Tonsillitis is inflammation of the palatine tonsils. When tonsillitis is caused by infection, it is termed infectious tonsillitis, which is caused by viruses (most common), bacteria, or fungi. Among the bacteria, group A Streptococcus (GAS) is the most frequent etiology. Diagnosis is based on history, risk factors, and clinical findings, with tests done, if indicated, by initial evaluation. Testing for group A Streptococcus (GAS) infection in the setting of tonsillitis is essential, as this infection can lead to rheumatic fever Rheumatic fever Acute rheumatic fever (ARF) is an autoimmune inflammatory process that usually follows Streptococcal pharyngitis. Acute rheumatic fever usually occurs 2-4 weeks after an untreated infection and affects the heart, skin, joints, and nervous system. Rheumatic Fever and glomerulonephritis in children and adolescents. Antibiotic treatment is recommended in a confirmed GAS infection for this population. For other etiologies, management depends on the causative organism and the treatment available.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
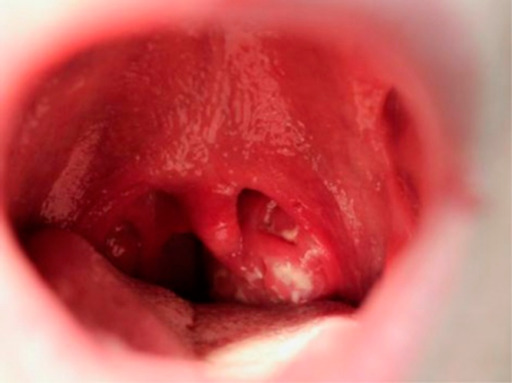
Infectious mononucleosis
pharyngitis demonstrating exudative tonsillitis and an enlarged uvula in a 19-year-old undergraduate university student 5 days after onset of infectious mononucleosis
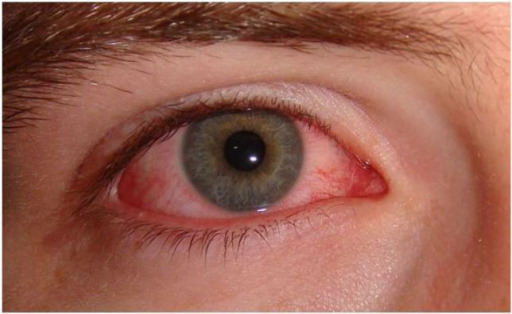
Presentation of viral tonsillitis
conjunctivitis, which is typically seen with viral infection of the pharynx
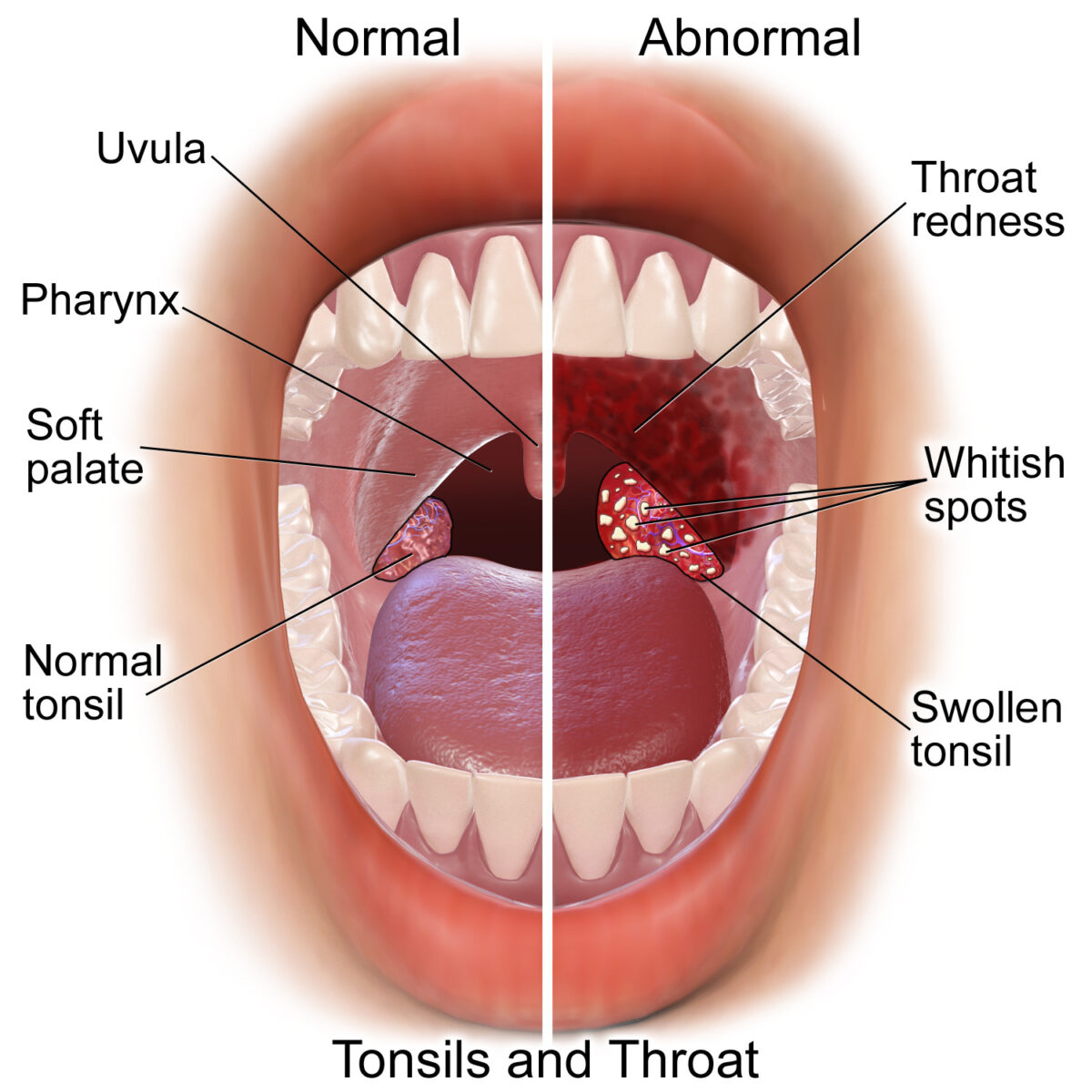
Comparison of normal oropharynx and acute pharyngitis/tonsillitis
throat redness, tonsillar or pharyngeal exudates, and swollen tonsils
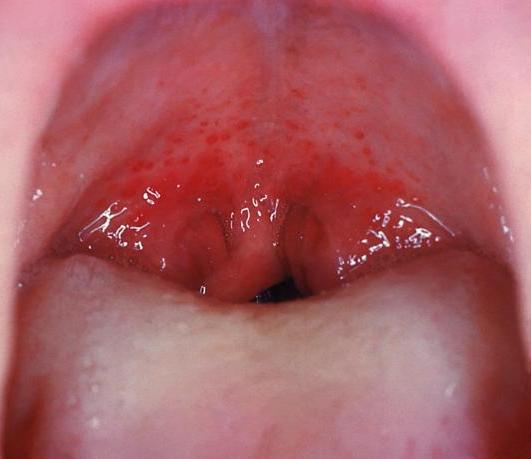
Streptococcal tonsillopharyngitis:
swollen tonsils and palatal petechiae noted in this infection secondary to Group A Streptococcus
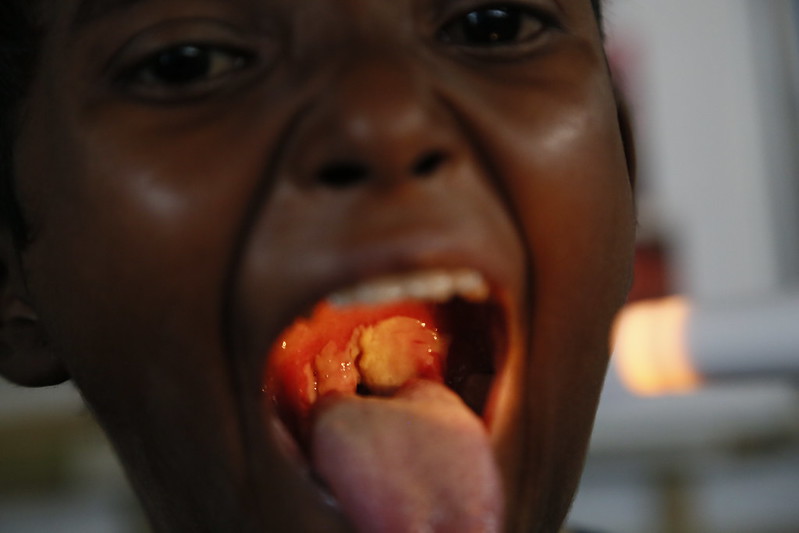
Diphtheria: pediatric patient with diphtheria presenting with the characteristic grayish-white membrane covering the posterior pharyngeal wall.
Image: “39015940254_849c8705a0_c” by Russell Watkins/Department for International Development . License: CC BY 2.0
Pseudomembranous candidiasis patient with oropharyngeal candidiasis infection
In these images, the infection is shown to affect the palate.
The diagnosis is clinical, as it is based on history and examination findings.
Group A Streptococcus Streptococcus Streptococcus is one of the two medically important genera of gram-positive cocci, the other being Staphylococcus. Streptococci are identified as different species on blood agar on the basis of their hemolytic pattern and sensitivity to optochin and bacitracin. There are many pathogenic species of streptococci, including S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, S. pneumoniae, and the viridans streptococci. Streptococcus infection:
Work-up for other etiologies:
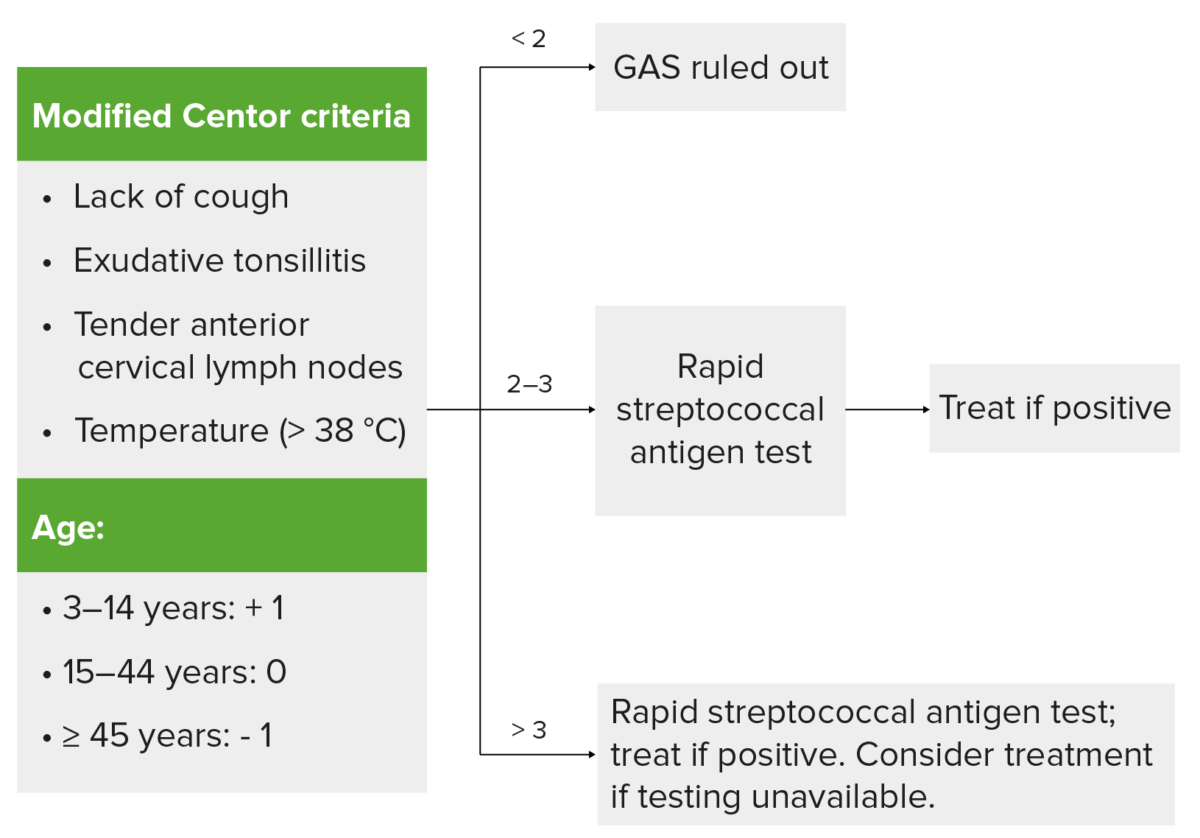
Use of Centor criteria for group A streptococcal (GAS) infection
Findings on the left given one point each (modified score based on age). If score is < 2, GAS infection (tonsillitis) is unlikely. For scores 2–3, rapid antigen detection test is performed. For score >3, proceed with testing and treat if positive. In cases where testing is unavailable, consider antibiotic treatment. Clinical judgment is still recommended in determining testing and treatment
The following are the complications associated with bacterial tonsillitis/ pharyngitis Pharyngitis Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the back of the throat (pharynx). Pharyngitis is usually caused by an upper respiratory tract infection, which is viral in most cases. It typically results in a sore throat and fever. Other symptoms may include a runny nose, cough, headache, and hoarseness. Pharyngitis:
The following conditions are differential diagnoses of tonsillitis: