Acute limb ischemia Ischemia A hypoperfusion of the blood through an organ or tissue caused by a pathologic constriction or obstruction of its blood vessels, or an absence of blood circulation. Ischemic Cell Damage (ALI) is a major vascular emergency because of the rapid decrease in limb perfusion that causes a potential threat to limb viability. The majority of cases are caused by arterial thrombosis Arterial Thrombosis Hypercoagulable States due to plaque Plaque Primary Skin Lesions progression or embolism, but ALI can also be caused by blockage of the venous drainage. The typical signs and symptoms of ALI are often referred to as the 6 Ps PS Invasive Mechanical Ventilation: pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, pallor, poikilothermia, paralysis, paresthesia, and pulselessness Pulselessness Cardiac Arrest. The diagnosis is made on the basis of clinical findings and Doppler Doppler Ultrasonography applying the doppler effect, with frequency-shifted ultrasound reflections produced by moving targets (usually red blood cells) in the bloodstream along the ultrasound axis in direct proportion to the velocity of movement of the targets, to determine both direction and velocity of blood flow. Ultrasound (Sonography) studies, but additional imaging may be required. Management is focused on revascularization Revascularization Thromboangiitis Obliterans (Buerger Disease). IV heparin is also administered. Nonviable limbs require amputation Amputation An amputation is the separation of a portion of the limb or the entire limb from the body, along with the bone. Amputations are generally indicated for conditions that compromise the viability of the limb or promote the spread of a local process that could manifest systemically. Amputation.
Last updated: May 28, 2025
Acute limb ischemia Ischemia A hypoperfusion of the blood through an organ or tissue caused by a pathologic constriction or obstruction of its blood vessels, or an absence of blood circulation. Ischemic Cell Damage (ALI) is a vascular emergency caused by a rapid decrease in limb perfusion.
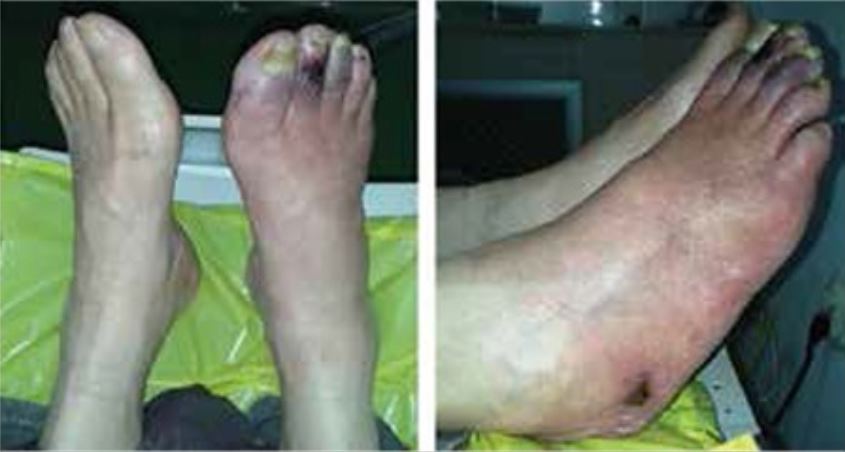
Skin changes and ulcers in a patient with type 2 diabetes mellitus and peripheral artery disease
Image: “Skin ulcers on the right foot” by Manevska N, Gjorceva DP, Ahmeti I, Todorovska L, Stojanoski S, Kocovska MZ. License: CC BY 2.5
Unrecognized hand ischemia after intraarterial drug injection:
Note the significant bluish discoloration of the ischemic right hand distal to the wrist. The patient presented with hypoesthesia distal to the wrist crease and a pathologic Allen test.
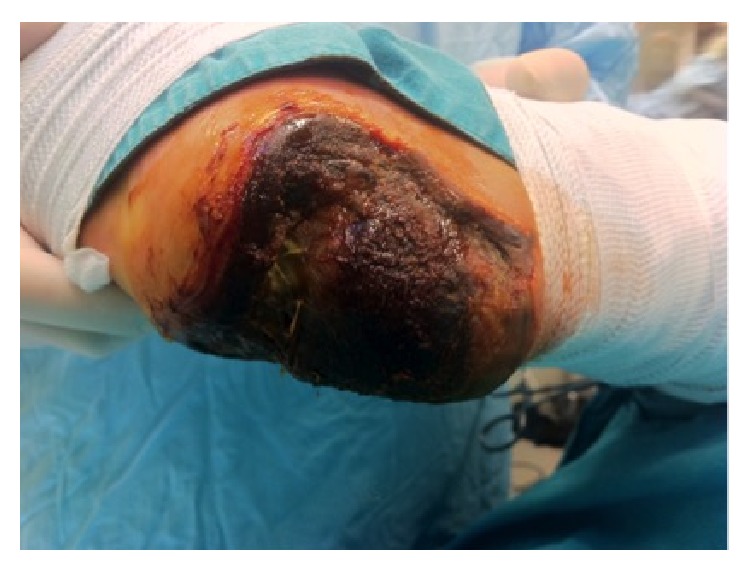
Full-thickness necrosis of the heel due to acute limb ischemia in a diabetic patient
Image: “Full thickness necrosis due to acute limb ischemia” by Bingol UA, Cinar C, Arslan H, Altındas M. License: CC BY 3.0Acute limb ischemia Ischemia A hypoperfusion of the blood through an organ or tissue caused by a pathologic constriction or obstruction of its blood vessels, or an absence of blood circulation. Ischemic Cell Damage is diagnosed on the basis of medical history, clinical presentation, physical examination, and vascular imaging.
Assess for the 6 Ps PS Invasive Mechanical Ventilation:

Intraoperative angiogram:
A: Superficial femoral and popliteal artery occlusion
B: Femoropopliteal predilatation
C: Postprocedural result after plaque excision with TurboHawk
The treatment approach depends on the severity or category of ischemic injury:
Complications: