Alcohol is one of the most commonly used addictive substances in the world. Alcohol use disorder (AUD) is defined as pathologic consumption of alcohol leading to impaired daily functioning. Acute alcohol intoxication presents with impairment in speech and motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology functions and can be managed in most cases with supportive care. Withdrawal from chronic alcohol use can have fatal consequences, including delirium Delirium Delirium is a medical condition characterized by acute disturbances in attention and awareness. Symptoms may fluctuate during the course of a day and involve memory deficits and disorientation. Delirium and seizures Seizures A seizure is abnormal electrical activity of the neurons in the cerebral cortex that can manifest in numerous ways depending on the region of the brain affected. Seizures consist of a sudden imbalance that occurs between the excitatory and inhibitory signals in cortical neurons, creating a net excitation. The 2 major classes of seizures are focal and generalized. Seizures, and is managed with benzodiazepines Benzodiazepines Benzodiazepines work on the gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA) receptor to produce inhibitory effects on the CNS. Benzodiazepines do not mimic GABA, the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in humans, but instead potentiate GABA activity. Benzodiazepines. Chronic AUD affects almost every part of the human body and has serious impacts on a person’s mental and physical health. Alcohol user disorder can be managed with psychotherapy Psychotherapy Psychotherapy is interpersonal treatment based on the understanding of psychological principles and mechanisms of mental disease. The treatment approach is often individualized, depending on the psychiatric condition(s) or circumstance. Psychotherapy as well as medications; however, the prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas is usually poor, with high rates of relapse Relapse Relapsing Fever and complications.
Last updated: Dec 10, 2024
Alcohol use disorder (AUD) is a chronic (> 12 months), problematic pattern of alcohol use causing significant distress.
There are varying definitions by different organizations for the classification of alcohol consumption.
Signs and symptoms of acute alcohol intoxication differ depending on the blood alcohol level.
Mild intoxication:
Moderate intoxication:
Severe intoxication:
Diagnosis:
Clinical Institute Withdrawal Assessment for Alcohol Scale Scale Dermatologic Examination (CIWA-A):
Diagnosis:
| Signs and symptoms | Most recent drink | |
|---|---|---|
| Mild |
|
6–24 hours |
| Seizures Seizures A seizure is abnormal electrical activity of the neurons in the cerebral cortex that can manifest in numerous ways depending on the region of the brain affected. Seizures consist of a sudden imbalance that occurs between the excitatory and inhibitory signals in cortical neurons, creating a net excitation. The 2 major classes of seizures are focal and generalized. Seizures | Generalized tonic clonic seizures Seizures A seizure is abnormal electrical activity of the neurons in the cerebral cortex that can manifest in numerous ways depending on the region of the brain affected. Seizures consist of a sudden imbalance that occurs between the excitatory and inhibitory signals in cortical neurons, creating a net excitation. The 2 major classes of seizures are focal and generalized. Seizures (single or multiple) | 12–48 hours |
| Hallucinations Hallucinations Subjectively experienced sensations in the absence of an appropriate stimulus, but which are regarded by the individual as real. They may be of organic origin or associated with mental disorders. Schizophrenia | Predominantly visual (other types can also occur) | 12–48 hours |
| Delirium Delirium Delirium is a medical condition characterized by acute disturbances in attention and awareness. Symptoms may fluctuate during the course of a day and involve memory deficits and disorientation. Delirium tremens |
|
> 48 hours |
Screening Screening Preoperative Care for misuse of alcohol must be incorporated into routine visits.
| Medication | Mechanism of action | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Naltrexone Naltrexone Derivative of noroxymorphone that is the n-cyclopropylmethyl congener of naloxone. It is a narcotic antagonist that is effective orally, longer lasting and more potent than naloxone, and has been proposed for the treatment of heroin addiction. Opioid Analgesics | Opioid Opioid Compounds with activity like opiate alkaloids, acting at opioid receptors. Properties include induction of analgesia or narcosis. Constipation receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors antagonists |
|
| Acamprosate | Modulates glutamate Glutamate Derivatives of glutamic acid. Included under this heading are a broad variety of acid forms, salts, esters, and amides that contain the 2-aminopentanedioic acid structure. Synthesis of Nonessential Amino Acids transmission |
|
| Disulfiram | Inhibits aldehyde dehydrogenase |
|
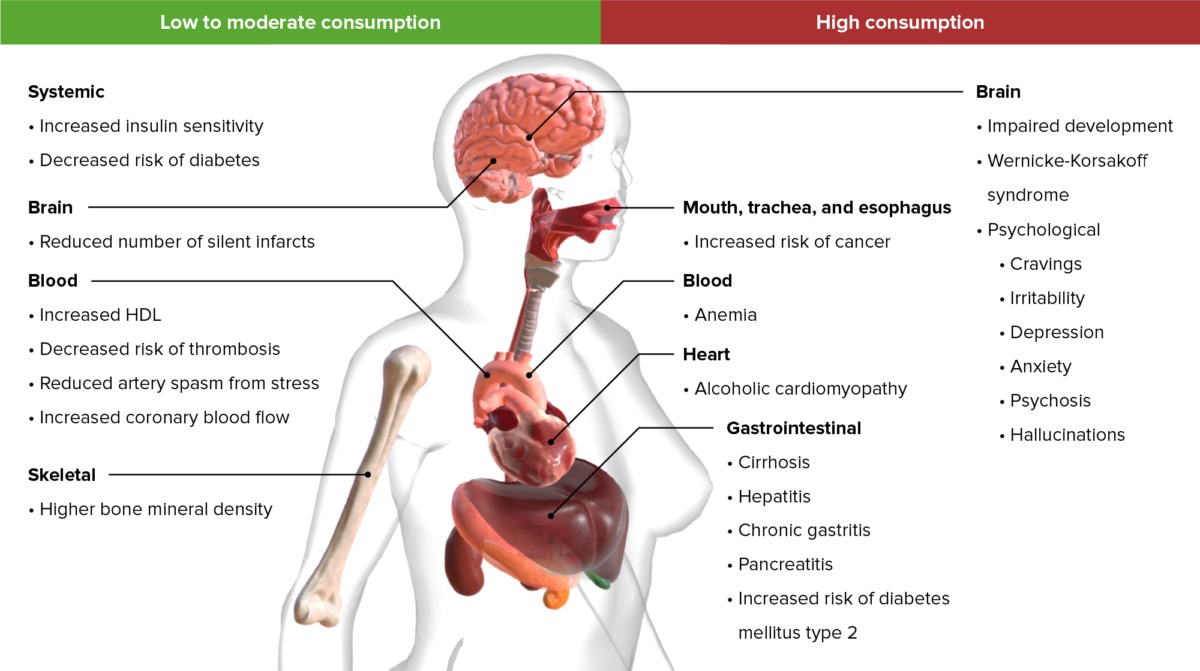
Important long-term effects resulting from low to high alcohol consumption
Image by BioDigital, edited by LecturioAlcohol consumption during pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care: