Osteochondritis dissecans ( OCD OCD Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is a condition characterized by obsessions (recurring and intrusive thoughts, urges, or images) and/or compulsions (repetitive actions the person is compelled to perform) that are time-consuming and associated with functional impairment. Obsessive-compulsive Disorder (OCD)) is an orthopedic disorder characterized by the detachment of a focal segment of subchondral bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types and cartilage Cartilage Cartilage is a type of connective tissue derived from embryonic mesenchyme that is responsible for structural support, resilience, and the smoothness of physical actions. Perichondrium (connective tissue membrane surrounding cartilage) compensates for the absence of vasculature in cartilage by providing nutrition and support. Cartilage: Histology as a result of focal aseptic necrosis Aseptic Necrosis Septic Arthritis. This can occur at any age, but it is most commonly seen in adolescents who participate in competitive sports. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship can be asymptomatic or may present with joint pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, stiffness, and swelling Swelling Inflammation that is worse with activity. The diagnosis can be made with imaging. Management depends on the severity, but can include restricted weight-bearing activity, physical therapy Physical Therapy Becker Muscular Dystrophy, or surgery.
Last updated: Mar 28, 2025
Osteochondritis dissecans ( OCD OCD Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is a condition characterized by obsessions (recurring and intrusive thoughts, urges, or images) and/or compulsions (repetitive actions the person is compelled to perform) that are time-consuming and associated with functional impairment. Obsessive-compulsive Disorder (OCD)) is a disorder characterized by aseptic necrosis Aseptic Necrosis Septic Arthritis of subchondral bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types that results in focal detachment and displacement Displacement The process by which an emotional or behavioral response that is appropriate for one situation appears in another situation for which it is inappropriate. Defense Mechanisms of bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types and cartilage Cartilage Cartilage is a type of connective tissue derived from embryonic mesenchyme that is responsible for structural support, resilience, and the smoothness of physical actions. Perichondrium (connective tissue membrane surrounding cartilage) compensates for the absence of vasculature in cartilage by providing nutrition and support. Cartilage: Histology into the joint space. The term osteochondritis is a misnomer, as histologic analysis reveals a lack of inflammatory cells.
The exact etiology is unknown. Many theories have been proposed, and OCD OCD Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is a condition characterized by obsessions (recurring and intrusive thoughts, urges, or images) and/or compulsions (repetitive actions the person is compelled to perform) that are time-consuming and associated with functional impairment. Obsessive-compulsive Disorder (OCD) is likely multifactorial.
Pathogenesis of osteochondritis dissecans:
Stages of progression in osteochondritis dissecans:
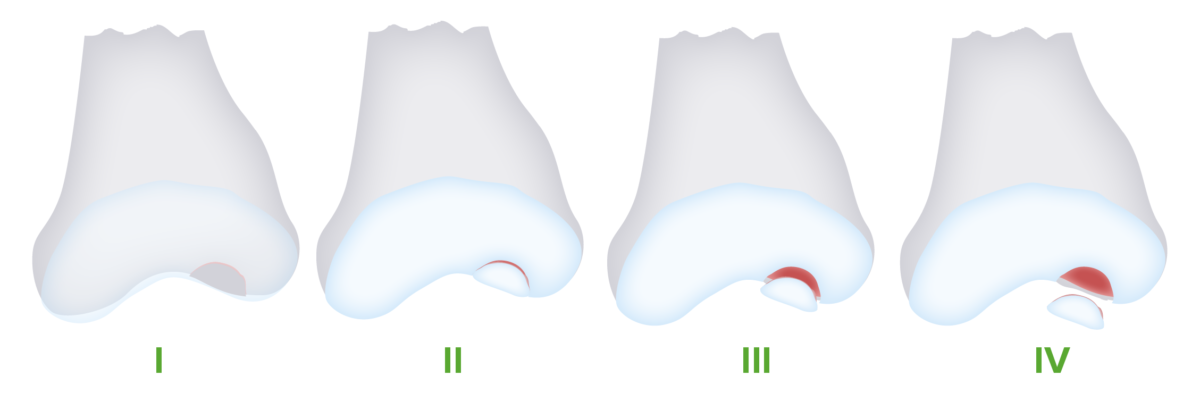
Osteochondritis dissecans progresses through 4 stages. With continued injury, the lesion fragments and becomes separated from the underlying bone, eventually becoming displaced in the joint space (loose body).
Image by Lecturio.Some patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship may be asymptomatic, with OCD OCD Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is a condition characterized by obsessions (recurring and intrusive thoughts, urges, or images) and/or compulsions (repetitive actions the person is compelled to perform) that are time-consuming and associated with functional impairment. Obsessive-compulsive Disorder (OCD) found incidentally on imaging. However, symptomatic individuals may experience:
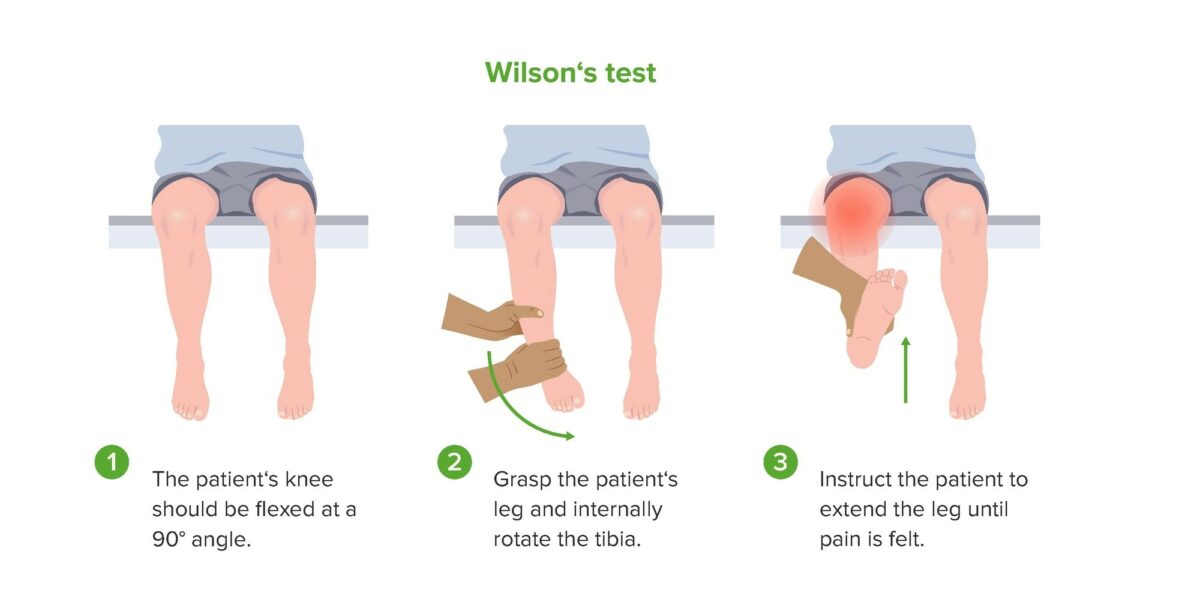
Demonstration of Wilson’s test, which may be positive in patients with osteochondritis dissecans of the knee.
Image by Lecturio.A diagnosis of OCD OCD Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is a condition characterized by obsessions (recurring and intrusive thoughts, urges, or images) and/or compulsions (repetitive actions the person is compelled to perform) that are time-consuming and associated with functional impairment. Obsessive-compulsive Disorder (OCD) should be suspected in adolescents with a characteristic presentation of joint pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways and involvement in repetitive activities and sports.
X-rays X-rays X-rays are high-energy particles of electromagnetic radiation used in the medical field for the generation of anatomical images. X-rays are projected through the body of a patient and onto a film, and this technique is called conventional or projectional radiography. X-rays of the affected joint are usually diagnostic and are the initial testing method of choice. However, these images can be normal in the early disease stages.
Knee:
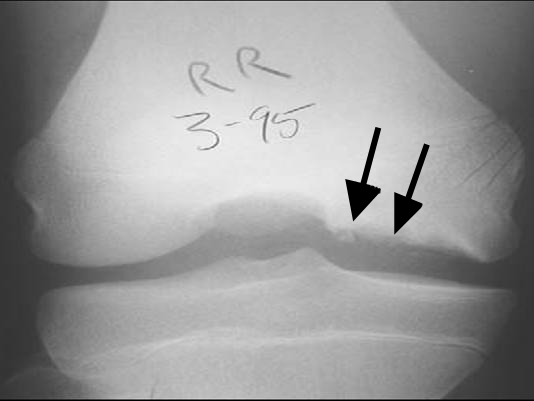
Knee X-ray of a patient with osteochondritis dissecans:
Note the fragmentation of the bone and the radiolucency underneath (arrows).
Elbow:
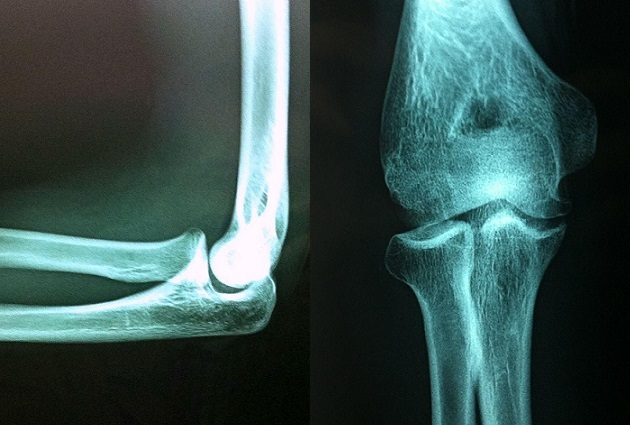
X-ray images from a 16-year-old athlete with osteochondritis dissecans of the elbow.
Shown is a radiolucent focus of the capitellum over the radial head.
Ankle:

X-ray images of an ankle showing osteochondritis dissecans of the superomedial talus.
Note the radiolucency and fragmentation (arrows).
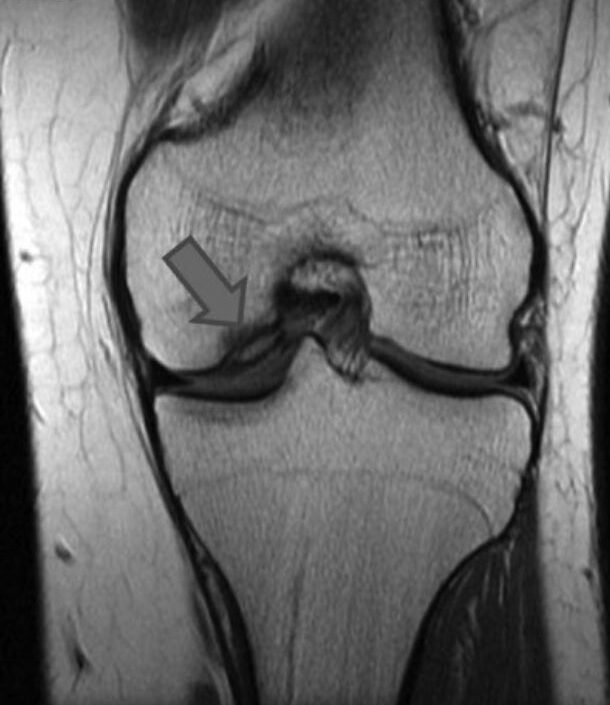
MRI of a knee showing an area of osteochondritis dissecans affecting the medial femoral condyle
Image: “The present state of treatments for articular cartilage defects in the knee” by Perera JR, Gikas PD, Bentley G. License: CC BY 3.0, cropped by Lecturio.The main goal of management is to achieve healing of the osteochondral lesion and return the affected joint to full function. Specialty referrals for sports medicine or orthopedic surgery may be needed.