The ductus arteriosus (DA) is a fetal blood vessel connecting the left pulmonary artery Pulmonary artery The short wide vessel arising from the conus arteriosus of the right ventricle and conveying unaerated blood to the lungs. Lungs: Anatomy to the aorta Aorta The main trunk of the systemic arteries. Mediastinum and Great Vessels: Anatomy. The DA allows blood to bypass pulmonary circulation Circulation The movement of the blood as it is pumped through the cardiovascular system. ABCDE Assessment. After birth, the DA remains open for up to 72 hours and then constricts and involutes, becoming the ligamentum arteriosum Ligamentum arteriosum Prenatal and Postnatal Physiology of the Neonate. Failure of this process to occur results in patent ductus arteriosus (PDA), a condition that causes up to 10% of congenital heart defects. Patent ductus arteriosus is twice as common in girls (especially premature infants Premature infants A human infant born before 37 weeks of gestation. Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS)) and causes a continuous machinery-like murmur on clinical examination. Patent ductus arteriosus may be associated with other cardiac defects; an echocardiogram Echocardiogram Transposition of the Great Arteries can confirm the diagnosis. Treatment aims at closure of the remnant structure either through pharmacological or surgical means.
Last updated: May 16, 2024
The ductus arteriosus (DA) is a fetal blood vessel connecting the left pulmonary artery Pulmonary artery The short wide vessel arising from the conus arteriosus of the right ventricle and conveying unaerated blood to the lungs. Lungs: Anatomy to the aorta Aorta The main trunk of the systemic arteries. Mediastinum and Great Vessels: Anatomy, bypassing the pulmonary circulation Circulation The movement of the blood as it is pumped through the cardiovascular system. ABCDE Assessment. Failure of the vessel to close and involute within 72 hours of birth results in a condition called patent ductus arteriosus (PDA).
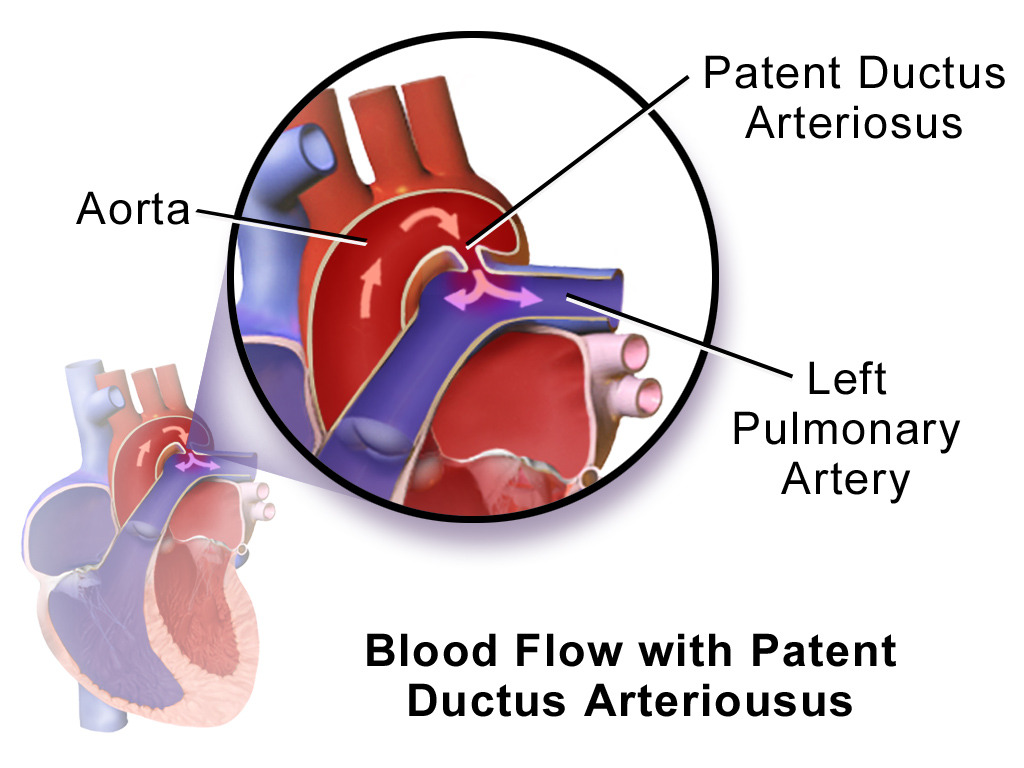
The DA:
The DA is a fetal blood vessel connecting the aorta (usually at the arch) to the left pulmonary artery. When this vessel persists after birth, it is termed PDA.
The severity of symptoms depends primarily on the degree of L-R shunt, which is dictated by size and length of the defect.
| Degree of shunt | Clinical presentation | Physical examination |
|---|---|---|
| Small shunt |
|
Murmur:
|
| Moderate shunt |
|
|
| Large shunt | Infant:
|
|
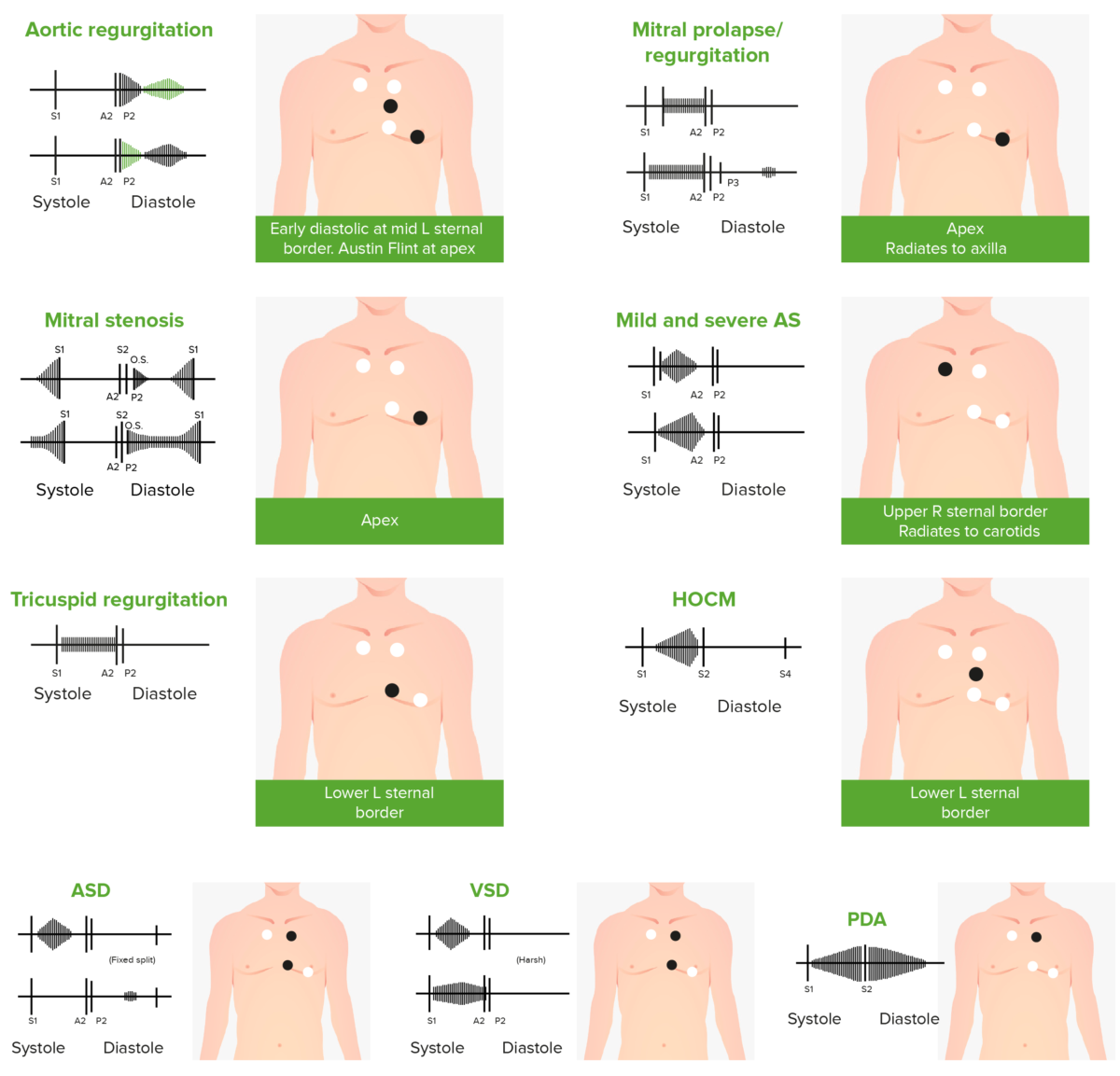
Phonocardiograms of abnormal heart sounds caused by the following cardiac defects:
aortic regurgitation, mitral valve prolapse, mitral stenosis (MS), aortic stenosis (AS), tricuspid regurgitation, hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM), atrial septal defect (ASD), ventricular septal defect (VSD), and patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
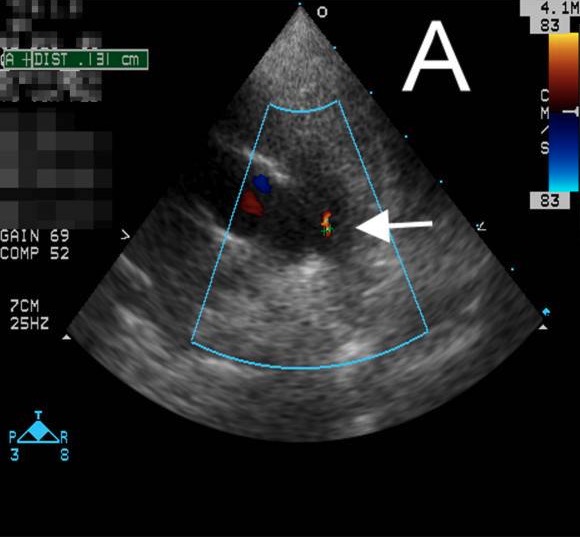
Echocardiogram showing PDA:
An echocardiogram depicting PDA with a small shunt (white arrow) found incidentally in a patient with Kawasaki disease
Continuous murmur of PDA should be differentiated from: