A “toddler’s fracture Fracture A fracture is a disruption of the cortex of any bone and periosteum and is commonly due to mechanical stress after an injury or accident. Open fractures due to trauma can be a medical emergency. Fractures are frequently associated with automobile accidents, workplace injuries, and trauma. Overview of Bone Fractures” is a spiral Spiral Computed tomography where there is continuous x-ray exposure to the patient while being transported in a spiral or helical pattern through the beam of irradiation. This provides improved three-dimensional contrast and spatial resolution compared to conventional computed tomography, where data is obtained and computed from individual sequential exposures. Computed Tomography (CT) or oblique fracture Oblique Fracture Overview of Bone Fractures of the distal tibia Tibia The second longest bone of the skeleton. It is located on the medial side of the lower leg, articulating with the fibula laterally, the talus distally, and the femur proximally. Knee Joint: Anatomy in toddlers resulting from a low-energy trauma with a rotational/twisting component. These fractures are often seen in children who are learning to walk and who do not have a specific history of trauma. The child can sometimes present with a painful limp or refusal to bear weight on the affected limb. Management comprises analgesia Analgesia Methods of pain relief that may be used with or in place of analgesics. Anesthesiology: History and Basic Concepts and immobilizing the injured leg Leg The lower leg, or just "leg" in anatomical terms, is the part of the lower limb between the knee and the ankle joint. The bony structure is composed of the tibia and fibula bones, and the muscles of the leg are grouped into the anterior, lateral, and posterior compartments by extensions of fascia. Leg: Anatomy for several weeks.
Last updated: Jan 20, 2025
Non-displaced spiral Spiral Computed tomography where there is continuous x-ray exposure to the patient while being transported in a spiral or helical pattern through the beam of irradiation. This provides improved three-dimensional contrast and spatial resolution compared to conventional computed tomography, where data is obtained and computed from individual sequential exposures. Computed Tomography (CT) fractures of the distal tibia Tibia The second longest bone of the skeleton. It is located on the medial side of the lower leg, articulating with the fibula laterally, the talus distally, and the femur proximally. Knee Joint: Anatomy are often called “toddler’s fractures,” as they are commonly seen in children who are just starting to walk.
Diagnosis of toddler’s fracture Fracture A fracture is a disruption of the cortex of any bone and periosteum and is commonly due to mechanical stress after an injury or accident. Open fractures due to trauma can be a medical emergency. Fractures are frequently associated with automobile accidents, workplace injuries, and trauma. Overview of Bone Fractures may be challenging due to lack of documented trauma and the inability of the child to localize injury:
Signs:
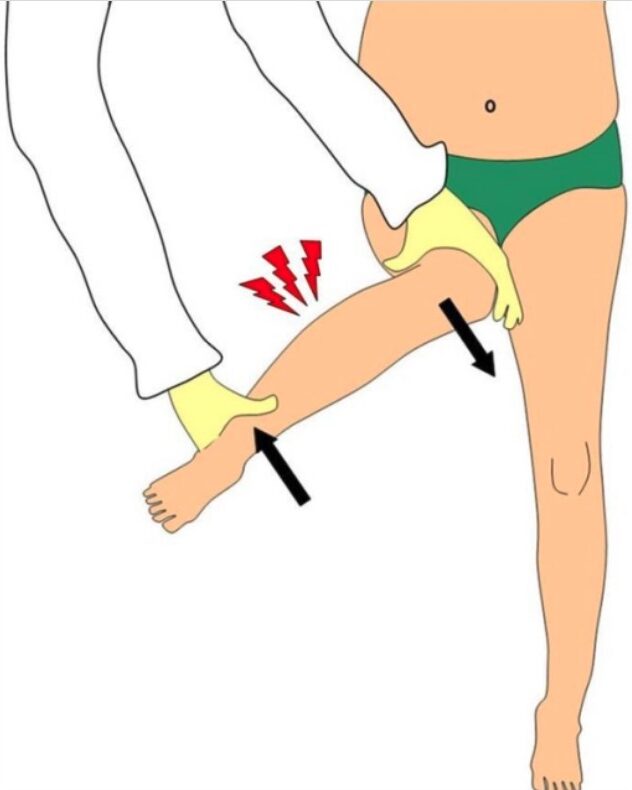
Exam finding for toddler’s fracture:
Gentle twisting of ankle and knee in opposite directions elicits tibial pain. During examination of the hip, rotational shear forces acting on the leg (arrows) can elicit pain in an injured tibia and this can be mistaken as a hip tenderness.
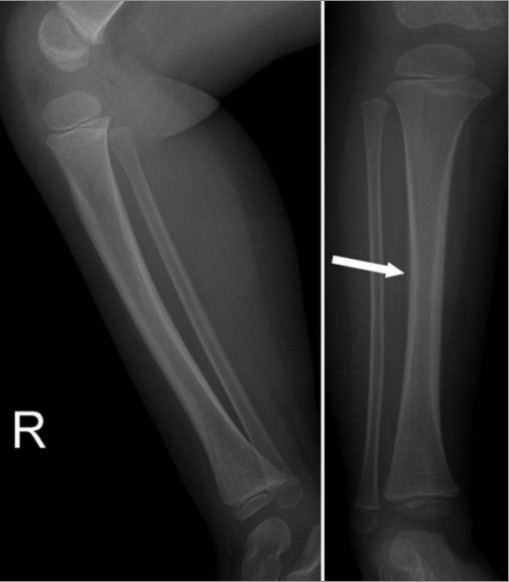
Toddler’s fracture:
Initial imaging in cases of spiral tibial fractures may be subtle or negative. In cases with high clinical suspicion, lower extremity radiographs repeated after 1–2 weeks may show new periosteal bone formation (white arrow), suggesting healing of a toddler’s fracture.
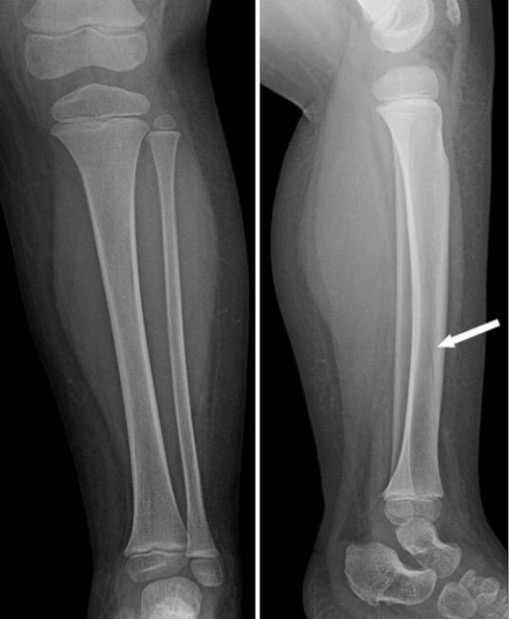
Spiral fracture on the left distal tibia:
Spiral tibia fractures can be sometimes seen on anterior and lateral view as a faint dark line (white arrow), which can often be mistaken for a nutritive vessel.
These fractures are usually non-displaced and are managed non-operatively.
Essential considerations in differential diagnosis of a child presenting with a limp:
Common fractures seen in pediatric age group: