Bradyarrhythmia is a rhythm in which the heart rate Heart rate The number of times the heart ventricles contract per unit of time, usually per minute. Cardiac Physiology is less than 60/min. Bradyarrhythmia can be physiologic, without symptoms or hemodynamic change. Pathologic bradyarrhythmia results in reduced cardiac output Cardiac output The volume of blood passing through the heart per unit of time. It is usually expressed as liters (volume) per minute so as not to be confused with stroke volume (volume per beat). Cardiac Mechanics and hemodynamic instability causing syncope Syncope Syncope is a short-term loss of consciousness and loss of postural stability followed by spontaneous return of consciousness to the previous neurologic baseline without the need for resuscitation. The condition is caused by transient interruption of cerebral blood flow that may be benign or related to a underlying life-threatening condition. Syncope, dizziness Dizziness An imprecise term which may refer to a sense of spatial disorientation, motion of the environment, or lightheadedness. Lateral Medullary Syndrome (Wallenberg Syndrome), or dyspnea Dyspnea Dyspnea is the subjective sensation of breathing discomfort. Dyspnea is a normal manifestation of heavy physical or psychological exertion, but also may be caused by underlying conditions (both pulmonary and extrapulmonary). Dyspnea. Bradyarrhythmia is due to dysfunction in the sinoatrial (SA) node, atrioventricular (AV) node, or the lower conduction system. Bradyarrhythmia can be associated with an intrinsic cardiac abnormality or with medications, electrolyte imbalances, and systemic diseases. Arrhythmia is detected by electrocardiogram Electrocardiogram An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The ECG provides 3-dimensional information about the conduction system of the heart, the myocardium, and other cardiac structures. Electrocardiogram (ECG) ( ECG ECG An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The ECG provides 3-dimensional information about the conduction system of the heart, the myocardium, and other cardiac structures. Electrocardiogram (ECG)). Additional tests such as event recorders are performed if symptoms are less frequent and require a longer observation period. There are bradyarrhythmias requiring no intervention. In symptomatic or life-threatening conduction abnormalities such as complete heart block, permanent pacemaker placement is the mainstay of treatment.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Bradyarrhythmia:
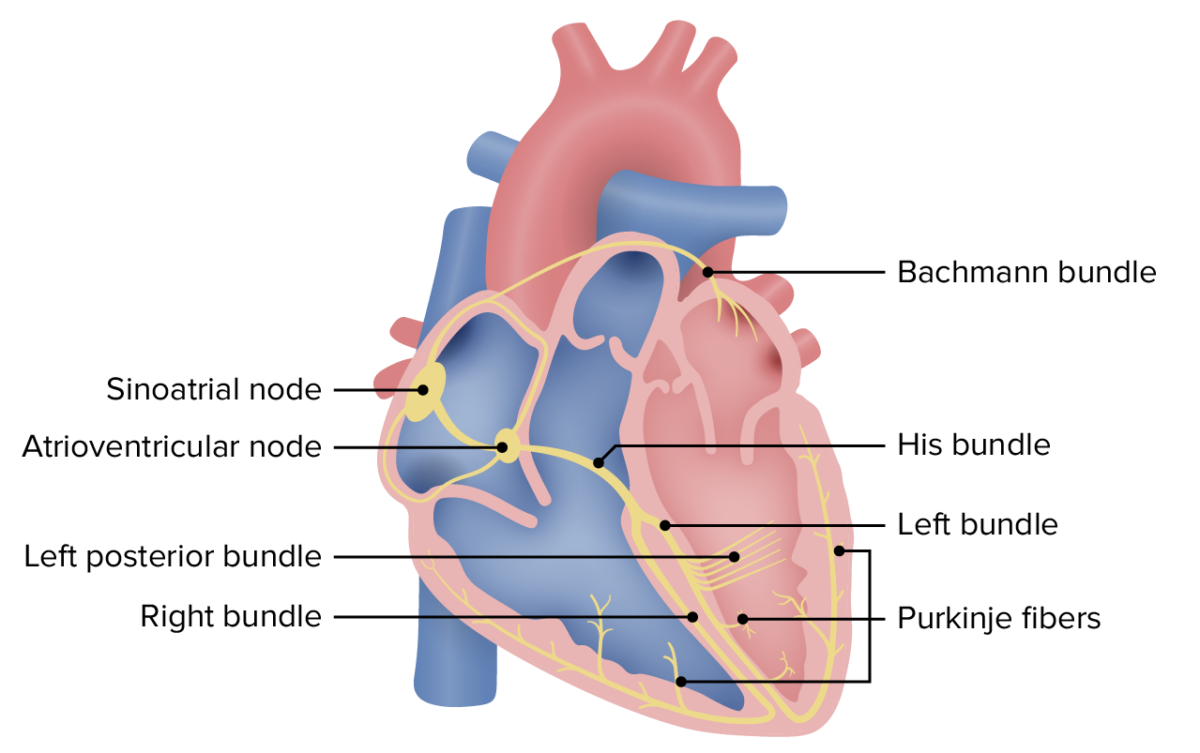
Conduction system of the heart
Image by Lecturio.Sequential Sequential Computed Tomography (CT) events of a cardiac cycle Cardiac cycle The cardiac cycle describes a complete contraction and relaxation of all 4 chambers of the heart during a standard heartbeat. The cardiac cycle includes 7 phases, which together describe the cycle of ventricular filling, isovolumetric contraction, ventricular ejection, and isovolumetric relaxation. Cardiac Cycle:
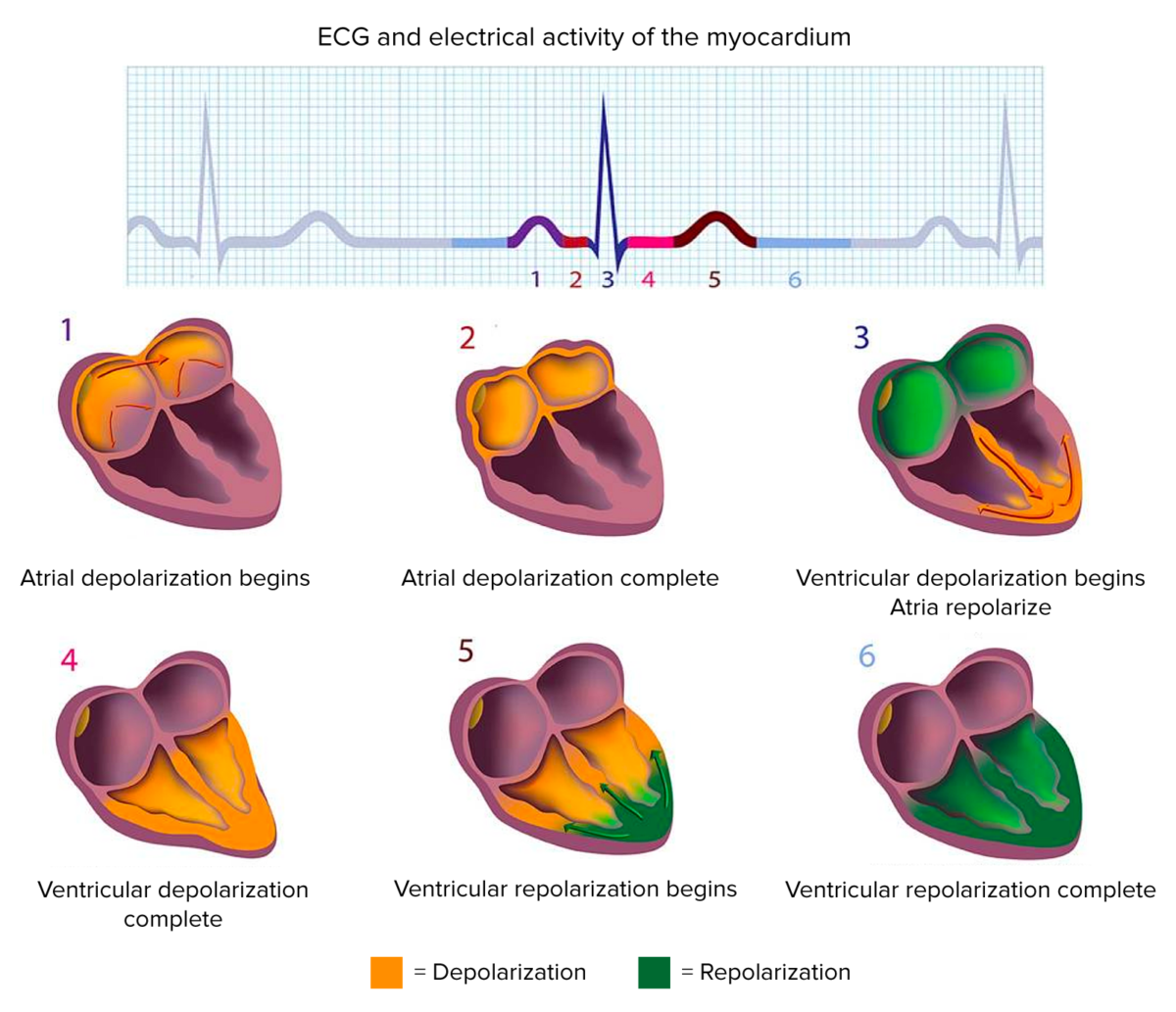
Electrocardiogram and electrical activity of the myocardium
Image by Lecturio.Intrinsic causes:
Extrinsic causes:
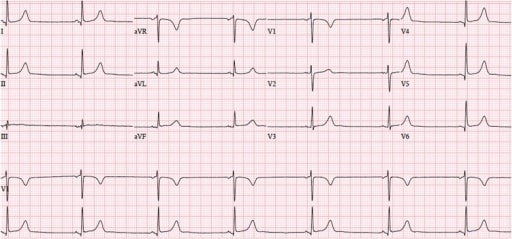
Sinus bradycardia (42/min) on ECG: Every P wave is followed by a QRS complex, accompanied by a normal PR interval, indicating sinus rhythm.
Image: “Sinus bradycardia at 42/min” by the Department of Medicine, University of Massachusetts Medical School, 55 Lake Avenue North, Worcester, MA, 01655, USA. License: CC BY 4.0.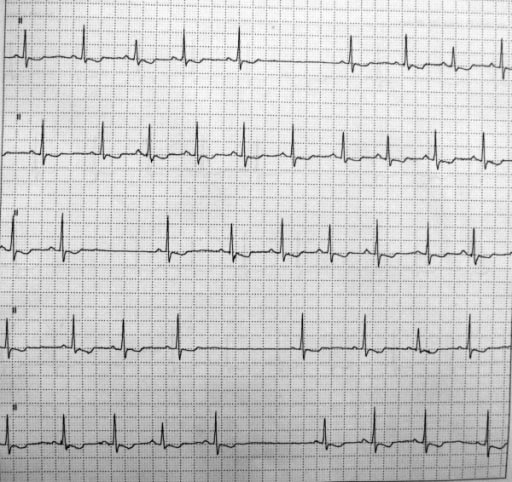
Holter monitor showing sinus pauses (top and bottom 2 tracings)
Image: “Bradycardia-tachycardia syndrome” by Department of Anesthesia, Narayana Hrudayalaya Institute of Medical Sciences, Bangalore, India. License: CC BY 2.0.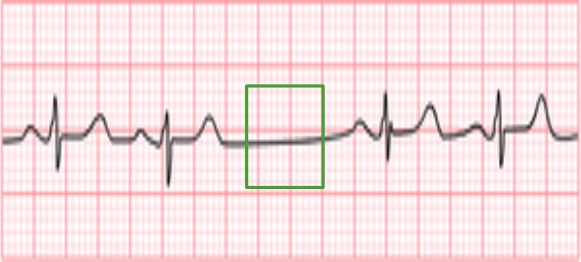
First-degree AV block: PR interval > 200 msec (green box)
Image by Lecturio.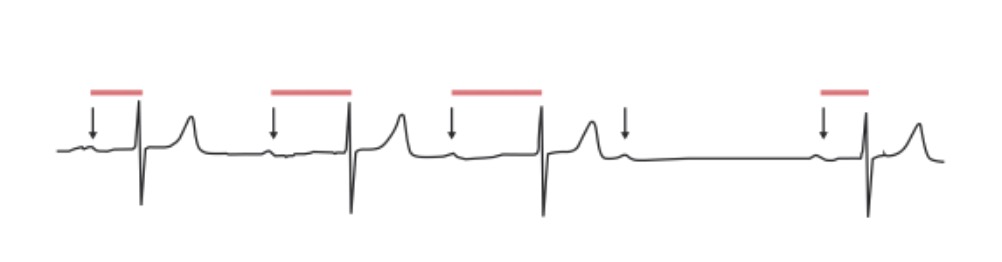
Second-degree AV block, Mobitz 1: The PR interval progressively lengthens in an irregular rhythm until a QRS complex is “dropped.” Arrows: P waves. Red lines: progressively prolonging PR interval.
Image by Lecturio.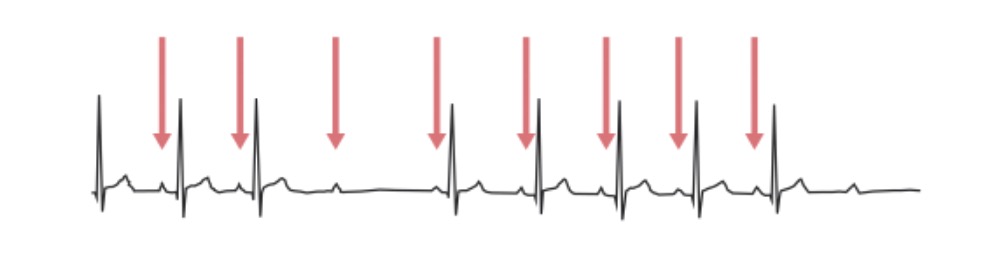
Second-degree AV block, Mobitz 2: ECG shows impulse from the SA node is periodically “dropped,” resulting in a normal P wave followed by a drop of the QRS complex and T wave. The red arrows indicate P waves.
Image by Lecturio.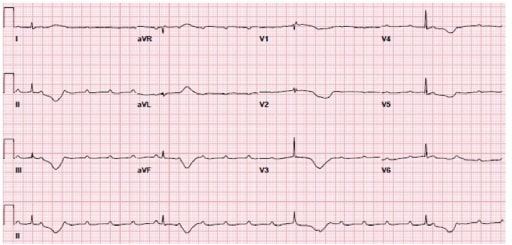
ECG showing complete heart block: Atrial activity (P wave) and ventricular (QRS) activity are independent of each other.
Image: “Complete heart block” by the Department of Medicine, Allegheny General Hospital, Pittsburgh, PA 15212, USA. License: CC BY 4.0.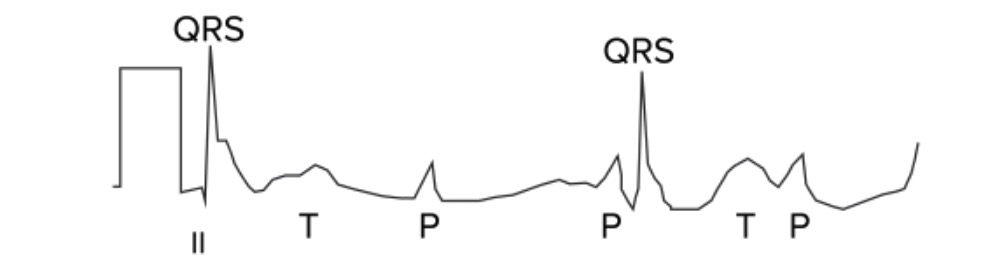
Third-degree AV block: The atria and ventricles are out of sync and follow their own pacemakers. In this ECG, there is complete asynchronicity between P waves and QRS complexes.
Image by Lecturio.Symptoms are related to bradyarrhythmia, causing low cardiac output Cardiac output The volume of blood passing through the heart per unit of time. It is usually expressed as liters (volume) per minute so as not to be confused with stroke volume (volume per beat). Cardiac Mechanics:
Assess hemodynamic stability of the patient with bradyarrhythmia:
Potential etiologies of conduction deficits: