The total number of cases of a given disease in a specified population at a designated time. It is differentiated from incidence, which refers to the number of new cases in the population at a given time. Measures of Disease Frequency of ocular disorders: Frequency increases with age.
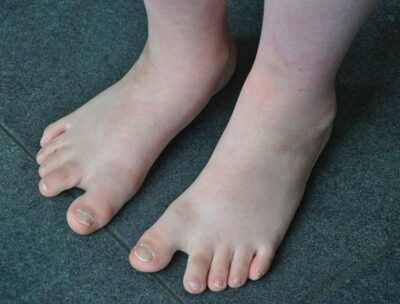
Feet of a 10-year-old boy with Down syndrome, with the typical large space between the large toe and the second toe
Image: “Feet of a boy with Down syndrome” by Loranchet. License: CC BY 3.0Screening Screening Preoperative Care is recommended prior to 20th week of gestation.
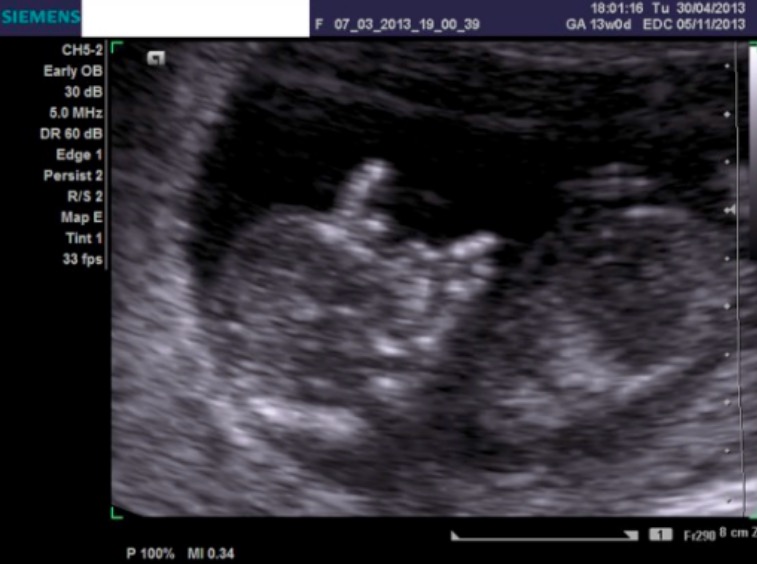
Trisomy 21 on ultrasound:
Ultrasound image of fetus at 12 weeks, showing nuchal translucency and presence of nasal bone
Given the pervasive nature of Down syndrome and the lack of a cure, the majority of management focuses on screening Screening Preoperative Care and prevention of the various clinical manifestations and complications associated with the syndrome.