Acute bronchitis is a common lower respiratory tract infection of the bronchi that accounts for many health care visits annually. It is most often due to viral causes in patients without chronic lung disease. Presenting symptoms include cough, with or without sputum, typically resolving within 1–3 weeks. Acute bronchitis is diagnosed clinically, although a chest X-ray helps clarify the diagnosis if pneumonia is suspected. Management is supportive, and antibiotics are not indicated in otherwise healthy adults.
Last updated: Apr 28, 2025
Acute bronchitis is an acute inflammation Acute Inflammation Inflammation of the large airways of the lower respiratory tract wherein the pulmonary parenchyma is not affected.
Acute bronchitis is a very common disease.
Acute bronchitis is most commonly caused by a viral infection, although bacterial causes are possible.
Acute bronchitis is characterized by infection and inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body’s defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation of the cells of the tissue lining the bronchi Bronchi The larger air passages of the lungs arising from the terminal bifurcation of the trachea. They include the largest two primary bronchi which branch out into secondary bronchi, and tertiary bronchi which extend into bronchioles and pulmonary alveoli. Bronchial Tree: Anatomy.
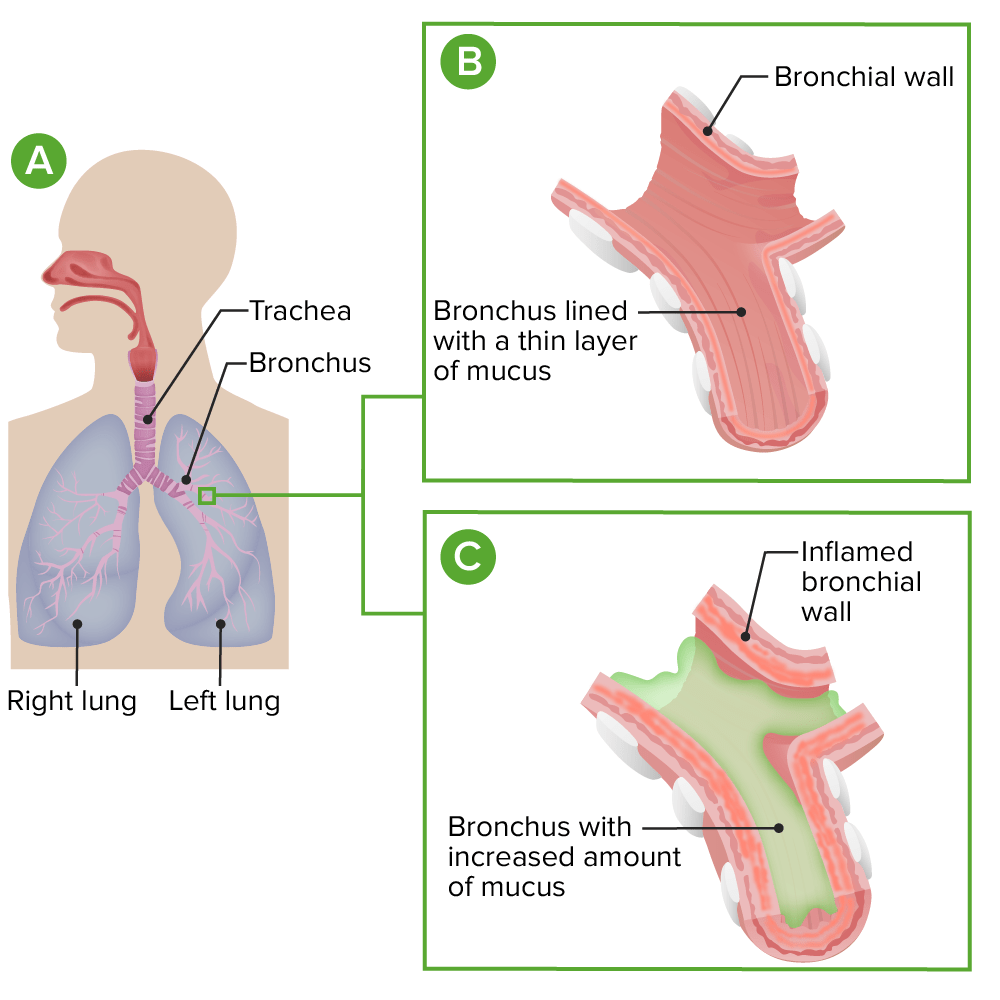
Pathophysiology of acute bronchitis
A: normal anatomy
B: detailed view of a normal bronchus
C: inflamed bronchi with excess mucus in acute bronchitis
Acute bronchitis is typically a self-limiting Self-Limiting Meningitis in Children condition with a prominent cough lasting 1–3 weeks.
Acute bronchitis is typically a clinical diagnosis that relies on history and exam, and should be suspected in patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with an acute onset of cough, which often follows a URI without findings of pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia. Additional workup may include:
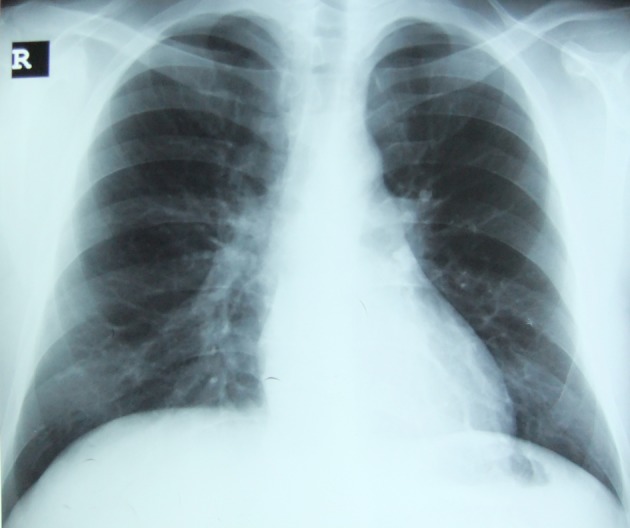
Chest X-ray showing bronchovascular prominance.
Image: “Chest radiography shows bronchovascular prominance on admission” by Sertogullarindan, B. et al. License: CC BY 2.0Acute bronchitis is typically a self-limiting Self-Limiting Meningitis in Children condition that usually requires only supportive care.
Antibiotics are specifically NOT recommended in acute bronchitis in otherwise healthy adults. There is strong evidence to support avoiding antibiotics, although inappropriate overprescribing is still common.