Polymyositis (PM) is an autoimmune inflammatory myopathy Myopathy Dermatomyositis caused by T cell-mediated muscle injury. The etiology of PM is unclear, but there are several genetic and environmental associations. Polymyositis is most common in middle-aged women and rarely affects children. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship present with progressive and symmetric proximal muscle weakness Proximal Muscle Weakness Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome and constitutional symptoms Constitutional Symptoms Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody (ANCA)-Associated Vasculitis. Complications may arise from respiratory, cardiac, or GI involvement. Diagnosis is based on clinical presentation and laboratory studies and confirmed using muscle biopsy Muscle Biopsy Trichinella/Trichinellosis. Management is with systemic glucocorticoids Systemic Glucocorticoids Glucocorticoids, immunosuppressants Immunosuppressants Immunosuppressants are a class of drugs widely used in the management of autoimmune conditions and organ transplant rejection. The general effect is dampening of the immune response. Immunosuppressants, and physiotherapy Physiotherapy Spinal Stenosis. All patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship should undergo cancer screening Screening Preoperative Care because there is a strong association with malignancy Malignancy Hemothorax.
Last updated: Jan 17, 2023
Polymyositis (PM) is an autoimmune inflammatory myopathy Myopathy Dermatomyositis that presents as symmetric proximal muscle weakness Proximal Muscle Weakness Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome. Antisynthetase syndrome Antisynthetase Syndrome Dermatomyositis is a subtype that shows the presence of antisynthetase antibodies Antisynthetase Antibodies Dermatomyositis and certain extramuscular manifestations.
The exact etiology is unknown.
Possible genetic predisposition:
Environmental factors:
Associated medical conditions:
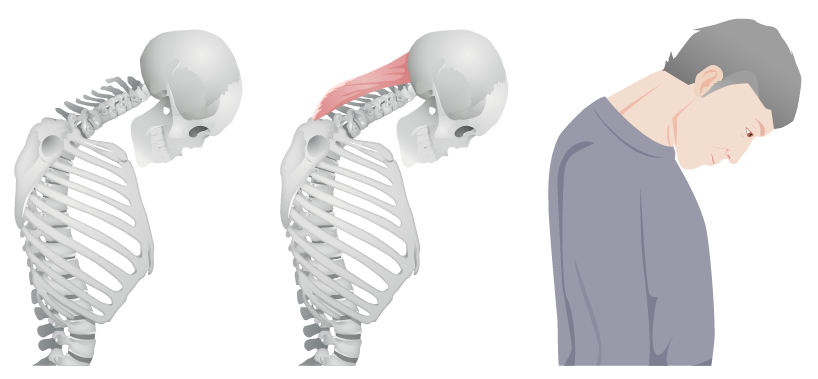
“Dropped head” in polymyositis: caused by weakness in the extensor muscles of the neck
Image by Lecturio.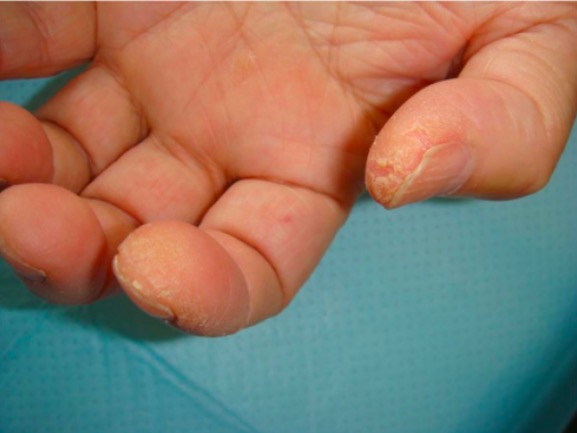
“Mechanic’s hands” associated with antisynthetase antibodies in polymyositis: hyperkeratosis resulting in fissures, roughness, and scaling on the pad of the thumb and the lateral aspect of the index finger
Image: “Patient 3” by Department of Respiratory Medicine, Kyorin University School of Medicine, 6-20-2 Shinkawa, Mitaka City, Tokyo 181-8611, Japan. License: CC BY 2.0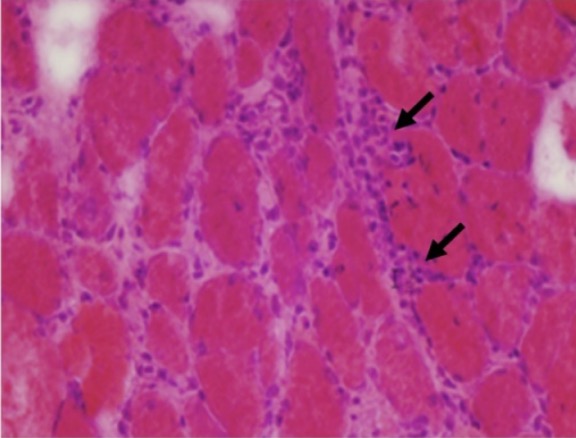
Histological findings in polymyositis:
Muscle biopsy from a patient with polymyositis showing endomysial inflammatory cells (arrows) and variations in fiber size
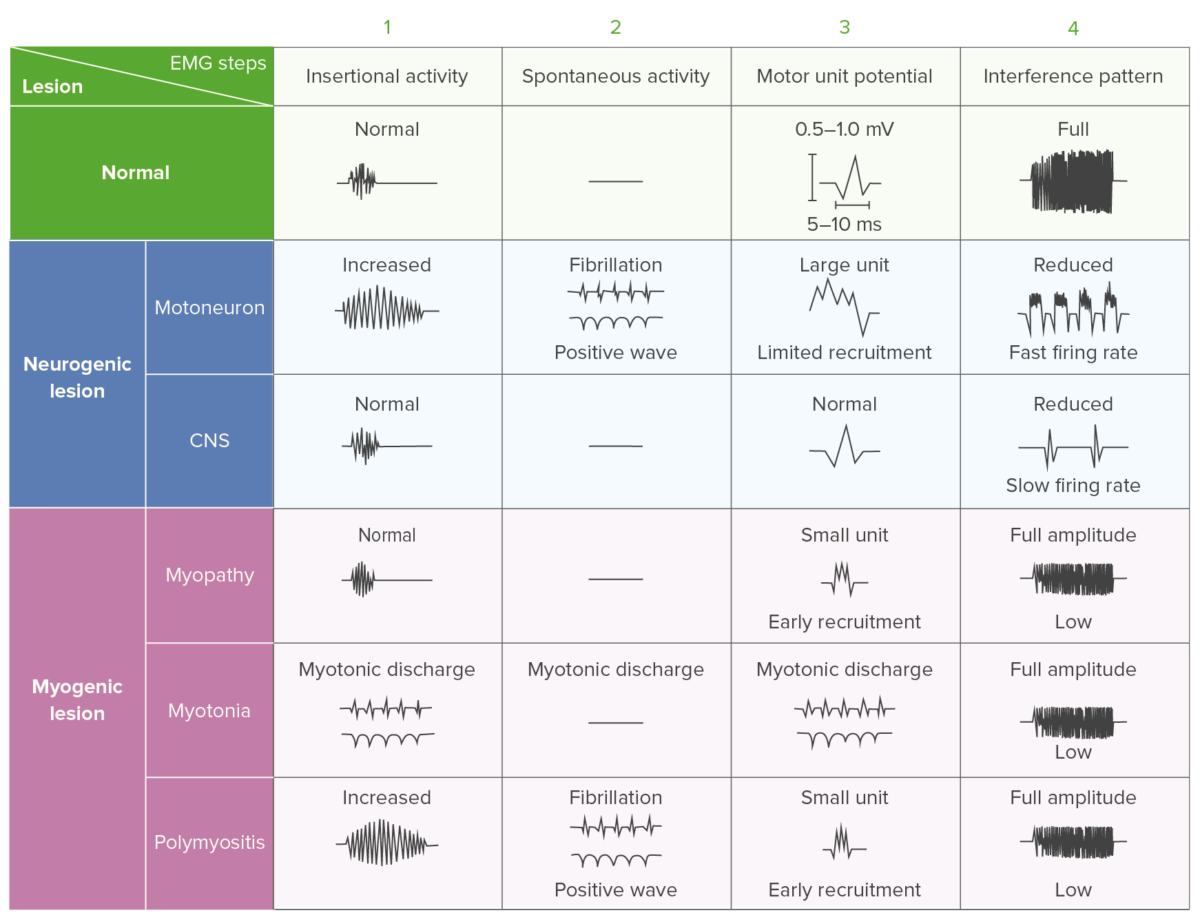
Electromyography findings in polymyositis: comparison chart showing the differences in EMG activity for different pathologies
Image by Lecturio.A multidisciplinary approach including pharmacological and non-pharmacological therapies is used in the management of PM.