Atrioventricular (AV) block is a bradyarrhythmia Bradyarrhythmia Bradyarrhythmia is a rhythm in which the heart rate is less than 60/min. Bradyarrhythmia can be physiologic, without symptoms or hemodynamic change. Pathologic bradyarrhythmia results in reduced cardiac output and hemodynamic instability causing syncope, dizziness, or dyspnea. Bradyarrhythmias caused by delay, or interruption, in the electrical conduction between the atria and the ventricles. Atrioventricular block occurs due to either anatomic or functional impairment, and is classified into 3 types. The 1st-degree block is due to delayed conduction through the AV node. The 2nd-degree block is characterized by progressive conduction delay or intermittently blocked conduction. The 3rd-degree block involves total interruption in conduction between the atria and ventricles, causing complete AV dissociation Dissociation Defense Mechanisms. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship may be asymptomatic or may present with syncope Syncope Syncope is a short-term loss of consciousness and loss of postural stability followed by spontaneous return of consciousness to the previous neurologic baseline without the need for resuscitation. The condition is caused by transient interruption of cerebral blood flow that may be benign or related to a underlying life-threatening condition. Syncope, chest pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, dyspnea Dyspnea Dyspnea is the subjective sensation of breathing discomfort. Dyspnea is a normal manifestation of heavy physical or psychological exertion, but also may be caused by underlying conditions (both pulmonary and extrapulmonary). Dyspnea, and bradycardia Bradycardia Bradyarrhythmia is a rhythm in which the heart rate is less than 60/min. Bradyarrhythmia can be physiologic, without symptoms or hemodynamic change. Pathologic bradyarrhythmia results in reduced cardiac output and hemodynamic instability causing syncope, dizziness, or dyspnea. Bradyarrhythmias depending on the severity of the block. Electrocardiography Electrocardiography Recording of the moment-to-moment electromotive forces of the heart as projected onto various sites on the body's surface, delineated as a scalar function of time. The recording is monitored by a tracing on slow moving chart paper or by observing it on a cardioscope, which is a cathode ray tube display. Electrocardiogram (ECG) ( ECG ECG An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The ECG provides 3-dimensional information about the conduction system of the heart, the myocardium, and other cardiac structures. Electrocardiogram (ECG)) establishes the diagnosis, and treatment is based on the type of block and hemodynamic stability of the patient.
Last updated: May 16, 2024
Atrioventricular (AV) block is a delay, or interruption, in the electrical impulse as it passes from the atria to the ventricles through the AV node or the His-Purkinje system. Atrioventricular block is classified based on the severity of the disruption.
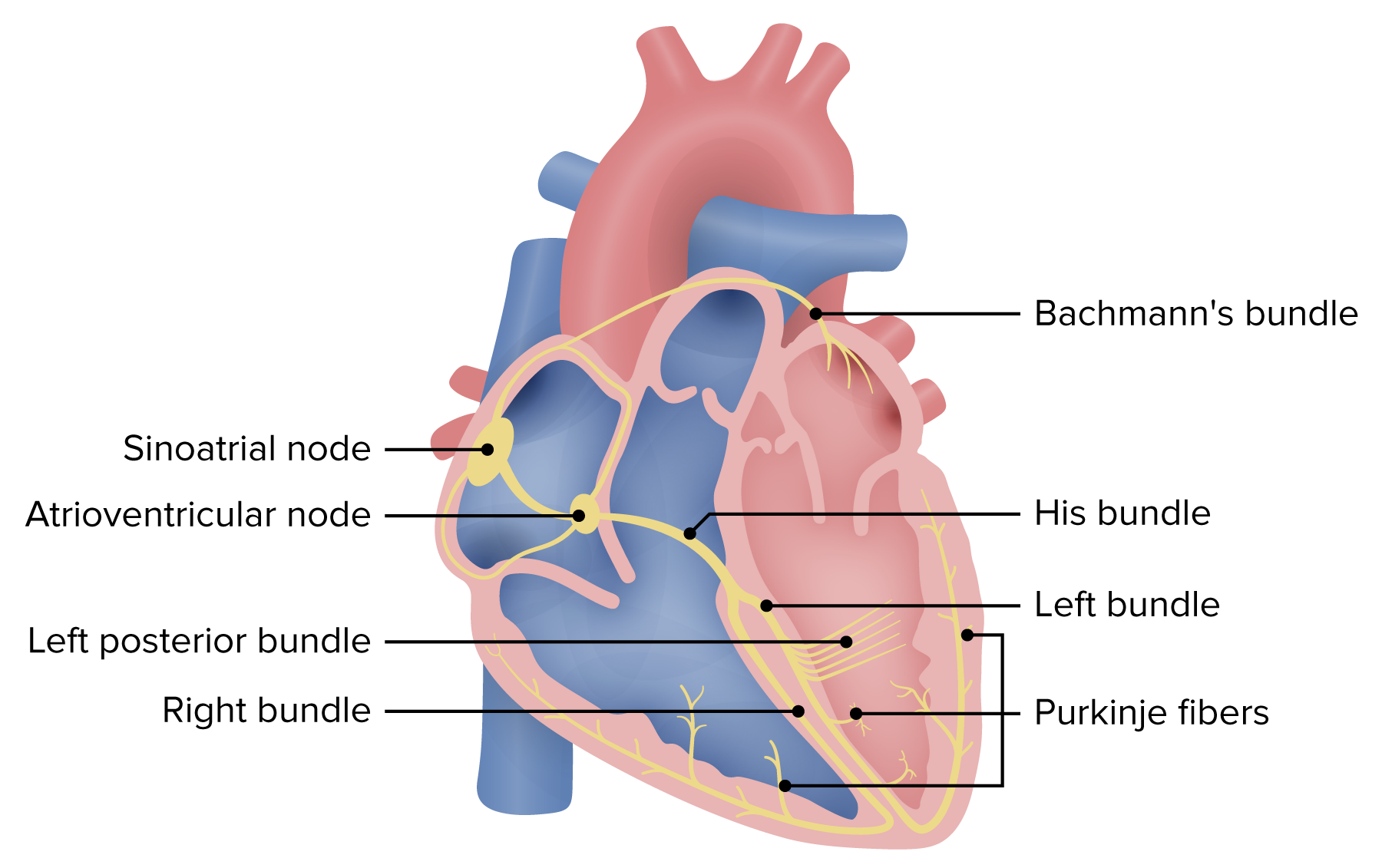
Schematic of the electrical system of the heart. Atrioventricular block may occur within the AV node, His bundle, or the bundle branches. Blocks at the level of the AV node or the His bundle will generally be narrow. Infrahisian (below the His bundle) blocks result in wide QRS complexes.
Image by Lecturio.Second-degree AV block is further divided into 2 subtypes:
The diagnosis is made by electrocardiography Electrocardiography Recording of the moment-to-moment electromotive forces of the heart as projected onto various sites on the body’s surface, delineated as a scalar function of time. The recording is monitored by a tracing on slow moving chart paper or by observing it on a cardioscope, which is a cathode ray tube display. Electrocardiogram (ECG) ( ECG ECG An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The ECG provides 3-dimensional information about the conduction system of the heart, the myocardium, and other cardiac structures. Electrocardiogram (ECG)), and the findings depend on the type of AV block.
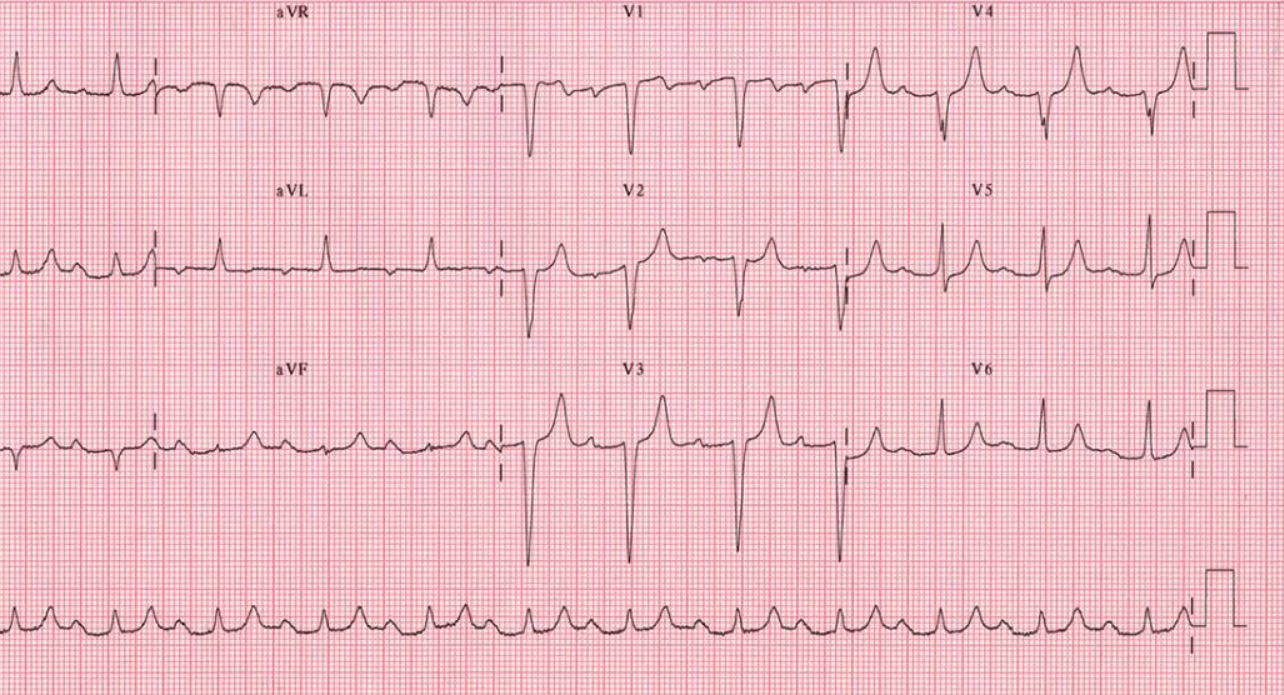
Twelve-lead ECG showing 1st-degree AV block: Notice the uniformly prolonged PR intervals. There are no “dropped” QRS complexes.
Image: “12-lead ECG ” by the Department of Cardiac Surgery, Tor Vergata University of Rome, Italy. License: CC BY 2.0.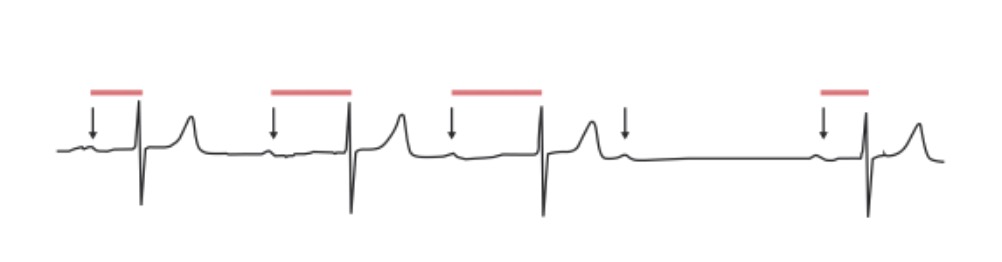
Second-degree AV block, Mobitz 1: The PR interval progressively lengthens in an irregular rhythm until a QRS complex is “dropped.” Arrows: P waves; red lines: progressively prolonging PR interval.
Image by Lecturio.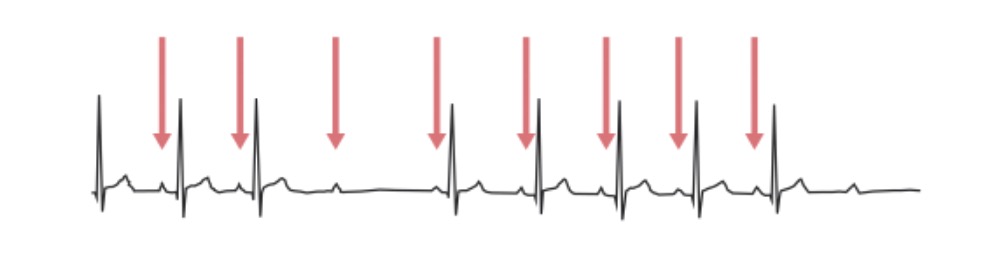
Second-degree AV block, Mobitz 2: ECG shows that the impulse from the SA node is periodically “dropped,” resulting in a normal P wave followed by a drop of the QRS complex and T wave. The red arrows indicate P waves.
Image by Lecturio.