The diaphragm is a large, dome-shaped muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity. The diaphragm consists of muscle fibers and a large central tendon, which is divided into right and left parts. As the primary muscle of inspiration Inspiration Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing, the diaphragm contributes 75% of the total inspiratory muscle force, and its contraction leads to flattening of the dome of the diaphragm. This flattening increases the volume of the thoracic cavity and allows the lungs Lungs Lungs are the main organs of the respiratory system. Lungs are paired viscera located in the thoracic cavity and are composed of spongy tissue. The primary function of the lungs is to oxygenate blood and eliminate CO2. Lungs: Anatomy to expand during inspiration Inspiration Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing.
Last updated: Nov 19, 2024
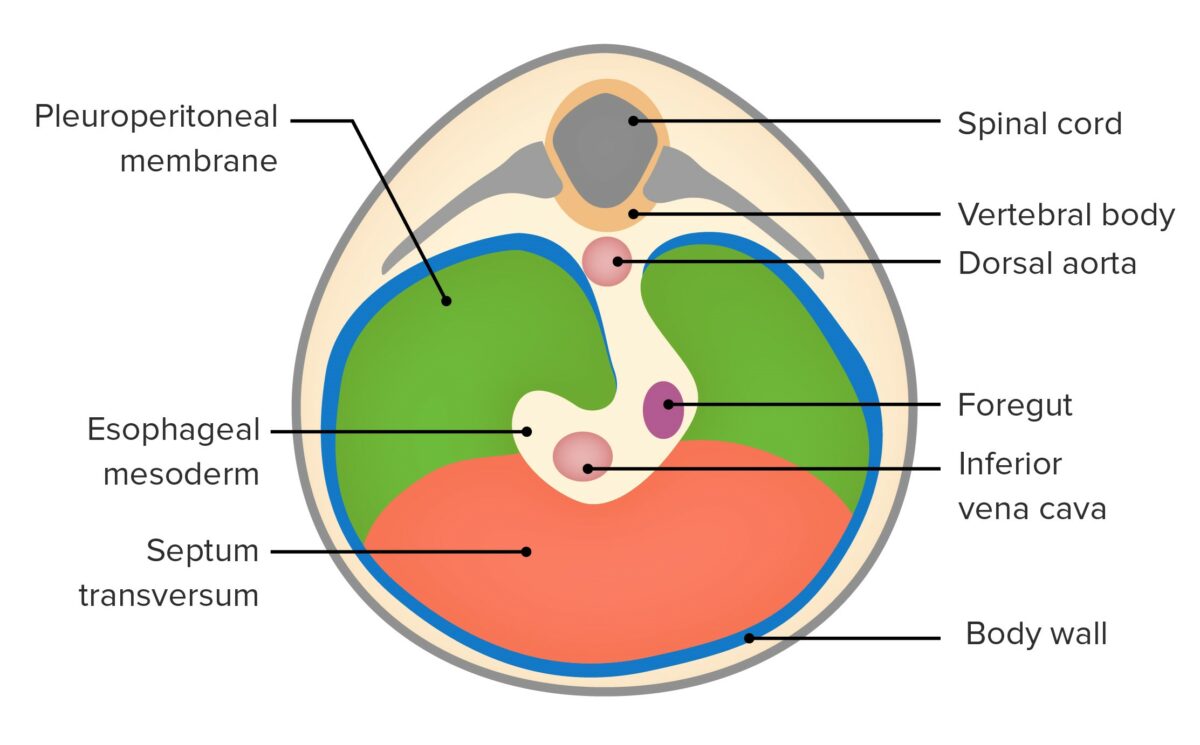
Developing diaphragm:
Embryonic development of the diaphragm from the pleuroperitoneal membranes and the septum transversum.
The diaphragm consists of 3 parts, all of which insert into the central tendon.
| Opening | Location | Passage for |
|---|---|---|
| Vena caval foramen | At level of T8–T9 |
|
| Esophageal hiatus | At level of T10 |
|
| Aortic hiatus | At level of T12 |
|
Minor diaphragmatic foramina (openings):
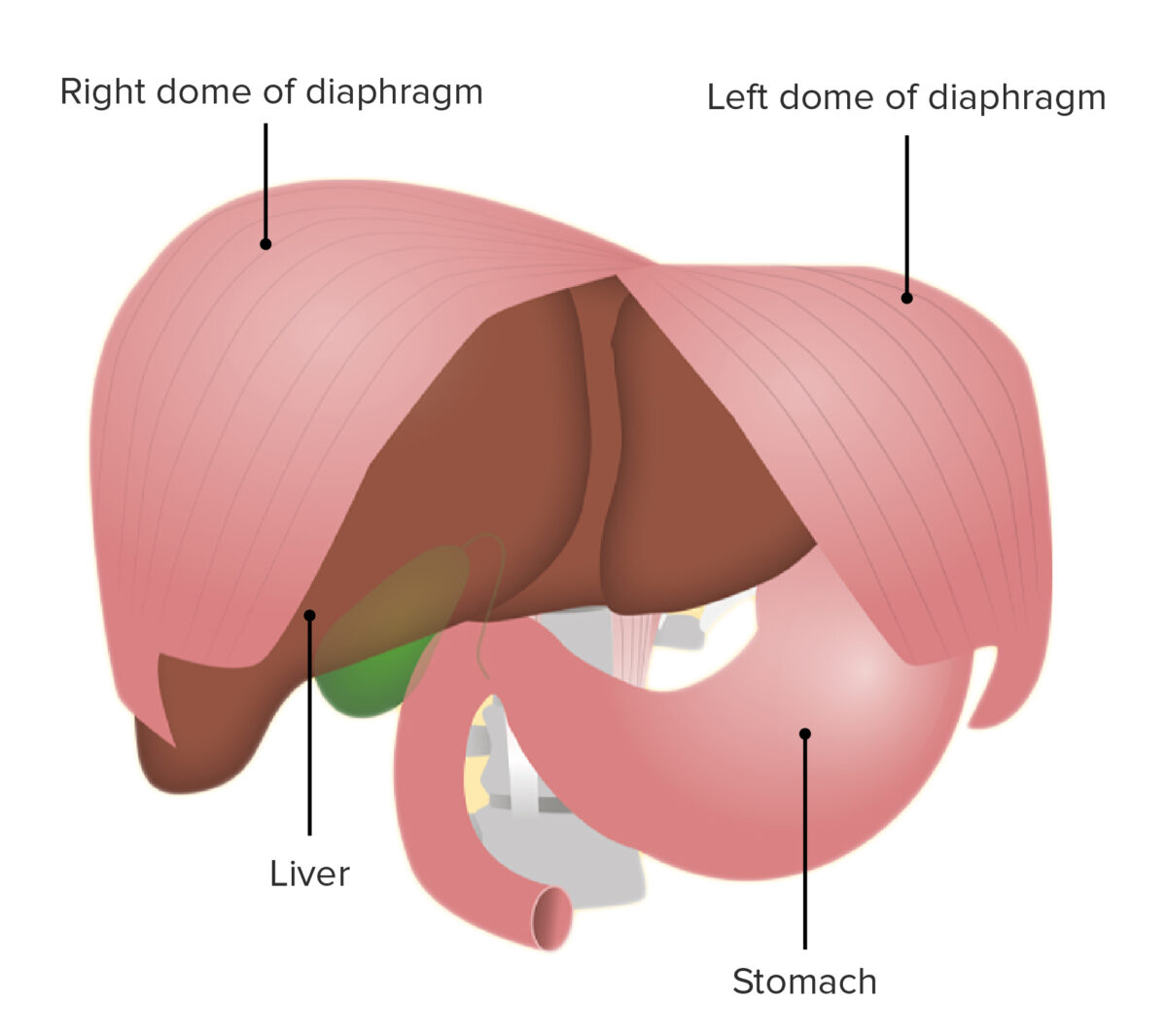
Diaphragm muscle:
The diaphragm muscle is higher on the right side, as it rests on top of the liver. The left side of the diaphragm is lower and is on top of the stomach.
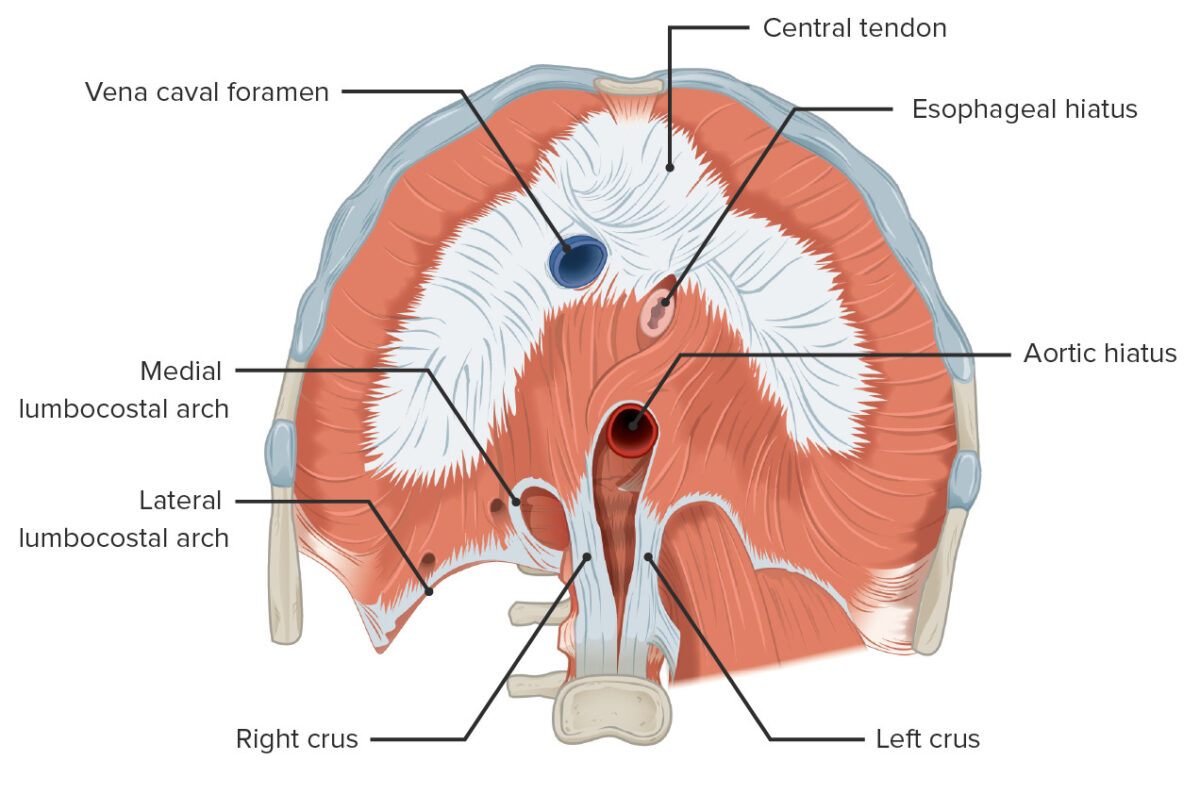
The anatomy of the diaphragm from an inferior view
Image by Lecturio.Inspiration Inspiration Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing:
Expiration Expiration Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing:

Respiration:
Image displays the changes of the thorax with the contracting and relaxing of the diaphragm muscle.
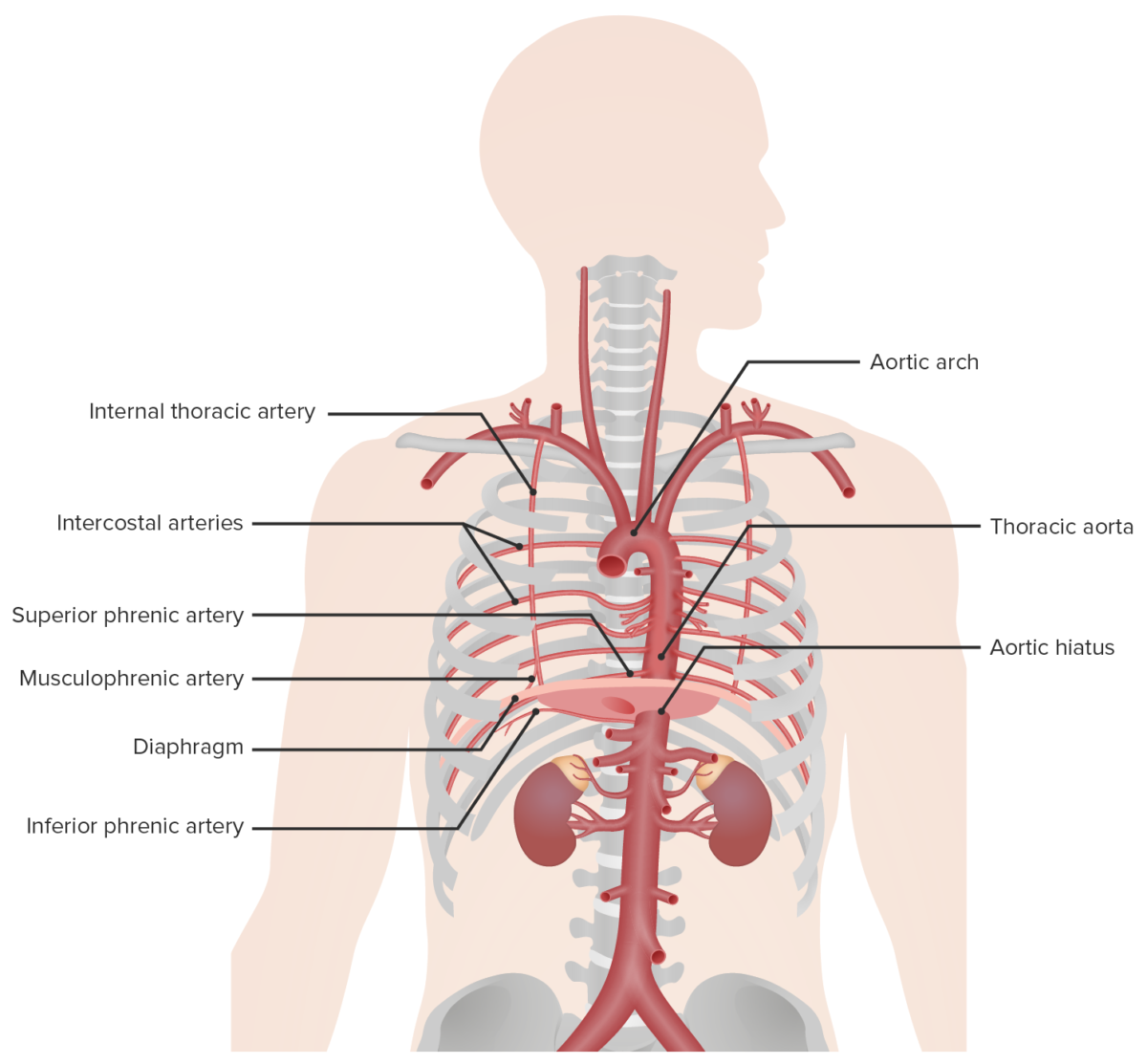
Blood supply of the diaphragm
Image by Lecturio.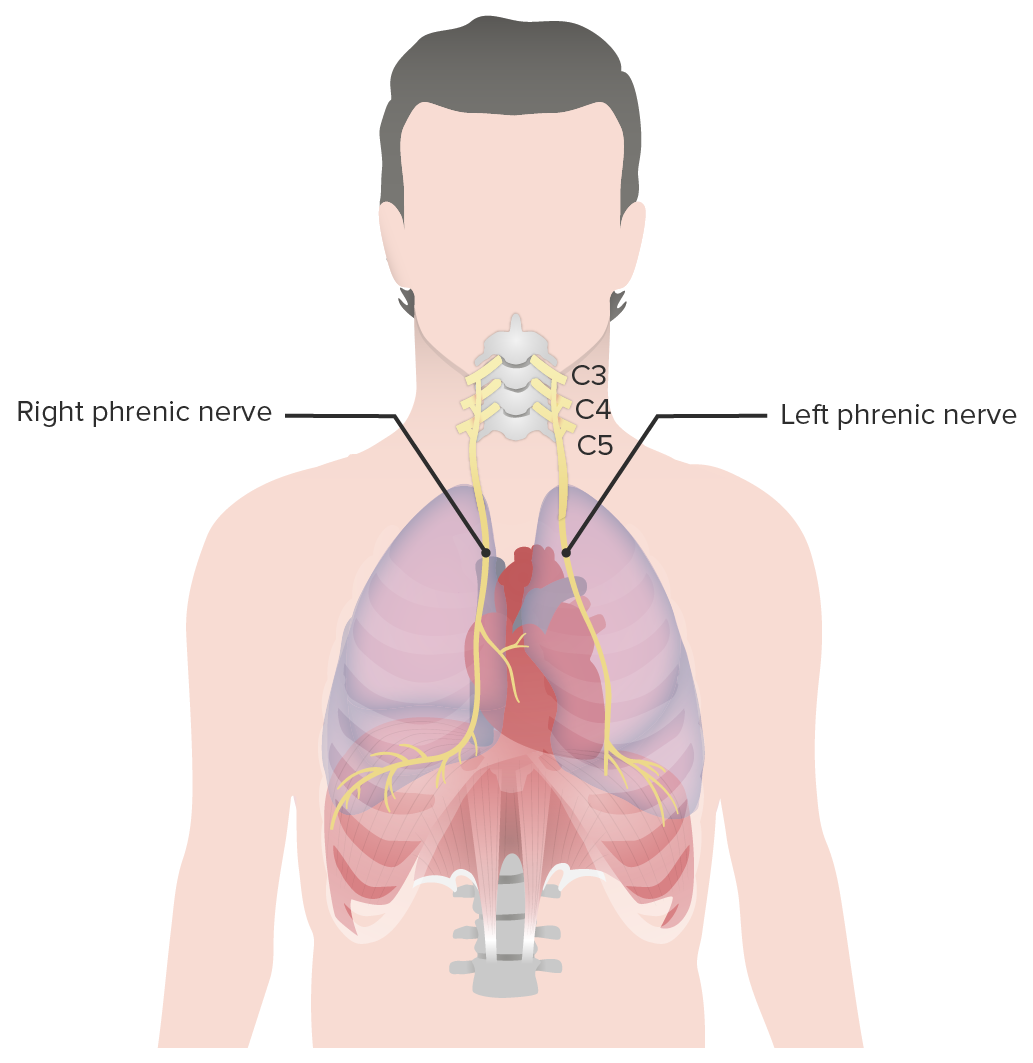
Phrenic nerves:
The left and right phrenic nerves provide innervation to the diaphragm.