Chronic eosinophilic leukemia (CEL) is a chronic myeloproliferative neoplasm caused by autonomous clonal proliferation of normal-appearing eosinophils Eosinophils Granular leukocytes with a nucleus that usually has two lobes connected by a slender thread of chromatin, and cytoplasm containing coarse, round granules that are uniform in size and stainable by eosin. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation, resulting in increased eosinophils Eosinophils Granular leukocytes with a nucleus that usually has two lobes connected by a slender thread of chromatin, and cytoplasm containing coarse, round granules that are uniform in size and stainable by eosin. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation in the peripheral blood and bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis. The disorder is a myeloid variant of hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) and is associated with tissue infiltration leading to end-organ damage. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship present with constitutional symptoms Constitutional Symptoms Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody (ANCA)-Associated Vasculitis along with signs and symptoms of anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types and thrombocytopenia Thrombocytopenia Thrombocytopenia occurs when the platelet count is < 150,000 per microliter. The normal range for platelets is usually 150,000-450,000/µL of whole blood. Thrombocytopenia can be a result of decreased production, increased destruction, or splenic sequestration of platelets. Patients are often asymptomatic until platelet counts are < 50,000/µL. Thrombocytopenia. Studies show absolute eosinophilic count ≥ 1.5 x 10⁹/L, with bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis blasts Blasts Injuries resulting when a person is struck by particles impelled with violent force from an explosion. Blast causes pulmonary contusion and hemorrhage, laceration of other thoracic and abdominal viscera, ruptured ear drums, and minor effects in the central nervous system. Blunt Chest Trauma (5%–19%). Evidence of clonal abnormality or elevated blasts Blasts Injuries resulting when a person is struck by particles impelled with violent force from an explosion. Blast causes pulmonary contusion and hemorrhage, laceration of other thoracic and abdominal viscera, ruptured ear drums, and minor effects in the central nervous system. Blunt Chest Trauma are needed; without either, idiopathic Idiopathic Dermatomyositis HES is the appropriate diagnosis. Nevertheless, both have a similar treatment approach. Management aims to reduce the burden of hypercellularity to prevent end-organ damage. Treatment options include corticosteroids Corticosteroids Chorioretinitis, chemotherapeutic agents, and interferon-α.
Last updated: May 17, 2024
Chronic eosinophilic leukemia, not otherwise specified (CEL, NOS) is a rare chronic myeloproliferative neoplasm typified by clonal eosinophilic expansion in the bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis with increased blasts Blasts Injuries resulting when a person is struck by particles impelled with violent force from an explosion. Blast causes pulmonary contusion and hemorrhage, laceration of other thoracic and abdominal viscera, ruptured ear drums, and minor effects in the central nervous system. Blunt Chest Trauma (< 20%).
Based on eosinophilias:
CEL, NOS is classified under chronic myeloproliferative neoplasms Neoplasms New abnormal growth of tissue. Malignant neoplasms show a greater degree of anaplasia and have the properties of invasion and metastasis, compared to benign neoplasms. Benign Bone Tumors (WHO classification):
Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis The development and formation of various types of blood cells. Hematopoiesis can take place in the bone marrow (medullary) or outside the bone marrow (extramedullary hematopoiesis). Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis starts with a hematopoietic stem cell, which is prompted to divide and differentiate with appropriate chemical stimuli (hemopoietic growth factors).
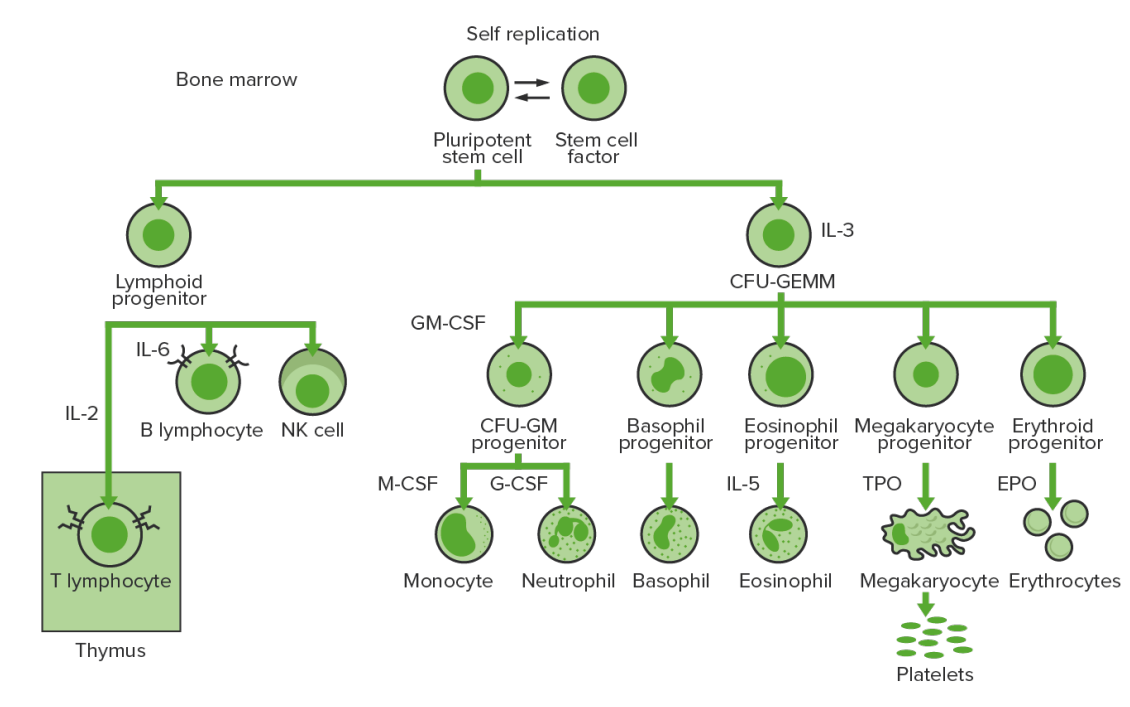
Bone-marrow hematopoiesis: proliferation and differentiation of the formed elements of blood.
CFU-GEMM: colony-forming unit–granulocyte, erythrocyte, monocyte, megakaryocyte
CFU-GM: colony-forming unit–granulocyte-macrophage
GM-CSF: granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor
M-CSF: macrophage colony-stimulating factor
G-CSF: granulocyte colony-stimulating factor
NK: natural killer
TPO: thrombopoietin
Chronic eosinophilic leukemia, not otherwise specified is a diagnosis of exclusion (requires ruling out other eosinophilic conditions) and is defined according to the WHO diagnostic criteria:
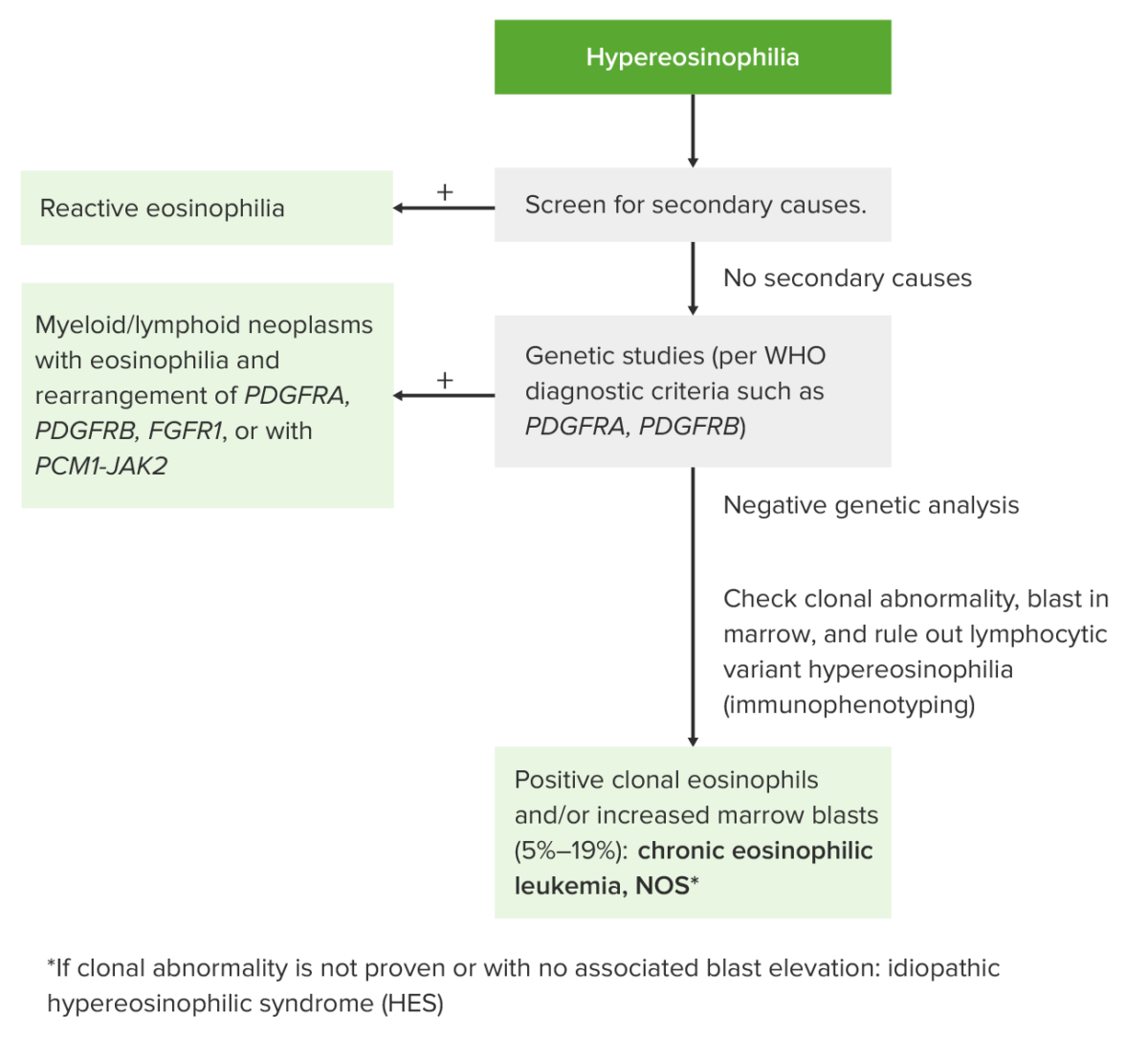
Approach to hypereosinophilia
Image by Lecturio.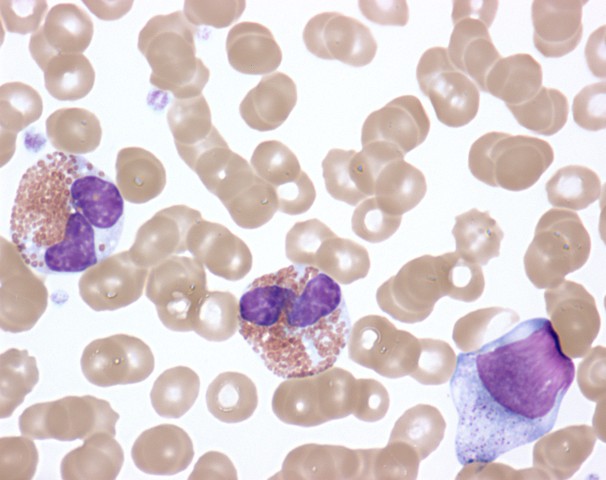
Activated eosinophils in the peripheral blood of a patient with hypereosinophilic syndrome showing cytoplasmic clearing, nuclear dysplasia, and the presence of immature forms
Image: “Activated Eosinophils in Idiopathic Hypereosinophilic Syndrome (9125007255)” by NIAID. License: CC BY 2.0