Supraventricular tachycardias are related disorders in which the elevation in heart rate Heart rate The number of times the heart ventricles contract per unit of time, usually per minute. Cardiac Physiology is driven by pathophysiology in the atria. This group falls under the larger umbrella of tachyarrhythmias and includes paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardias (PSVTs), ventricular pre-excitation syndromes (i.e. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome), atrial flutter Atrial flutter Atrial flutter is a regular supraventricular tachycardia characterized by an atrial heart rate between 240/min and 340/min (typically 300/min), atrioventricular (AV) node conduction block, and a "sawtooth" pattern on an electrocardiogram (ECG). Atrial Flutter, multifocal atrial tachycardia Multifocal atrial tachycardia Tachyarrhythmias, and atrial fibrillation Atrial fibrillation Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and the most common kind of arrhythmia. It is caused by rapid, uncontrolled atrial contractions and uncoordinated ventricular responses. Atrial Fibrillation. Sinus tachycardia Tachycardia Abnormally rapid heartbeat, usually with a heart rate above 100 beats per minute for adults. Tachycardia accompanied by disturbance in the cardiac depolarization (cardiac arrhythmia) is called tachyarrhythmia. Sepsis in Children (> 100/min) is not a pathologic arrhythmia. The diagnosis of these conditions can be made using electrocardiogram Electrocardiogram An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The ECG provides 3-dimensional information about the conduction system of the heart, the myocardium, and other cardiac structures. Electrocardiogram (ECG) ( ECG ECG An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The ECG provides 3-dimensional information about the conduction system of the heart, the myocardium, and other cardiac structures. Electrocardiogram (ECG)), and treatment differs depending on the condition.
Last updated: May 16, 2024
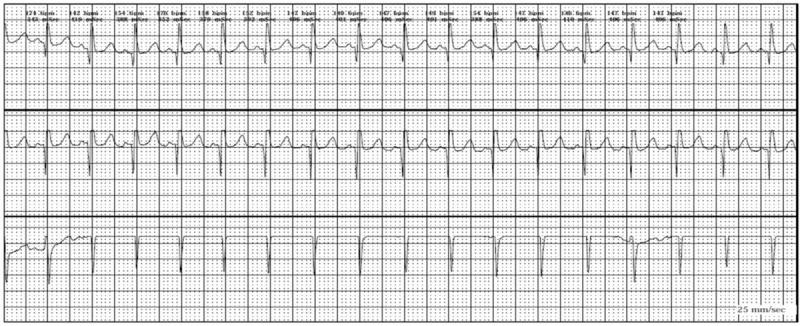
Sinus tachycardia
Image: “Sinus tachycardia” by Faculty of Medicine, Zagazig University, Zagazig City, Egypt. License: CC BY 4.0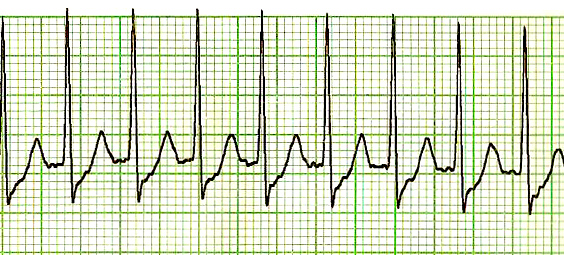
Example of an ECG tracing of supraventricular tachycardia with a regular rhythm, hidden P wave morphology, narrow complex QRS < 120 ms, and a rate > 150/min (approximately 188/min).
Image: “SVT Lead II-2” by James Heilman, MD. License: Public DomainTreat hemodynamic instability via urgent direct current (DC) cardioversion Cardioversion Atrial Fibrillation if present.
AVNRT and AVRT:
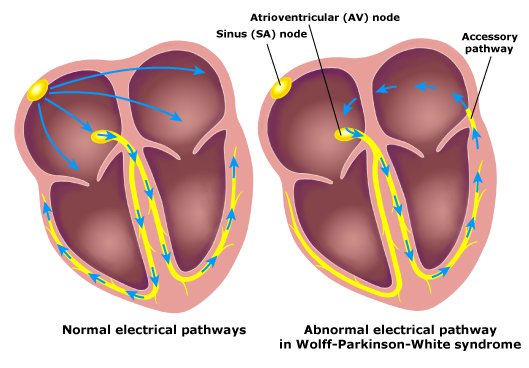
Normal electrical pathway versus the abnormal accessory pathway that causes WPW
Image: “WPW” by Tom Lück. License: CC BY 3.0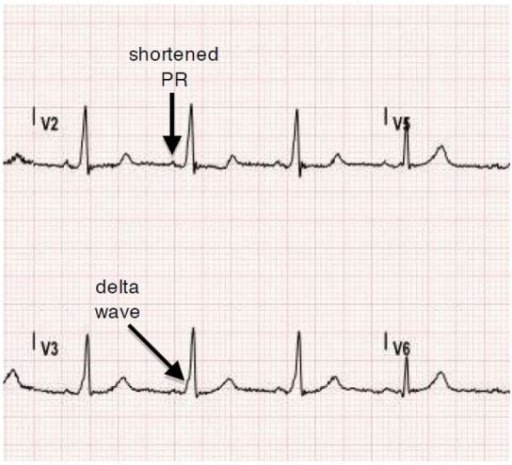
Normal sinus rhythm ECG obtained from a patient with Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome (WPW). Note delta waves and shortened PR interval.
Image: “Tachyarrhythmia in Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome” by University of California, Irvine, Department of Emergency Medicine, Irvine, California. License: CC BY 4.0Treatment is indicated in patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with symptomatic tachyarrhythmias to prevent RVR.
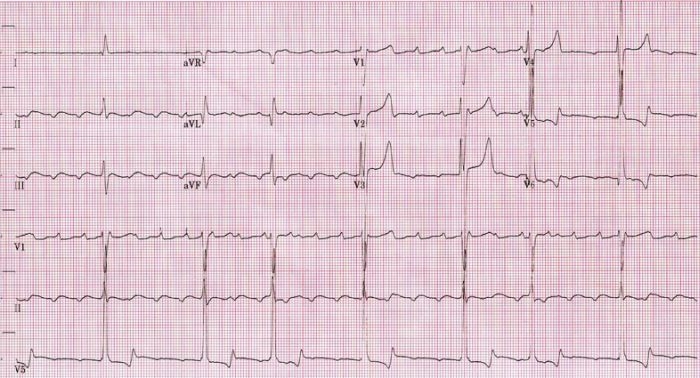
ECG showing slow atrial flutter at an atrial cycle length of 400 ms (atrial rate of 150/min)
Image: “Atrial rate of 150bpm” by Dept. of Cardiology, Beth Israel Medical Center. 16th street and 1st avenue. New York, New York 10003, USA. License: CC BY 2.5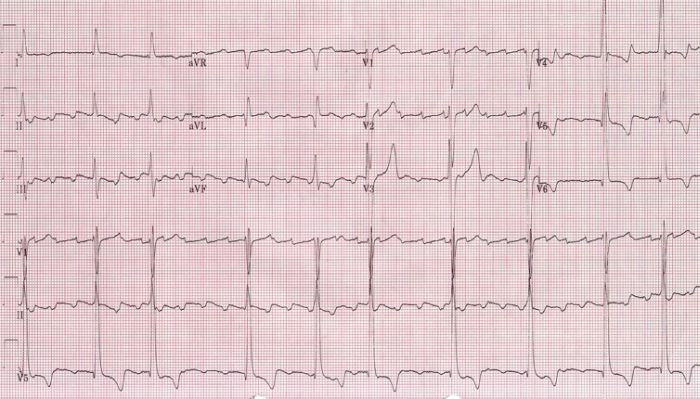
ECG showing a faster atrial flutter at an atrial cycle length of 280 ms (atrial rate of 214/min)
Image: “Atrial rate of 214 bpm” by Dept. of Cardiology, Beth Israel Medical Center. 16th street and 1st avenue. New York, New York 10003, USA. License: CC BY 2.5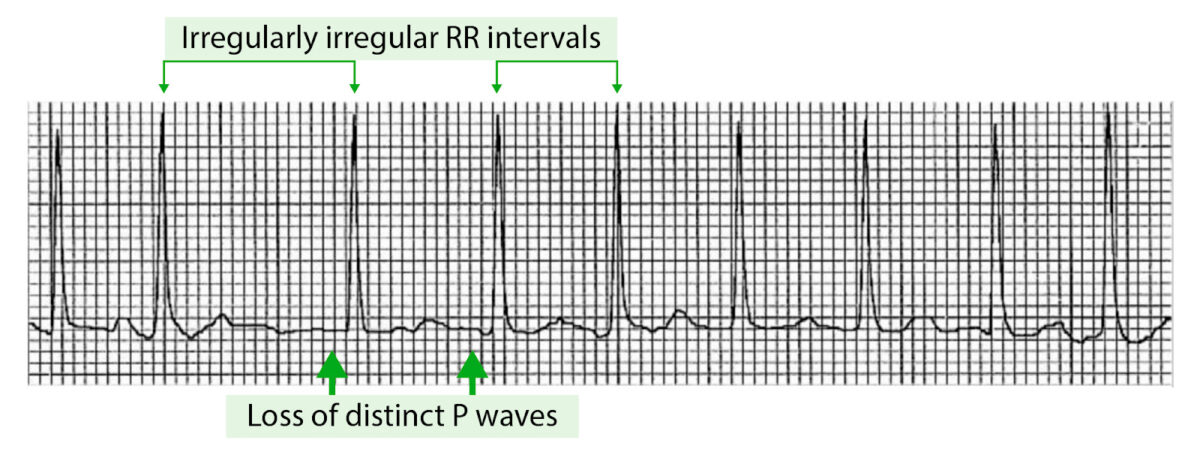
Example of an ECG tracing showing atrial fibrillation with irregularly irregular RR intervals and loss of P waves
Image by Lecturio.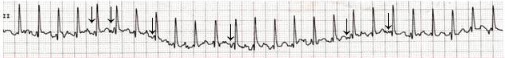
ECG of a 3-year-old child who developed multifocal atrial tachycardia following an iatrogenic overdose of epinephrine accidentally administered intravenously.
Notice the different P-wave morphologies; flat (junctional), negative, and positive p-waves are evident (arrows).
The following conditions may be associated with the development of tachyarrhythmias: