Histoplasmosis is an infection caused by Histoplasma capsulatum, a dimorphic fungus. The fungus exists as a mold Mold Mycology at low temperatures and as yeast Yeast A general term for single-celled rounded fungi that reproduce by budding. Brewers' and bakers' yeasts are saccharomyces cerevisiae; therapeutic dried yeast is yeast, dried. Mycology at high temperatures. H. capsulatum is the most common endemic fungal infection in the US and is most prevalent in the midwestern and southeastern states along the Ohio and Mississippi River valleys. Transmission is through inhalation, and exposure to soils containing bird or bat droppings increases the risk of infection. Most infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease are asymptomatic; however, immunocompromised immunocompromised A human or animal whose immunologic mechanism is deficient because of an immunodeficiency disorder or other disease or as the result of the administration of immunosuppressive drugs or radiation. Gastroenteritis individuals generally develop acute pulmonary infection, chronic infection, or even disseminated disease. Diagnosis is via different modalities, with the visualization and/or growth of the causative organism made using direct microscopy, histopathology, or culture studies. Management is dependent on disease severity. The antifungal Antifungal Azoles medications that are used include amphotericin B Amphotericin B Macrolide antifungal antibiotic produced by streptomyces nodosus obtained from soil of the orinoco river region of venezuela. Polyenes and itraconazole Itraconazole A triazole antifungal agent that inhibits cytochrome p-450-dependent enzymes required for ergosterol synthesis. Azoles.
Last updated: May 26, 2025
Histoplasmosis is an infection caused by a dimorphic fungus. Remember the following mnemonic to recall how the fungus exists:
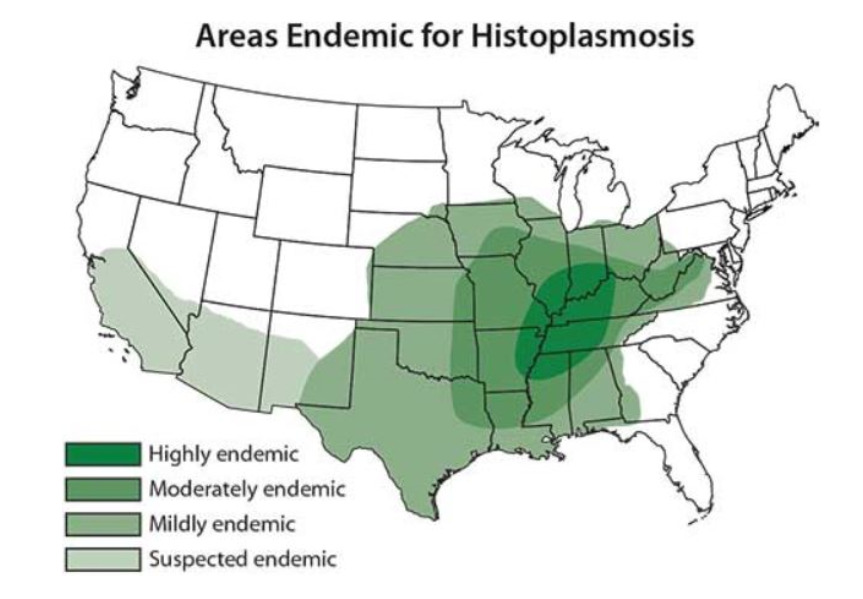
Map of the United States illustrating the areas endemic for histoplasmosis
Image: “Map showing areas endemic for histoplasmosis in the US” by CDC. License: Public DomainClinical presentation varies depending on host immune status and underlying risk factors.
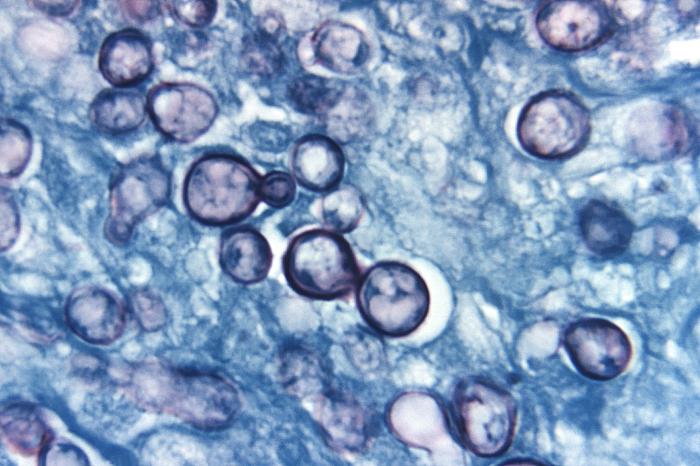
Photomicrograph of a methenamine silver-stained tissue sample extracted from a patient with histoplasmosis:
Note the presence of typical yeast cells, some of which were undergoing replication by budding.
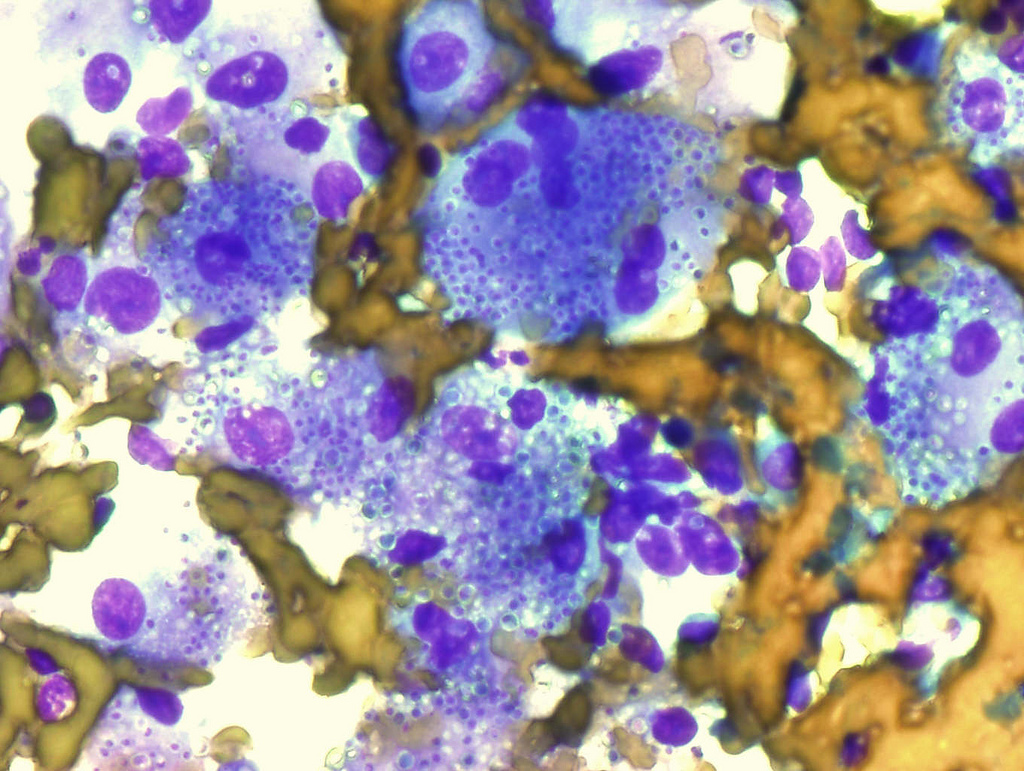
Macrophages in lymph node containing numerous Histoplasma capsulatum (Diff-Quick stain)
Image: “Macrophages in lymph node containing numerous Histoplasma capsulatum” by Rosen Y. License: CC BY-SA 2.0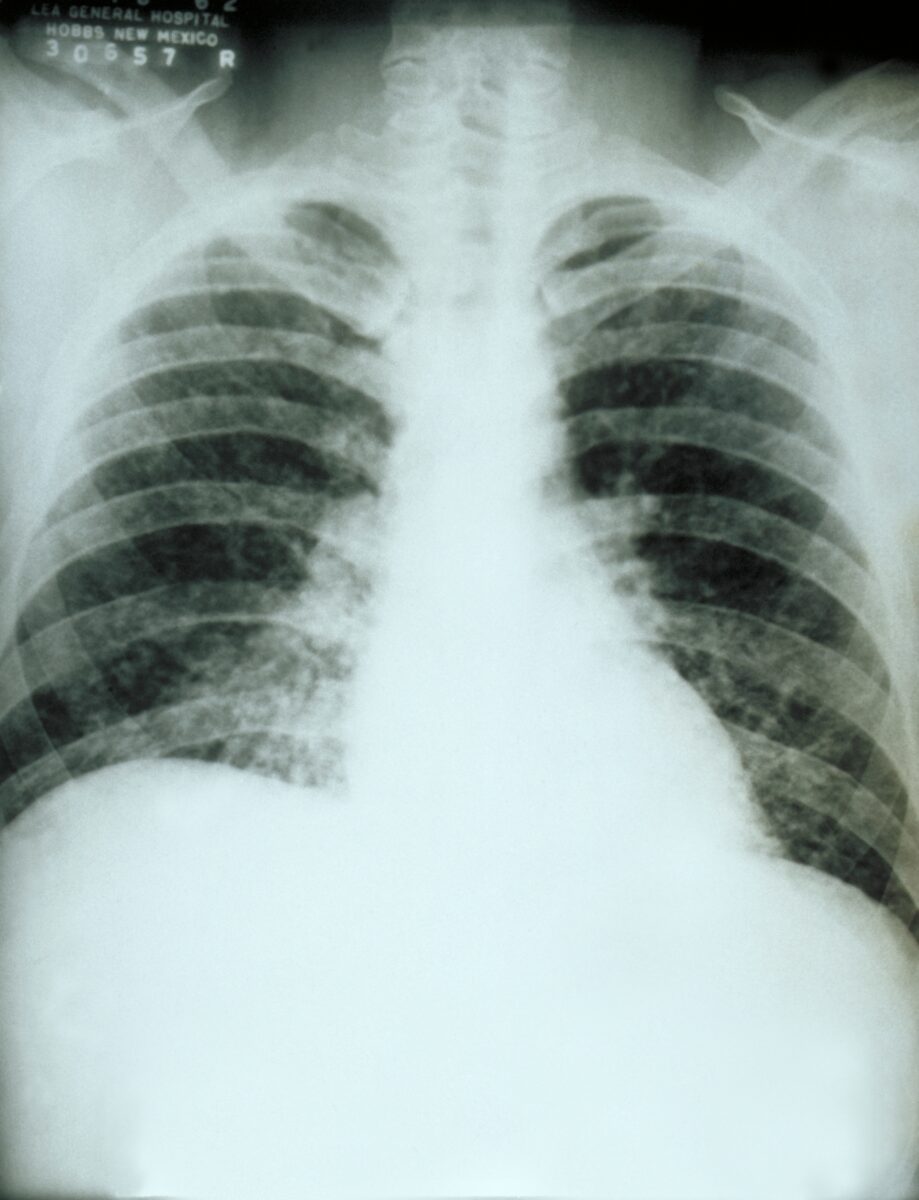
Chest X-ray:
Diffuse pulmonary infiltration due to acute pulmonary histoplasmosis caused by Histoplasma capsulatum
| Condition | Treatment |
|---|---|
| Moderate pulmonary disease Pulmonary disease Diseases involving the respiratory system. Blastomyces/Blastomycosis or symptoms lasting > 4 weeks | Itraconazole Itraconazole A triazole antifungal agent that inhibits cytochrome p-450-dependent enzymes required for ergosterol synthesis. Azoles |
| Moderately severe to severe pulmonary disease Pulmonary disease Diseases involving the respiratory system. Blastomyces/Blastomycosis | Amphotericin B Amphotericin B Macrolide antifungal antibiotic produced by streptomyces nodosus obtained from soil of the orinoco river region of venezuela. Polyenes + itraconazole Itraconazole A triazole antifungal agent that inhibits cytochrome p-450-dependent enzymes required for ergosterol synthesis. Azoles |
| Chronic pulmonary histoplasmosis | Itraconazole Itraconazole A triazole antifungal agent that inhibits cytochrome p-450-dependent enzymes required for ergosterol synthesis. Azoles |
| Mild disseminated histoplasmosis: mild symptoms with single focus (no CNS involvement) | Itraconazole Itraconazole A triazole antifungal agent that inhibits cytochrome p-450-dependent enzymes required for ergosterol synthesis. Azoles |
| Severe disseminated histoplasmosis without CNS involvement | Amphotericin B Amphotericin B Macrolide antifungal antibiotic produced by streptomyces nodosus obtained from soil of the orinoco river region of venezuela. Polyenes + itraconazole Itraconazole A triazole antifungal agent that inhibits cytochrome p-450-dependent enzymes required for ergosterol synthesis. Azoles |
| CNS involvement | Amphotericin B Amphotericin B Macrolide antifungal antibiotic produced by streptomyces nodosus obtained from soil of the orinoco river region of venezuela. Polyenes (prolonged) + itraconazole Itraconazole A triazole antifungal agent that inhibits cytochrome p-450-dependent enzymes required for ergosterol synthesis. Azoles |