Aplastic anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types ( AA AA Amyloidosis) is a rare, life-threatening condition characterized by pancytopenia and hypocellularity of the bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis (in the absence of any abnormal cells) reflecting damage to hematopoietic stem cells Hematopoietic stem cells Progenitor cells from which all blood cells derived. They are found primarily in the bone marrow and also in small numbers in the peripheral blood. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis. Aplastic anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types can be acquired or inherited, however, most cases of AA AA Amyloidosis are acquired and caused by autoimmune damage to hematopoietic stem cells Hematopoietic stem cells Progenitor cells from which all blood cells derived. They are found primarily in the bone marrow and also in small numbers in the peripheral blood. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis. Specifically known acquired causes and associations of AAs include medications, chemicals, high doses of whole-body radiation Radiation Emission or propagation of acoustic waves (sound), electromagnetic energy waves (such as light; radio waves; gamma rays; or x-rays), or a stream of subatomic particles (such as electrons; neutrons; protons; or alpha particles). Osteosarcoma, viral infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease, immune diseases, and pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care. Inherited or constitutional syndromes associated with AA AA Amyloidosis include Fanconi anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types, dyskeratosis Dyskeratosis Dermatomyositis congenita, and Down syndrome Down syndrome Down syndrome, or trisomy 21, is the most common chromosomal aberration and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental delay. Both boys and girls are affected and have characteristic craniofacial and musculoskeletal features, as well as multiple medical anomalies involving the cardiac, gastrointestinal, ocular, and auditory systems. Down syndrome (Trisomy 21). Therapies include transfusion support, immunosuppression, and bone marrow transplantation Bone marrow transplantation Transfer of hematopoietic stem cells from bone marrow or blood between individuals within the same species (homologous transplantation) or transfer within the same individual (autologous transplantation). Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation has been used as an alternative to bone marrow transplantation in the treatment of a variety of neoplasms. Organ Transplantation.
Last updated: May 17, 2024
Inherited conditions:
Acquired AA AA Amyloidosis:
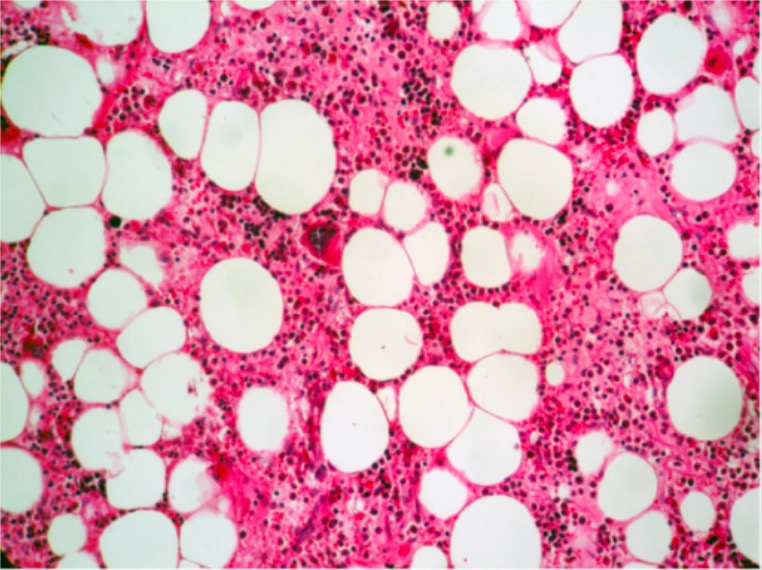
Normal hematopoiesis (all 3 cell lines present) with a megakaryocyte near the center of the field (H&E, 200x)
Image: “Histologic findings” by Department of Pathology, Ibn Sina University Hospital, Rabat, Morocco. License: CC BY 2.0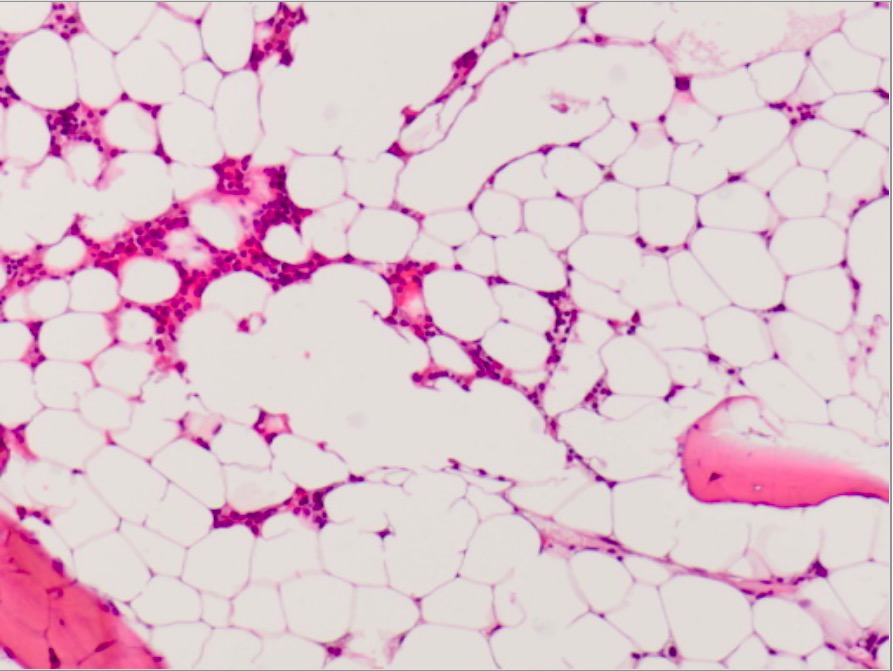
Microscopic photograph of bone marrow in AA:
Markedly hypocellular bone marrow from a patient with acquired AA (showing only scant hematopoiesis and mostly fat cells)
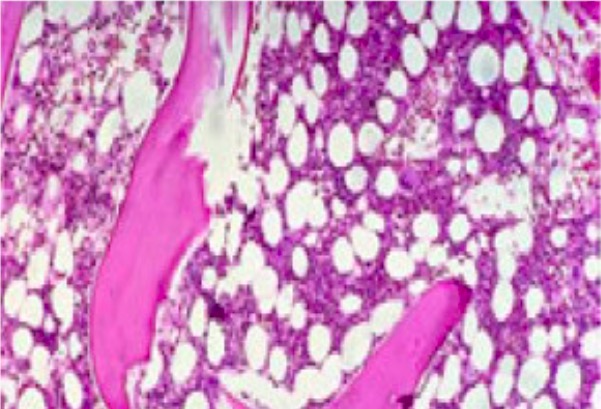
Bone marrow with approximately 50% cellularity (consistent with bone marrow from a 50-year-old healthy person)
Image: “Mild hypoblastic marrow” by Hasnaa Aboelwafa et al. License: CC BY 2.0, cropped by Lecturio.Pancytopenia with a hypocellular bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis showing: