Dog and cat bites Cat bites Dog and cat bites can cause superficial and deep tissue destruction, as well as serious wound infections. Cat bites are more frequent in adult women and result in puncture wounds. Dog and Cat Bites can cause superficial and deep tissue destruction, as well as serious wound infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease. Dog bites Dog bites Dog and cat bites can cause superficial and deep tissue destruction, as well as serious wound infections. Dog bites occur more frequently in men and children and often cause crushing or tearing trauma. Dog and Cat Bites occur more frequently in men and children and often cause crushing Crushing Blunt Chest Trauma or tearing trauma. Cat bites Cat bites Dog and cat bites can cause superficial and deep tissue destruction, as well as serious wound infections. Cat bites are more frequent in adult women and result in puncture wounds. Dog and Cat Bites are more frequent in adult women and result in puncture wounds. Because puncture wounds allow inoculation of bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology into the deep tissues, cat bites Cat bites Dog and cat bites can cause superficial and deep tissue destruction, as well as serious wound infections. Cat bites are more frequent in adult women and result in puncture wounds. Dog and Cat Bites are more frequently associated with infection. The diagnosis is clinical, and cultures should be obtained if the wound appears infected. Management requires fastidious Fastidious Bordetella wound care and antibiotics for high-risk or infected wounds.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
International data are lacking, but statistics in the United States include:
| Dog bites Dog bites Dog and cat bites can cause superficial and deep tissue destruction, as well as serious wound infections. Dog bites occur more frequently in men and children and often cause crushing or tearing trauma. Dog and Cat Bites | Cat bites Cat bites Dog and cat bites can cause superficial and deep tissue destruction, as well as serious wound infections. Cat bites are more frequent in adult women and result in puncture wounds. Dog and Cat Bites |
|---|---|
| Approximately 90% of all animal bites | Approximately 10% of all animal bites |
| Men > women | Women > men |
| Children > adults | Adults > children |
| Less often result from provocation | More often result from provocation |
In addition to the risk of contracting the rabies Rabies Acute viral CNS infection affecting mammals, including humans. It is caused by rabies virus and usually spread by contamination with virus-laden saliva of bites inflicted by rabid animals. Important animal vectors include the dog, cat, bat, fox, raccoon, skunk, and wolf. Rabies Virus virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology from an animal bite, wound infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease can be caused by the following organisms:
| Dog bites Dog bites Dog and cat bites can cause superficial and deep tissue destruction, as well as serious wound infections. Dog bites occur more frequently in men and children and often cause crushing or tearing trauma. Dog and Cat Bites | Cat bites Cat bites Dog and cat bites can cause superficial and deep tissue destruction, as well as serious wound infections. Cat bites are more frequent in adult women and result in puncture wounds. Dog and Cat Bites | Both |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Patient-related factors:
Bite-related factors:
| Dog bites Dog bites Dog and cat bites can cause superficial and deep tissue destruction, as well as serious wound infections. Dog bites occur more frequently in men and children and often cause crushing or tearing trauma. Dog and Cat Bites | Cat bites Cat bites Dog and cat bites can cause superficial and deep tissue destruction, as well as serious wound infections. Cat bites are more frequent in adult women and result in puncture wounds. Dog and Cat Bites | |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Children: head, face,
neck
Neck
The part of a human or animal body connecting the head to the rest of the body.
Peritonsillar Abscess Adults: hands, arms |
Extremities |
| Wound type | Crushing Crushing Blunt Chest Trauma and tearing | Puncture |
| Consequences | Deeper structures are often damaged (tendons, bones, and blood vessels). | Inoculates bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology into the deep tissues |
| Risk of deep infection | Less likely | More likely (and requires shorter time to manifest) |
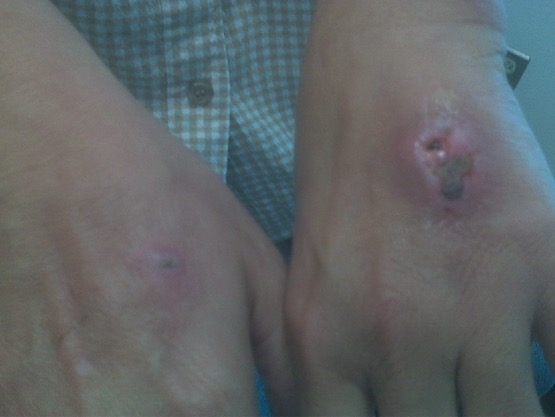
Bilateral, ulcerative, nodular wounds on the dorsum of a patient’s hands after sustaining dog bites
Image: “Ulcerative, nodular wounds” by Warren Alpert Brown University School of Medicine, 1125 North Main Street, Providence, RI 02906, USA. License: CC BY 4.0The diagnosis of a cat or dog bite is clinical, but the following may be utilized in select cases:
Management may vary based on practice location. The following information is based on US and UK guidelines.
Outpatient management:
| Medication | Adult dose | Pediatric dose |
|---|---|---|
| 1st-line | ||
| Amoxicillin Amoxicillin A broad-spectrum semisynthetic antibiotic similar to ampicillin except that its resistance to gastric acid permits higher serum levels with oral administration. Penicillins–clavulanate | 875/125 mg every 12 hours | |
| Alternative: if allergy Allergy An abnormal adaptive immune response that may or may not involve antigen-specific IgE Type I Hypersensitivity Reaction to penicillin Penicillin Rheumatic Fever | ||
| Cefuroxime | 500 mg 2 times daily | |
| Trimethoprim Trimethoprim The sulfonamides are a class of antimicrobial drugs inhibiting folic acid synthesize in pathogens. The prototypical drug in the class is sulfamethoxazole. Although not technically sulfonamides, trimethoprim, dapsone, and pyrimethamine are also important antimicrobial agents inhibiting folic acid synthesis. The agents are often combined with sulfonamides, resulting in a synergistic effect. Sulfonamides and Trimethoprim– sulfamethoxazole Sulfamethoxazole A bacteriostatic antibacterial agent that interferes with folic acid synthesis in susceptible bacteria. Its broad spectrum of activity has been limited by the development of resistance. Sulfonamides and Trimethoprim | 160/800 mg 2 times daily | 4–6 mg/kg of trimethoprim Trimethoprim The sulfonamides are a class of antimicrobial drugs inhibiting folic acid synthesize in pathogens. The prototypical drug in the class is sulfamethoxazole. Although not technically sulfonamides, trimethoprim, dapsone, and pyrimethamine are also important antimicrobial agents inhibiting folic acid synthesis. The agents are often combined with sulfonamides, resulting in a synergistic effect. Sulfonamides and Trimethoprim 2 times daily |
| Doxycycline | 100 mg 2 times daily | N/A |
| Ciprofloxacin Ciprofloxacin A broad-spectrum antimicrobial carboxyfluoroquinoline. Fluoroquinolones | 500–750 mg 2 times daily | |
| Levofloxacin Levofloxacin The l-isomer of ofloxacin. Fluoroquinolones | 750 mg daily | |
| Moxifloxacin Moxifloxacin A fluoroquinolone that acts as an inhibitor of DNA topoisomerase II and is used as a broad-spectrum antibacterial agent. Fluoroquinolones | 400 mg daily | |
| Alternative: anaerobic coverage | ||
| Clindamycin Clindamycin An antibacterial agent that is a semisynthetic analog of lincomycin. Lincosamides | 300–450 mg 3 times daily | 10 mg/kg 3 times daily |
| Metronidazole Metronidazole A nitroimidazole used to treat amebiasis; vaginitis; trichomonas infections; giardiasis; anaerobic bacteria; and treponemal infections. Pyogenic Liver Abscess | 500 mg 3 times daily | N/A |
For severe infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease:
| Medication | Adult dose | Pediatric dose |
|---|---|---|
| 1st-line | ||
| Ampicillin Ampicillin Semi-synthetic derivative of penicillin that functions as an orally active broad-spectrum antibiotic. Penicillins– sulbactam Sulbactam A beta-lactamase inhibitor with very weak antibacterial action. The compound prevents antibiotic destruction of beta-lactam antibiotics by inhibiting beta-lactamases, thus extending their spectrum activity. Combinations of sulbactam with beta-lactam antibiotics have been used successfully for the therapy of infections caused by organisms resistant to the antibiotic alone. Cephalosporins | 1.5–3 g every 6–8 hours | |
| Piperacillin Piperacillin Semisynthetic, broad-spectrum, ampicillin derived ureidopenicillin antibiotic proposed for pseudomonas infections. It is also used in combination with other antibiotics. Penicillins– tazobactam Tazobactam A penicillanic acid and sulfone derivative and potent beta-lactamase inhibitor that enhances the activity of other anti-bacterial agents against beta-lactamase producing bacteria. Cephalosporins | 3.375 g every 6–8 hours | N/A |
| Alternative: if allergy Allergy An abnormal adaptive immune response that may or may not involve antigen-specific IgE Type I Hypersensitivity Reaction to penicillin Penicillin Rheumatic Fever | ||
| Ceftriaxone Ceftriaxone A broad-spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic and cefotaxime derivative with a very long half-life and high penetrability to meninges, eyes and inner ears. Cephalosporins | 1 g every 12 hours | N/A |
| Cefoxitin | 1 g every 6–8 hours | |
| Cefuroxime | 1 g every 12 hours | |
| Trimethoprim Trimethoprim The sulfonamides are a class of antimicrobial drugs inhibiting folic acid synthesize in pathogens. The prototypical drug in the class is sulfamethoxazole. Although not technically sulfonamides, trimethoprim, dapsone, and pyrimethamine are also important antimicrobial agents inhibiting folic acid synthesis. The agents are often combined with sulfonamides, resulting in a synergistic effect. Sulfonamides and Trimethoprim– sulfamethoxazole Sulfamethoxazole A bacteriostatic antibacterial agent that interferes with folic acid synthesis in susceptible bacteria. Its broad spectrum of activity has been limited by the development of resistance. Sulfonamides and Trimethoprim | 5–10 mg/kg/day (of trimethoprim Trimethoprim The sulfonamides are a class of antimicrobial drugs inhibiting folic acid synthesize in pathogens. The prototypical drug in the class is sulfamethoxazole. Although not technically sulfonamides, trimethoprim, dapsone, and pyrimethamine are also important antimicrobial agents inhibiting folic acid synthesis. The agents are often combined with sulfonamides, resulting in a synergistic effect. Sulfonamides and Trimethoprim component) | 8–10 mg/kg/day* (of trimethoprim Trimethoprim The sulfonamides are a class of antimicrobial drugs inhibiting folic acid synthesize in pathogens. The prototypical drug in the class is sulfamethoxazole. Although not technically sulfonamides, trimethoprim, dapsone, and pyrimethamine are also important antimicrobial agents inhibiting folic acid synthesis. The agents are often combined with sulfonamides, resulting in a synergistic effect. Sulfonamides and Trimethoprim component) divided in 2 doses |
| Doxycycline | 100 mg 2 times daily | N/A |
| Ciprofloxacin Ciprofloxacin A broad-spectrum antimicrobial carboxyfluoroquinoline. Fluoroquinolones | 400 mg 2 times daily | |
| Levofloxacin Levofloxacin The l-isomer of ofloxacin. Fluoroquinolones | 750 mg daily | |
| Moxifloxacin Moxifloxacin A fluoroquinolone that acts as an inhibitor of DNA topoisomerase II and is used as a broad-spectrum antibacterial agent. Fluoroquinolones | 400 mg daily | |
| Alternative: anaerobic coverage | ||
| Clindamycin Clindamycin An antibacterial agent that is a semisynthetic analog of lincomycin. Lincosamides | 600 mg every 8 hours | 20–40 mg/kg/day divided in 3–4 doses Maximum: 2.7 g/day |
| Metronidazole Metronidazole A nitroimidazole used to treat amebiasis; vaginitis; trichomonas infections; giardiasis; anaerobic bacteria; and treponemal infections. Pyogenic Liver Abscess | 500 mg every 8 hours | N/A |
Wounds at low risk for infection (e.g., abrasions Abrasions Corneal Abrasions, Erosion, and Ulcers) do not require antibiotic prophylaxis Prophylaxis Cephalosporins. Antibiotic prophylaxis Prophylaxis Cephalosporins (for 3–5 days) is indicated for:
High-risk wounds:
High-risk conditions:
Managed similar to dog and cat bites Cat bites Dog and cat bites can cause superficial and deep tissue destruction, as well as serious wound infections. Cat bites are more frequent in adult women and result in puncture wounds. Dog and Cat Bites with the addition of testing and treatment for potential exposure to HIV HIV Anti-HIV Drugs, hepatitis B Hepatitis B Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Most individuals with acute HBV infection are asymptomatic or have mild, self-limiting symptoms. Chronic infection can be asymptomatic or create hepatic inflammation, leading to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis B Virus, and hepatitis C Hepatitis C Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection can be transmitted through infectious blood or body fluids and may be transmitted during childbirth or through IV drug use or sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C virus can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis, ranging from a mild to a serious, lifelong illness including liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis C Virus.
Infection after a human bite is often polymicrobial. Common organisms include:
Diagnosis Codes:
Coding for animal bites requires multiple codes: one for the type of wound (e.g., laceration Laceration Torn, ragged, mangled wounds. Blunt Chest Trauma, puncture) with its location, and an external cause code to specify the animal.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ICD-10-CM | S61.421A | Puncture wound without foreign body Foreign Body Foreign Body Aspiration of right hand Hand The hand constitutes the distal part of the upper limb and provides the fine, precise movements needed in activities of daily living. It consists of 5 metacarpal bones and 14 phalanges, as well as numerous muscles innervated by the median and ulnar nerves. Hand: Anatomy, initial encounter |
| ICD-10-CM | W54.0XXA | Bitten by dog, initial encounter |
| ICD-10-CM | W55.01XA | Bitten by cat, initial encounter |
Procedures/Interventions:
These codes are used for the management of the bite wound itself, which may include irrigation and debridement Debridement The removal of foreign material and devitalized or contaminated tissue from or adjacent to a traumatic or infected lesion until surrounding healthy tissue is exposed. Stevens-Johnson Syndrome to clean the wound, and suturing for simple, clean lacerations.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CPT | 11042 | Debridement Debridement The removal of foreign material and devitalized or contaminated tissue from or adjacent to a traumatic or infected lesion until surrounding healthy tissue is exposed. Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, subcutaneous tissue Subcutaneous tissue Loose connective tissue lying under the dermis, which binds skin loosely to subjacent tissues. It may contain a pad of adipocytes, which vary in number according to the area of the body and vary in size according to the nutritional state. Soft Tissue Abscess; first 20 sq cm or less |
| CPT | 12031 | Repair, intermediate, wounds of scalp, axillae, trunk and/or extremities (excluding hands and feet); 2.5 cm or less |
Medications:
These codes are for prophylactic medications given to prevent infection. This includes antibiotics like amoxicillin-clavulanate, a tetanus Tetanus Tetanus is a bacterial infection caused by Clostridium tetani, a gram-positive obligate anaerobic bacterium commonly found in soil that enters the body through a contaminated wound. C. tetani produces a neurotoxin that blocks the release of inhibitory neurotransmitters and causes prolonged tonic muscle contractions. Tetanus toxoid Toxoid Preparations of pathogenic organisms or their derivatives made nontoxic and intended for active immunologic prophylaxis. They include deactivated toxins. Anatoxin toxoids are distinct from anatoxins that are tropanes found in cyanobacteria. Vaccination booster, and, if indicated, the rabies Rabies Acute viral CNS infection affecting mammals, including humans. It is caused by rabies virus and usually spread by contamination with virus-laden saliva of bites inflicted by rabid animals. Important animal vectors include the dog, cat, bat, fox, raccoon, skunk, and wolf. Rabies Virus vaccine Vaccine Suspensions of killed or attenuated microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa), antigenic proteins, synthetic constructs, or other bio-molecular derivatives, administered for the prevention, amelioration, or treatment of infectious and other diseases. Vaccination series.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| RxNorm | 105822 | Amoxicillin Amoxicillin A broad-spectrum semisynthetic antibiotic similar to ampicillin except that its resistance to gastric acid permits higher serum levels with oral administration. Penicillins / Clavulanate (ingredient) |
| CPT | 90715 | Tetanus Tetanus Tetanus is a bacterial infection caused by Clostridium tetani, a gram-positive obligate anaerobic bacterium commonly found in soil that enters the body through a contaminated wound. C. tetani produces a neurotoxin that blocks the release of inhibitory neurotransmitters and causes prolonged tonic muscle contractions. Tetanus, diphtheria Diphtheria Diphtheria is an infectious disease caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae that most often results in respiratory disease with membranous inflammation of the pharynx, sore throat, fever, swollen glands, and weakness. The hallmark sign is a sheet of thick, gray material covering the back of the throat. Diphtheria toxoids and acellular pertussis Pertussis Pertussis, or whooping cough, is a potentially life-threatening highly contagious bacterial infection of the respiratory tract caused by Bordetella pertussis. The disease has 3 clinical stages, the second and third of which are characterized by an intense paroxysmal cough, an inspiratory whoop, and post-tussive vomiting. Pertussis (Whooping Cough) vaccine Vaccine Suspensions of killed or attenuated microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa), antigenic proteins, synthetic constructs, or other bio-molecular derivatives, administered for the prevention, amelioration, or treatment of infectious and other diseases. Vaccination (Tdap) |
| CPT | 90675 | Rabies Rabies Acute viral CNS infection affecting mammals, including humans. It is caused by rabies virus and usually spread by contamination with virus-laden saliva of bites inflicted by rabid animals. Important animal vectors include the dog, cat, bat, fox, raccoon, skunk, and wolf. Rabies Virus vaccine Vaccine Suspensions of killed or attenuated microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa), antigenic proteins, synthetic constructs, or other bio-molecular derivatives, administered for the prevention, amelioration, or treatment of infectious and other diseases. Vaccination, for intramuscular use |
Complications:
This code is for cellulitis Cellulitis Cellulitis is a common infection caused by bacteria that affects the dermis and subcutaneous tissue of the skin. It is frequently caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. The skin infection presents as an erythematous and edematous area with warmth and tenderness. Cellulitis, a common complication of an infected animal bite, particularly from cat bites Cat bites Dog and cat bites can cause superficial and deep tissue destruction, as well as serious wound infections. Cat bites are more frequent in adult women and result in puncture wounds. Dog and Cat Bites which can introduce bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology like Pasteurella multocida Pasteurella Multocida A species of gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria normally found in the flora of the mouth and respiratory tract of animals and birds. It causes shipping fever; hemorrhagic bacteremia; and intestinal disease in animals. In humans, disease usually arises from a wound infection following a bite or scratch from domesticated animals. Dog and Cat Bites deep into tissue.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ICD-10-CM | L03.115 | Cellulitis Cellulitis Cellulitis is a common infection caused by bacteria that affects the dermis and subcutaneous tissue of the skin. It is frequently caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. The skin infection presents as an erythematous and edematous area with warmth and tenderness. Cellulitis of right hand Hand The hand constitutes the distal part of the upper limb and provides the fine, precise movements needed in activities of daily living. It consists of 5 metacarpal bones and 14 phalanges, as well as numerous muscles innervated by the median and ulnar nerves. Hand: Anatomy |