Tetralogy of Fallot is the most common cyanotic congenital heart disease. The disease is the confluence of 4 pathologic cardiac features: overriding aorta Aorta The main trunk of the systemic arteries. Mediastinum and Great Vessels: Anatomy, ventricular septal defect, right ventricular outflow obstruction, and right ventricular hypertrophy Hypertrophy General increase in bulk of a part or organ due to cell enlargement and accumulation of fluids and secretions, not due to tumor formation, nor to an increase in the number of cells (hyperplasia). Cellular Adaptation. The timing and severity of presentation usually depend on the degree of right ventricular outflow obstruction. Definitive diagnosis is usually established by echocardiogram Echocardiogram Transposition of the Great Arteries. Chest X-ray X-ray Penetrating electromagnetic radiation emitted when the inner orbital electrons of an atom are excited and release radiant energy. X-ray wavelengths range from 1 pm to 10 nm. Hard x-rays are the higher energy, shorter wavelength x-rays. Soft x-rays or grenz rays are less energetic and longer in wavelength. The short wavelength end of the x-ray spectrum overlaps the gamma rays wavelength range. The distinction between gamma rays and x-rays is based on their radiation source. Pulmonary Function Tests may show the classic boot-shaped heart. Definitive treatment involves surgical repair. Long-term prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas is good for surgically corrected disease, but cardiovascular morbidity Morbidity The proportion of patients with a particular disease during a given year per given unit of population. Measures of Health Status is common.
Last updated: Jun 18, 2025
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is the most common cyanotic congenital heart disease and has the following 4 (tetra) features:
DROP:
PROVe:
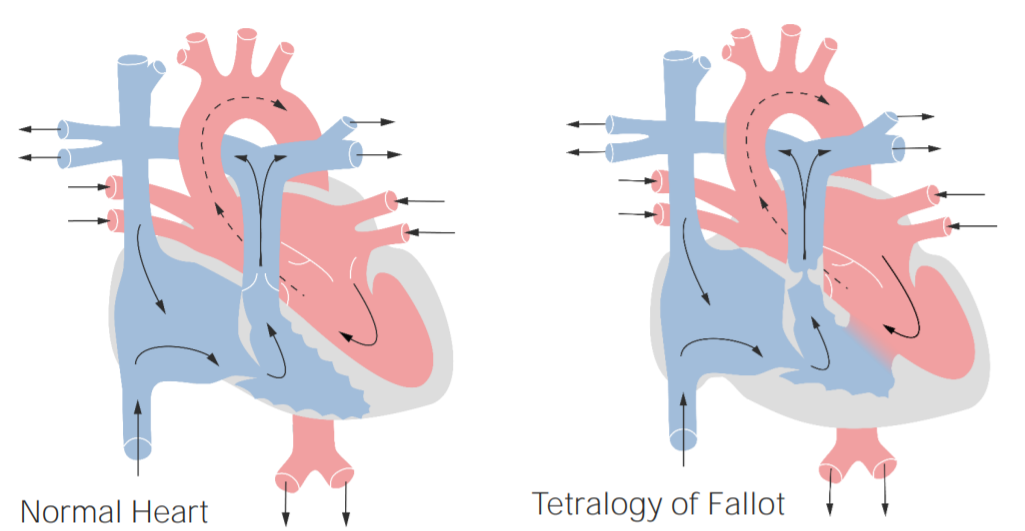
Anatomy and physiology of tetralogy of Fallot
Left: normal heart
Right: tetralogy of Fallot
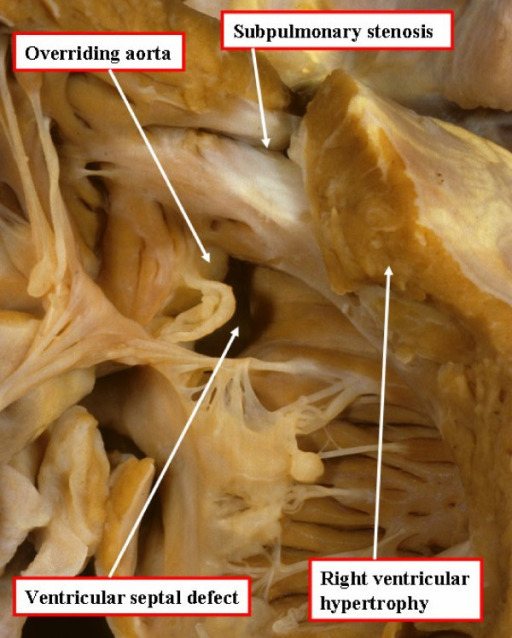
Cardinal features of tetralogy of Fallot: autopsy specimen opened through the anterior wall of the right ventricle
Image: “Tetralogy of Fallot autopsy” by North Carolina Children’s Heart Center, Department of Pediatrics, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC, USA. License: CC BY 2.0Age of presentation is inversely proportional to the degree of RVOT obstruction.
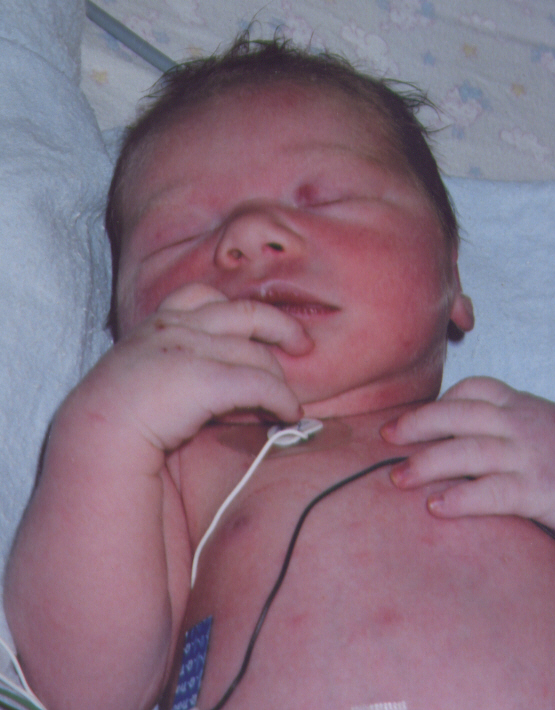
Cyanosis in a neonate due to congenital heart disease:
The infant in the image displays cyanosis due to poor perfusion caused by congenital heart disease (in this case, transposition of the great vessels, but all cyanosis due to congenital heart disease looks similar). Cyanosis can be subtle and is most clearly seen around the lips and fingertips.
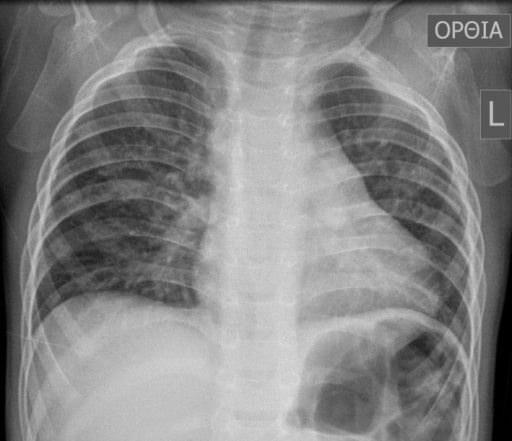
Boot-shaped heart: chest X-ray of a 16-month-old boy with tetralogy of Fallot
Image: “Typical preoperative chest X‐ray of a 16‐month‐old boy with tetralogy of Fallot” by Andrew C. Chatzis et al. License: CC BY 4.0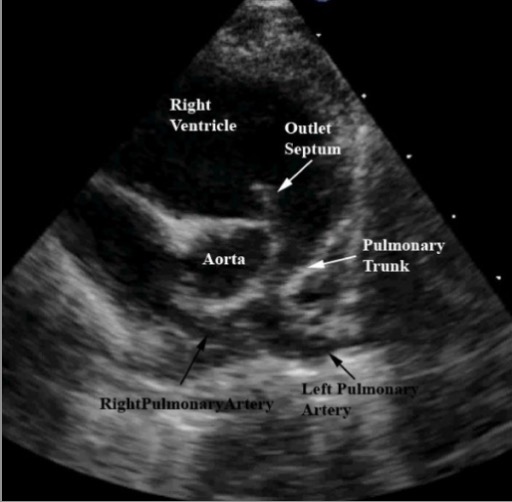
Echocardiogram of an individual with tetralogy of Fallot:
A parasternal short-axis view demonstrating deviation of the outlet septum into the right ventricular outflow tract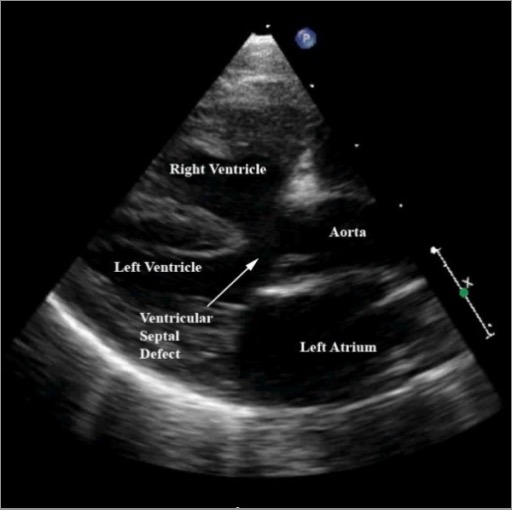
Echocardiogram of an individual with tetralogy of Fallot:
A modified parasternal long-axis view demonstrating characteristic features, including a large ventricular septal defect, aortic override (aorta displaced over the ventricular septal defect), and right ventricular hypertrophy
Definitive:
Palliative: