Ankylosing spondylitis (also known as Bechterew’s disease or Marie-Strümpell disease) is a seronegative spondyloarthropathy characterized by chronic and indolent inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body's defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation of the axial Axial Computed Tomography (CT) skeleton. Severe disease can lead to fusion and rigidity Rigidity Continuous involuntary sustained muscle contraction which is often a manifestation of basal ganglia diseases. When an affected muscle is passively stretched, the degree of resistance remains constant regardless of the rate at which the muscle is stretched. This feature helps to distinguish rigidity from muscle spasticity. Megacolon of the spine Spine The human spine, or vertebral column, is the most important anatomical and functional axis of the human body. It consists of 7 cervical vertebrae, 12 thoracic vertebrae, and 5 lumbar vertebrae and is limited cranially by the skull and caudally by the sacrum. Vertebral Column: Anatomy. Ankylosing spondylitis is most often seen in young men and is strongly associated with HLA-B27. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship will have progressive back pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways (which improves with activity), morning stiffness, and decreased range of motion Range of motion The distance and direction to which a bone joint can be extended. Range of motion is a function of the condition of the joints, muscles, and connective tissues involved. Joint flexibility can be improved through appropriate muscle strength exercises. Examination of the Upper Limbs of the spine Spine The human spine, or vertebral column, is the most important anatomical and functional axis of the human body. It consists of 7 cervical vertebrae, 12 thoracic vertebrae, and 5 lumbar vertebrae and is limited cranially by the skull and caudally by the sacrum. Vertebral Column: Anatomy. Extra-articular manifestations include fatigue Fatigue The state of weariness following a period of exertion, mental or physical, characterized by a decreased capacity for work and reduced efficiency to respond to stimuli. Fibromyalgia, enthesitis, anterior uveitis Uveitis Uveitis is the inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented middle layer of the eye, which comprises the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. The condition is categorized based on the site of disease; anterior uveitis is the most common. Diseases of the Uvea, restrictive lung disease, and inflammatory bowel disease. The diagnosis is based on the clinical history, physical exam, and imaging demonstrating sacroiliitis and bridging syndesmophytes. Most patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship are managed with physical therapy Physical Therapy Becker Muscular Dystrophy and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs ( NSAIDs NSAIDS Primary vs Secondary Headaches). More severe cases may require tumor Tumor Inflammation necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage factor-alpha inhibitors or surgery.
Last updated: May 7, 2025
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a seronegative spondyloarthropathy characterized by chronic and indolent inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body’s defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation of the axial Axial Computed Tomography (CT) skeleton.
To remember the seronegative arthropathies, use the mnemonic “PAIR.”
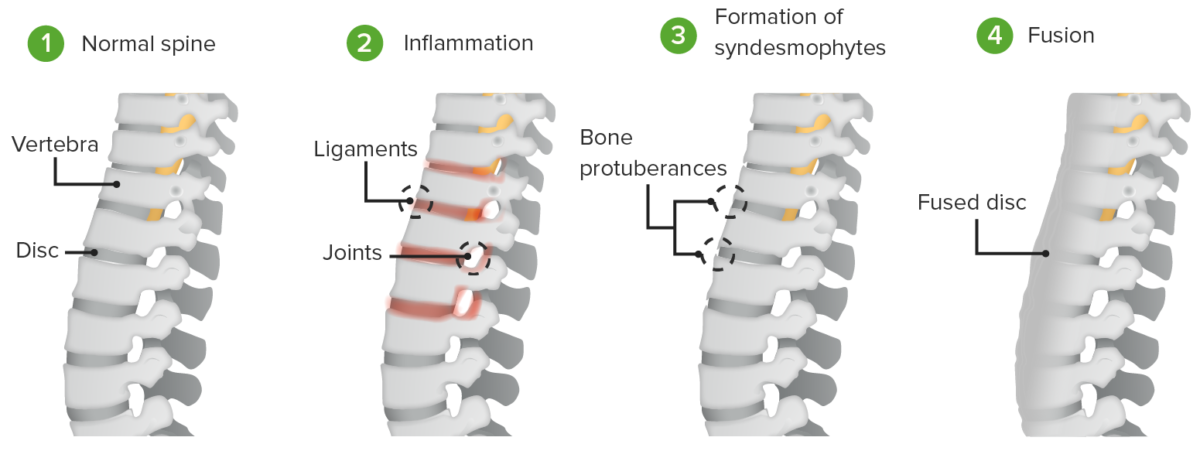
Pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis:
Inflammation induces the formation of syndesmophytes and the fusion of the intervertebral discs and vertebral bodies.
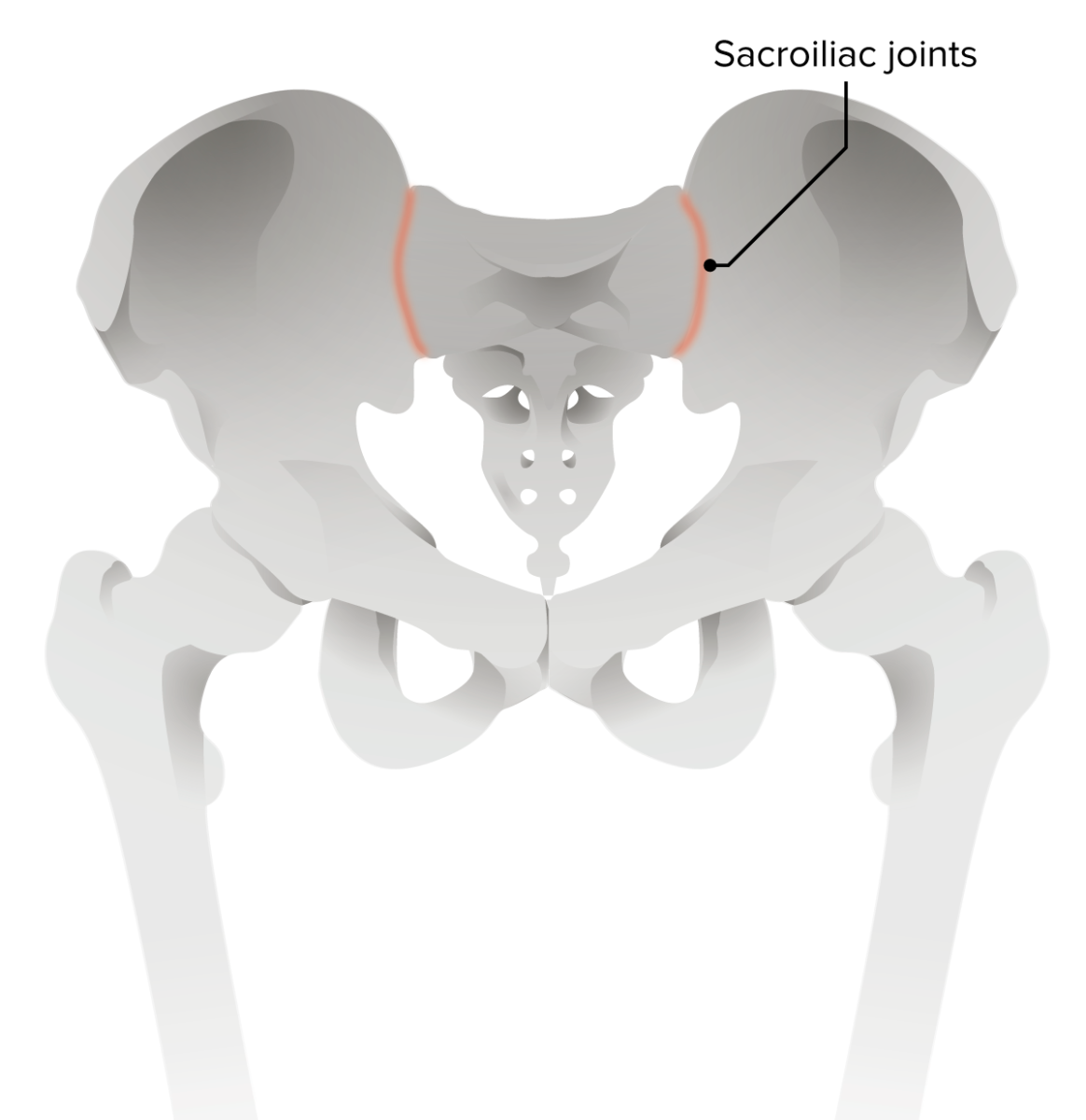
Pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis:
Erosion of the iliac side of sacroiliac joints is the earliest radiologic sign of ankylosing spondylitis.
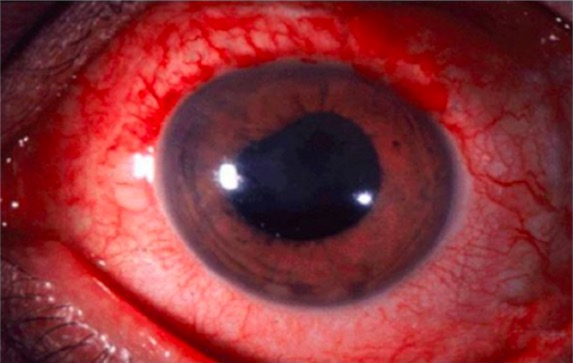
Anterior uveitis is a common extra-articular manifestation of ankylosing spondylitis.
Image: “Anterior uveitis” by Christopher J. Gilani et al. License: CC BY 4.0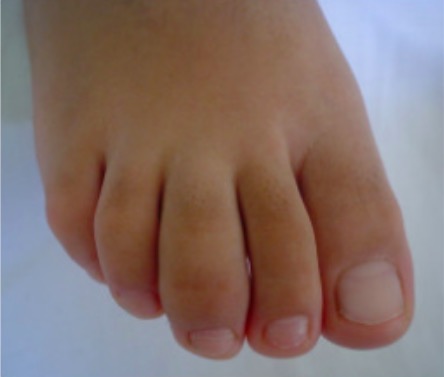
Dactylitis of the 3rd digit in ankylosing spondylitis
Image: “Involvement of the feet in patients with SpA” by Department of Rheumatology, Hospital General de México, Faculty of Medicine, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Dr, Balmis 148, Colonia Doctores, México, DF 06720, Mexico. License: CC BY 2.0, cropped by Lecturio.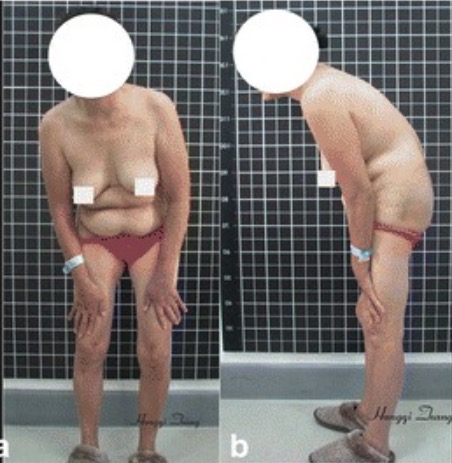
Stooped, forward-flexed position in a patient with ankylosing spondylitis
Image: “Preoperative imaging” by Hongqi Zhang et al. License: CC BY 4.0, cropped by Lecturio.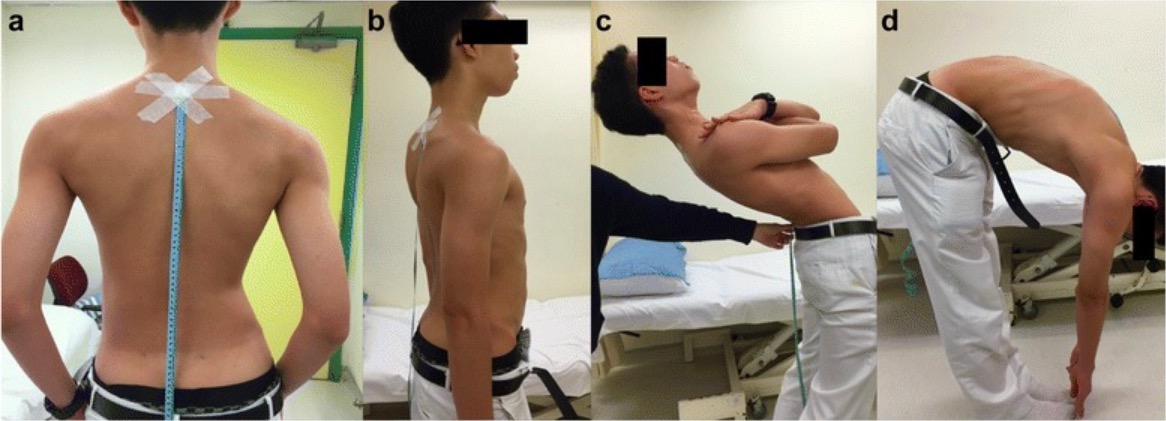
The Schober test: a photograph of a patient demonstrating the Schober test for spinal mobility. After the marks are placed 10 cm and 5 cm away from the spinal process of L5, the patient is asked to bend over. If distance does not increase by > 5 cm, the patient has reduced lumbar flexion indicative of ankylosing spondylitis.
Image: “Schober test” by Kamil Eyvazov et al. License: CC BY 4.0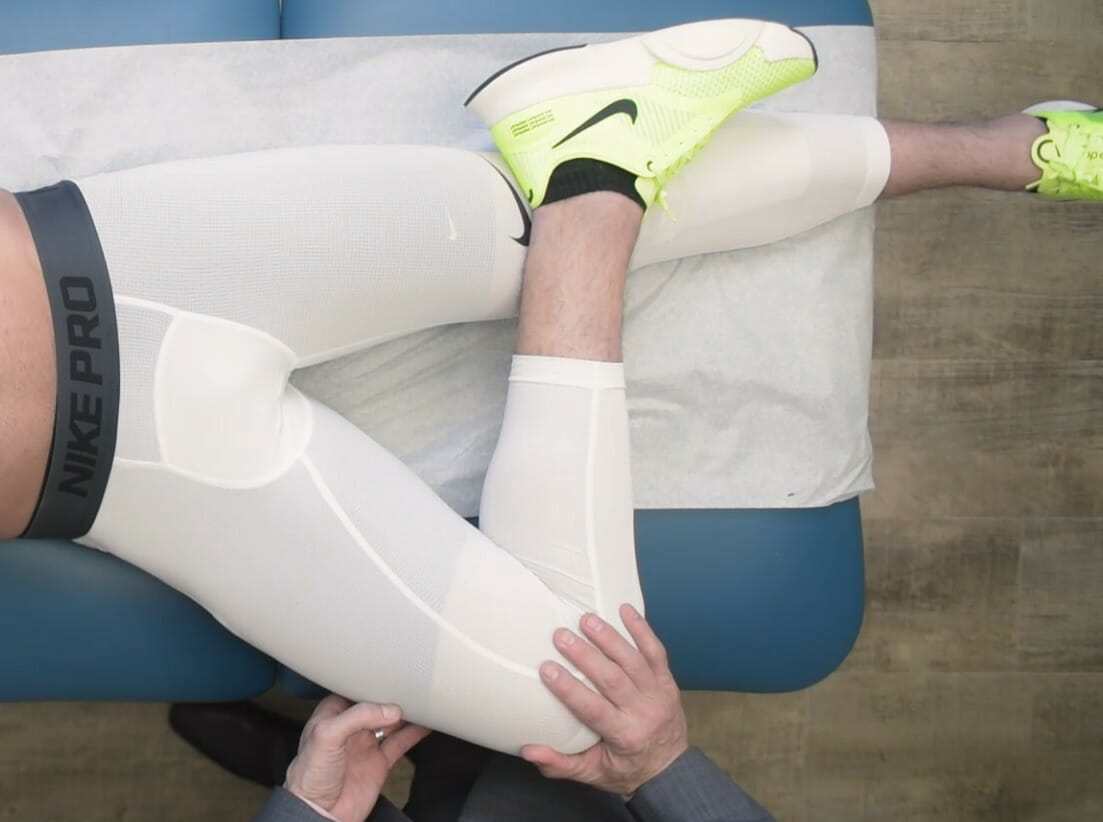
The FABER test:
This test may be used to detect hip, lumbar, or sacroiliac joint pathology. These signs are often positive in ankylosing spondylitis.
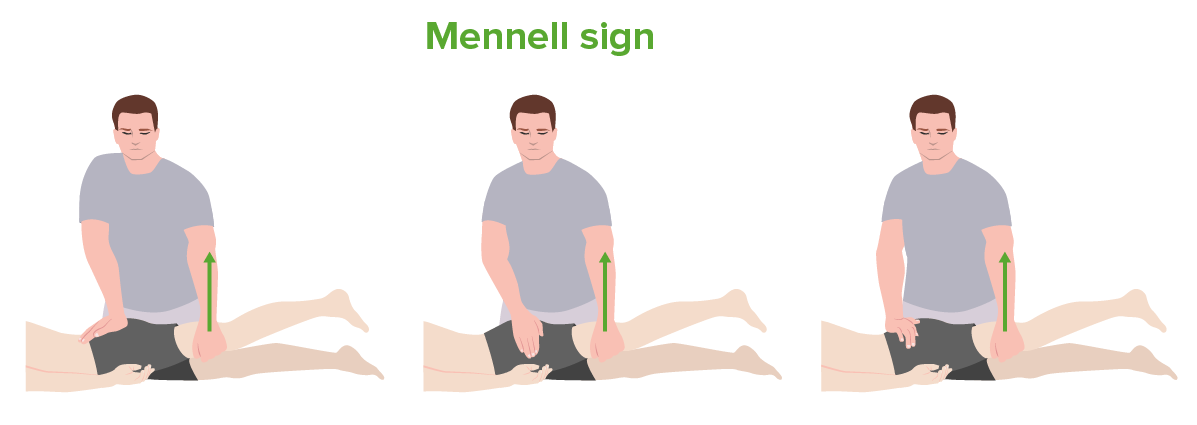
The Mennell sign:
From left to right: testing of the sacroiliac joint, hip joint, and lumbar spine. This test may be used in the evaluation for ankylosing spondylitis.
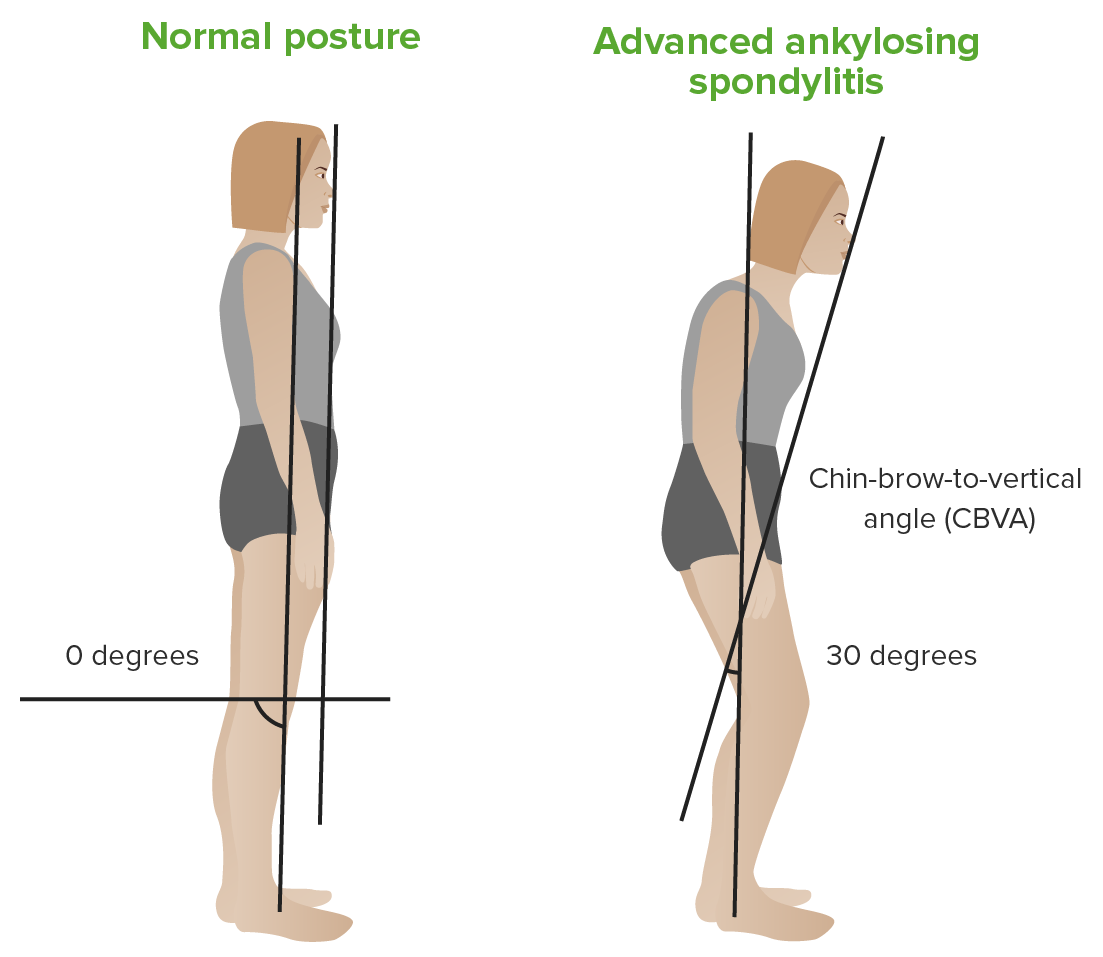
Chin–brow vertical angle:
Left: patient with a normal back
Right: patient with ankylosing spondylitis
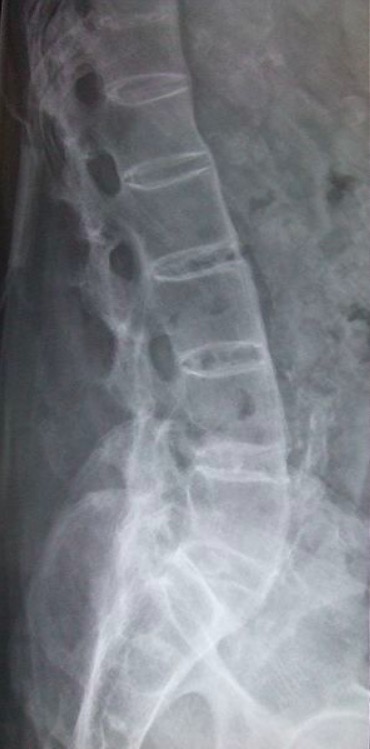
Lateral lumbar spine radiograph in ankylosing spondylitis:
This image demonstrates squaring of the vertebrae with a “bamboo stick” appearance due to bridging syndesmophytes.
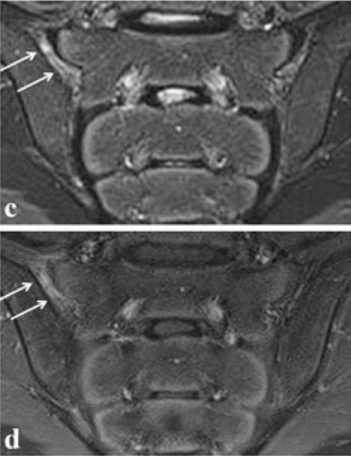
MRI of the sacroiliac joint in ankylosing spondylitis:
The arrows point to enhancement of the right sacroiliac joint, indicating sacroiliitis.
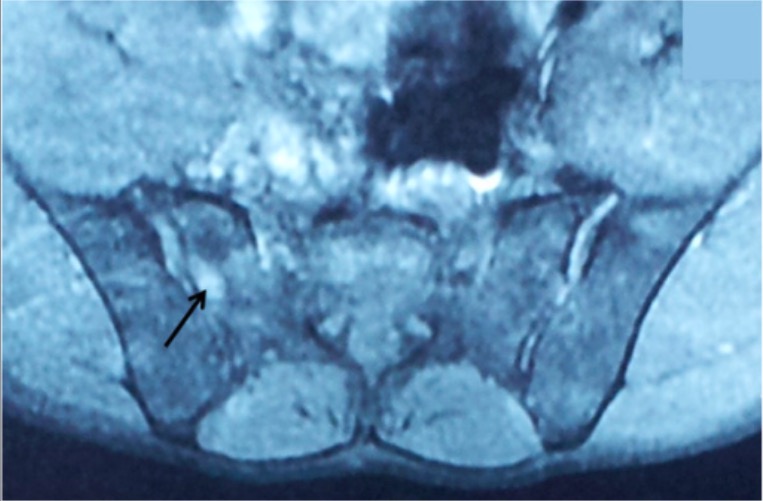
MRI of the sacroiliac joints in ankylosing spondylitis:
This image shows bilateral sacroiliitis with a hyperintense signal on T2 (arrow) at the SI joint.
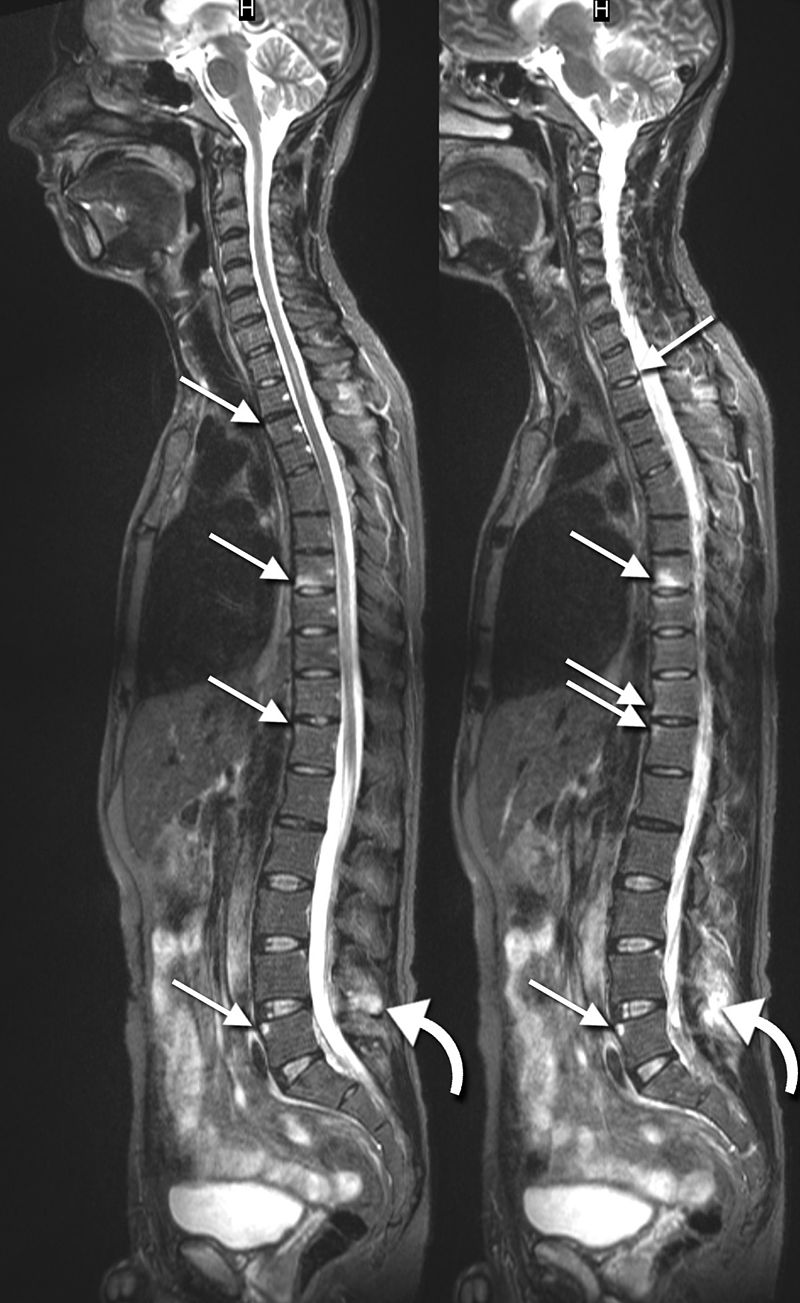
Sagittal MRIs in ankylosing spondylitis:
These images show inflammatory lesions in the thoracic and lumbar spine (arrows). Inflammatory lesions of the spinous process are also shown at L4 (curved arrows).
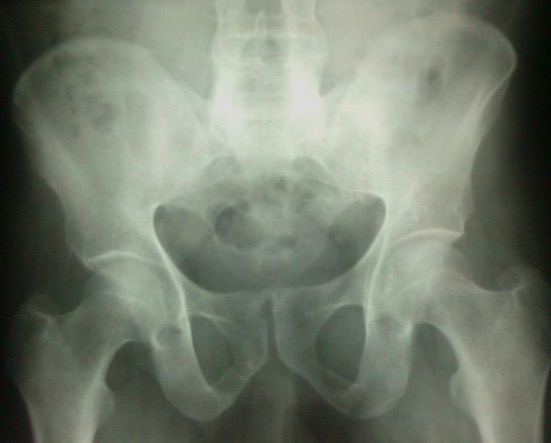
Radiograph of the pelvis in ankylosing spondylitis:
This image demonstrates advanced sacroiliitis with fusion of the SI joints.
Management requires a multidisciplinary approach to reduce pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, increase range of motion Range of motion The distance and direction to which a bone joint can be extended. Range of motion is a function of the condition of the joints, muscles, and connective tissues involved. Joint flexibility can be improved through appropriate muscle strength exercises. Examination of the Upper Limbs, decrease inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body’s defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation, and improve quality Quality Activities and programs intended to assure or improve the quality of care in either a defined medical setting or a program. The concept includes the assessment or evaluation of the quality of care; identification of problems or shortcomings in the delivery of care; designing activities to overcome these deficiencies; and follow-up monitoring to ensure effectiveness of corrective steps. Quality Measurement and Improvement of life.