Small bowel obstruction (SBO) is an interruption of the flow of the intraluminal contents through the small intestine; it is classified as mechanical (due to physical blockage) or functional (due to disruption of normal motility). The most common cause of SBO in the Western countries is postsurgical adhesions. Small bowel obstruction typically presents with nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, distention, constipation, and/or obstipation. The diagnosis is established via imaging. Up to 80% of all cases will resolve with supportive management (bowel rest, intravenous (IV) hydration, and nasogastric decompression). However, surgery is required for persistent or complicated cases.
Last updated: Mar 4, 2024
Small bowel obstruction Bowel obstruction Any impairment, arrest, or reversal of the normal flow of intestinal contents toward the anal canal. Ascaris/Ascariasis ( SBO SBO Small bowel obstruction (SBO) is an interruption of the flow of the intraluminal contents through the small intestine, and is classified as mechanical (due to physical blockage) or functional (due to disruption of normal motility). The most common cause of SBO in the Western countries is post-surgical adhesions. Small bowel obstruction typically presents with nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, distention, constipation, and/or obstipation. Small Bowel Obstruction) is the interruption of the flow Flow Blood flows through the heart, arteries, capillaries, and veins in a closed, continuous circuit. Flow is the movement of volume per unit of time. Flow is affected by the pressure gradient and the resistance fluid encounters between 2 points. Vascular resistance is the opposition to flow, which is caused primarily by blood friction against vessel walls. Vascular Resistance, Flow, and Mean Arterial Pressure of intraluminal contents through the small bowel Small bowel The small intestine is the longest part of the GI tract, extending from the pyloric orifice of the stomach to the ileocecal junction. The small intestine is the major organ responsible for chemical digestion and absorption of nutrients. It is divided into 3 segments: the duodenum, the jejunum, and the ileum. Small Intestine: Anatomy ( duodenum Duodenum The shortest and widest portion of the small intestine adjacent to the pylorus of the stomach. It is named for having the length equal to about the width of 12 fingers. Small Intestine: Anatomy, jejunum Jejunum The middle portion of the small intestine, between duodenum and ileum. It represents about 2/5 of the remaining portion of the small intestine below duodenum. Small Intestine: Anatomy, or ileum Ileum The distal and narrowest portion of the small intestine, between the jejunum and the ileocecal valve of the large intestine. Small Intestine: Anatomy).
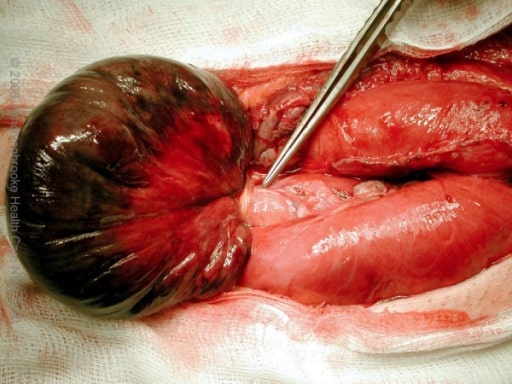
Gangrenous small bowel with closed-loop obstruction caused by an omental band adhesion
Image: “Intra-operative photograph” by the Department of Surgery, Hinchingbrooke Hospital, Hinchingbrooke Healthcare NHS Trust, Huntingdon, Cambridgeshire, UK. License: CC BY 2.0.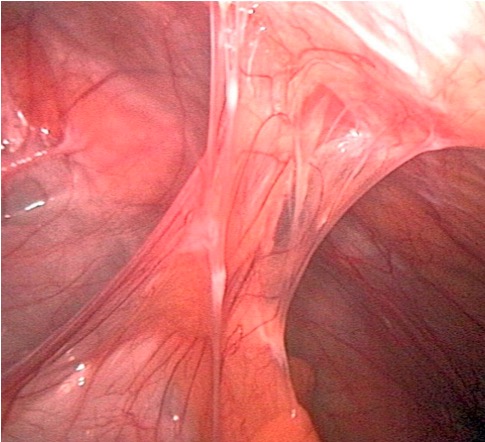
Adhesions that can develop after surgery are the most common cause of bowel obstruction
Image by Kevin Pei, PD.Minimum lab tests to order when SBO SBO Small bowel obstruction (SBO) is an interruption of the flow of the intraluminal contents through the small intestine, and is classified as mechanical (due to physical blockage) or functional (due to disruption of normal motility). The most common cause of SBO in the Western countries is post-surgical adhesions. Small bowel obstruction typically presents with nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, distention, constipation, and/or obstipation. Small Bowel Obstruction is suspected:[13]
Findings consistent with SBO SBO Small bowel obstruction (SBO) is an interruption of the flow of the intraluminal contents through the small intestine, and is classified as mechanical (due to physical blockage) or functional (due to disruption of normal motility). The most common cause of SBO in the Western countries is post-surgical adhesions. Small bowel obstruction typically presents with nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, distention, constipation, and/or obstipation. Small Bowel Obstruction:[6]
X-ray X-ray Penetrating electromagnetic radiation emitted when the inner orbital electrons of an atom are excited and release radiant energy. X-ray wavelengths range from 1 pm to 10 nm. Hard x-rays are the higher energy, shorter wavelength x-rays. Soft x-rays or grenz rays are less energetic and longer in wavelength. The short wavelength end of the x-ray spectrum overlaps the gamma rays wavelength range. The distinction between gamma rays and x-rays is based on their radiation source. Pulmonary Function Tests (initial test of choice):
Computed tomography (CT) scan:
Small bowel follow-through Small Bowel Follow-Through Imaging of the Intestines:[13]
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): if CT is contraindicated (children, pregnant women)
Bedside imaging (abdominal US):
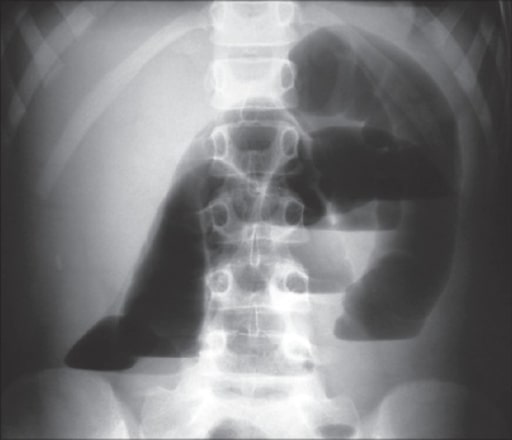
X-ray showing intestinal loops with air-fluid levels consistent with SBO
Image: “X-ray” by the Department of Surgery, University Hospital of Ioannina, Greece. License: CC BY 2.0.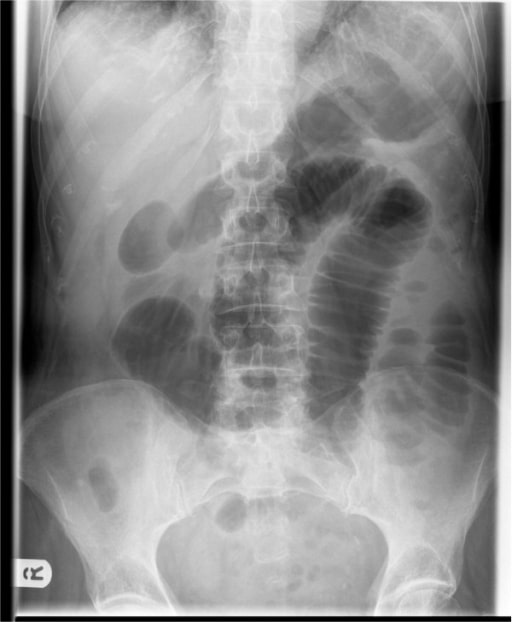
Abdominal X-ray showing dilated small bowel loops consistent with SBO
Image: “Abdominal X-ray” by the Department of General Surgery, Sunderland Royal Hospital, Kayll Road, Sunderland SR4 7TP, UK. License: CC BY 2.0.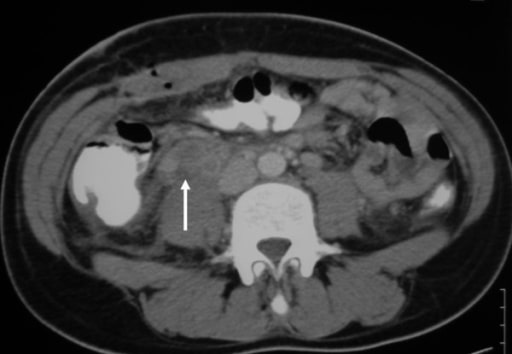
A CT scan showing the transition zone (arrow) with proximal bowel dilation and distal bowel decompression
Image: “Abdominal CT Scan” by the 2nd Department of Surgery, Athens University School of Medicine, Aretaieion Hospital, Athens, Greece. License: CC BY 2.0.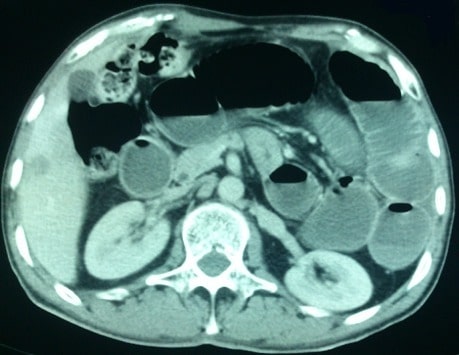
A CT scan showing a hernia causing a small obstruction with air-fluid levels
Image: “Abdominal CT scan” by the Service des Urgences Chirurgicales Viscérales, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Ibn Rochd, Casablanca, Morocco. License: CC BY 2.0.Severity assessment[1]
| Grade | Description | Radiographic | Operative criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Partial SBO SBO Small bowel obstruction (SBO) is an interruption of the flow of the intraluminal contents through the small intestine, and is classified as mechanical (due to physical blockage) or functional (due to disruption of normal motility). The most common cause of SBO in the Western countries is post-surgical adhesions. Small bowel obstruction typically presents with nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, distention, constipation, and/or obstipation. Small Bowel Obstruction | Minimal bowel distention | Minimal bowel distention with no evidence of obstruction |
| II | Complete SBO SBO Small bowel obstruction (SBO) is an interruption of the flow of the intraluminal contents through the small intestine, and is classified as mechanical (due to physical blockage) or functional (due to disruption of normal motility). The most common cause of SBO in the Western countries is post-surgical adhesions. Small bowel obstruction typically presents with nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, distention, constipation, and/or obstipation. Small Bowel Obstruction with viable bowel (not compromised) | Bowel distention with transition point without bowel compromise | Bowel distention with transition point without bowel compromise |
| III | Complete SBO SBO Small bowel obstruction (SBO) is an interruption of the flow of the intraluminal contents through the small intestine, and is classified as mechanical (due to physical blockage) or functional (due to disruption of normal motility). The most common cause of SBO in the Western countries is post-surgical adhesions. Small bowel obstruction typically presents with nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, distention, constipation, and/or obstipation. Small Bowel Obstruction with compromised but viable bowel | Bowel distention with transition point associated with impending bowel compromise, complete obstruction, and/or no distal contrast flow Flow Blood flows through the heart, arteries, capillaries, and veins in a closed, continuous circuit. Flow is the movement of volume per unit of time. Flow is affected by the pressure gradient and the resistance fluid encounters between 2 points. Vascular resistance is the opposition to flow, which is caused primarily by blood friction against vessel walls. Vascular Resistance, Flow, and Mean Arterial Pressure | Bowel distention with impending bowel compromise |
| IV | Complete
SBO
SBO
Small bowel obstruction (SBO) is an interruption of the flow of the intraluminal contents through the small intestine, and is classified as mechanical (due to physical blockage) or functional (due to disruption of normal motility). The most common cause of SBO in the Western countries is post-surgical adhesions. Small bowel obstruction typically presents with nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, distention, constipation, and/or obstipation.
Small Bowel Obstruction with:
|
Complete
SBO
SBO
Small bowel obstruction (SBO) is an interruption of the flow of the intraluminal contents through the small intestine, and is classified as mechanical (due to physical blockage) or functional (due to disruption of normal motility). The most common cause of SBO in the Western countries is post-surgical adhesions. Small bowel obstruction typically presents with nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, distention, constipation, and/or obstipation.
Small Bowel Obstruction with:
|
Bowel distention with localized perforation Perforation A pathological hole in an organ, blood vessel or other soft part of the body, occurring in the absence of external force. Esophagitis or free fluid |
| V | Perforation Perforation A pathological hole in an organ, blood vessel or other soft part of the body, occurring in the absence of external force. Esophagitis with diffuse peritoneal contamination | Bowel perforation Bowel perforation Perforated viscus or GI perforation represents a condition in which the integrity of the GI wall is lost with subsequent leakage of enteric contents into the peritoneal cavity, resulting in peritonitis. The causes of perforated viscus include trauma, bowel ischemia, infections, or ulcerative conditions, all of which ultimately lead to a full-thickness disruption of the intestinal wall. Perforated Viscus with free air and free fluid | Bowel distention with perforation Perforation A pathological hole in an organ, blood vessel or other soft part of the body, occurring in the absence of external force. Esophagitis, free fluid, and evidence of diffuse peritonitis Peritonitis Inflammation of the peritoneum lining the abdominal cavity as the result of infectious, autoimmune, or chemical processes. Primary peritonitis is due to infection of the peritoneal cavity via hematogenous or lymphatic spread and without intra-abdominal source. Secondary peritonitis arises from the abdominal cavity itself through rupture or abscess of intra-abdominal organs. Penetrating Abdominal Injury |
General diagnostic checklist for initial assessment[1–3,6-11,13]
The general principles of diagnostic evaluation are summarized below from US sources. Additional international recommendations can be reviewed from the World Society of Emergency Surgery.
Indications for surgery:
Initial medical management:
Signs of improvement over the next 24–48 hours:
No signs of improvement over the next 24–48 hours: