Testicular cancer is the most common solid malignancy Malignancy Hemothorax affecting men 15–35 years of age. Most of the testicular cancers are of the germ cell tumor Tumor Inflammation type, and they can be classified as seminomas and nonseminomas. The most common presentation of testicular cancer is a painless testicular mass Mass Three-dimensional lesion that occupies a space within the breast Imaging of the Breast. Diagnosis is via physical exam, testicular ultrasonography, and serum tumor Tumor Inflammation markers. Additional imaging helps with staging Staging Methods which attempt to express in replicable terms the extent of the neoplasm in the patient. Grading, Staging, and Metastasis and assessment of metastasis Metastasis The transfer of a neoplasm from one organ or part of the body to another remote from the primary site. Grading, Staging, and Metastasis. Treatment consists of surgical inguinal orchiectomy, and further adjuvant Adjuvant Substances that augment, stimulate, activate, potentiate, or modulate the immune response at either the cellular or humoral level. The classical agents (freund's adjuvant, bcg, corynebacterium parvum, et al.) contain bacterial antigens. Some are endogenous (e.g., histamine, interferon, transfer factor, tuftsin, interleukin-1). Their mode of action is either non-specific, resulting in increased immune responsiveness to a wide variety of antigens, or antigen-specific, i.e., affecting a restricted type of immune response to a narrow group of antigens. The therapeutic efficacy of many biological response modifiers is related to their antigen-specific immunoadjuvanticity. Vaccination therapy is based on disease pathology and stage. Subsequent strategies include disease surveillance Surveillance Developmental Milestones and Normal Growth, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy Chemotherapy Osteosarcoma. Disease prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas is excellent, as testicular cancer is one of the most curable solid neoplasms Neoplasms New abnormal growth of tissue. Malignant neoplasms show a greater degree of anaplasia and have the properties of invasion and metastasis, compared to benign neoplasms. Benign Bone Tumors.
Last updated: May 17, 2024
The mechanisms are not fully known, but different factors appear to play a role in the development of testicular cancer.
| Type | Subtype | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Seminoma |
|
|
| Nonseminoma | Yolk sac Yolk Sac The first of four extra-embryonic membranes to form during embryogenesis. In reptiles and birds, it arises from endoderm and mesoderm to incorporate the egg yolk into the digestive tract for nourishing the embryo. In placental mammals, its nutritional function is vestigial; however, it is the source of intestinal mucosa; blood cells; and germ cells. It is sometimes called the vitelline sac, which should not be confused with the vitelline membrane of the egg. Embryoblast and Trophoblast Development or testicular endodermal sinus tumor Tumor Inflammation |
|
| Choriocarcinoma Choriocarcinoma A malignant metastatic form of trophoblastic tumors. Unlike the hydatidiform mole, choriocarcinoma contains no chorionic villi but rather sheets of undifferentiated cytotrophoblasts and syncytiotrophoblasts (trophoblasts). It is characterized by the large amounts of chorionic gonadotropin produced. Tissue origins can be determined by DNA analyses: placental (fetal) origin or non-placental origin. Gestational Trophoblastic Disease |
|
|
| Embryonal carcinoma |
|
|
| Teratoma Teratoma A true neoplasm composed of a number of different types of tissue, none of which is native to the area in which it occurs. It is composed of tissues that are derived from three germinal layers, the endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm. They are classified histologically as mature (benign) or immature (malignant). Imaging of the Mediastinum |
|
|
| Mixed GCT |
|
|
| Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Leydig cell tumor Tumor Inflammation |
|
| Sertoli cell tumor Tumor Inflammation |
|
| Testicular lymphoma Lymphoma A general term for various neoplastic diseases of the lymphoid tissue. Imaging of the Mediastinum |
|
Focused genitourinary exam:
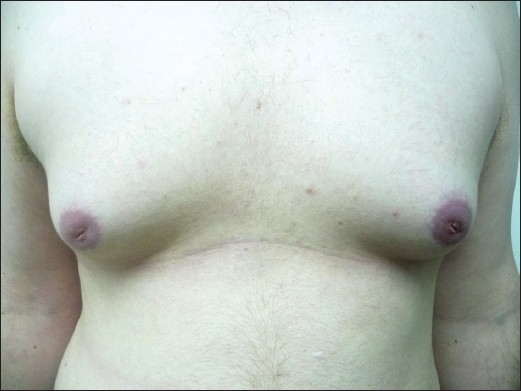
Bilateral gynecomastia in a patient
Image: “Finasteride induced Gynecomastia: Case report and Review of the Literature” by Ramot Y, Czarnowicki T, Zlotogorski A. License: CC BY 2.0Obtain tumor Tumor Inflammation markers:
Testicular cancer is staged according to the TNM Staging System TNM staging system Grading, Staging, and Metastasis of the American Joint Committee on Cancer and the Union for International Cancer Control (UICC).
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| I | Limited to testis, no lymph nodes Lymph Nodes They are oval or bean shaped bodies (1 – 30 mm in diameter) located along the lymphatic system. Lymphatic Drainage System: Anatomy, no metastasis Metastasis The transfer of a neoplasm from one organ or part of the body to another remote from the primary site. Grading, Staging, and Metastasis |
| II | Testis +
lymph nodes
Lymph Nodes
They are oval or bean shaped bodies (1 – 30 mm in diameter) located along the lymphatic system.
Lymphatic Drainage System: Anatomy, no
metastasis
Metastasis
The transfer of a neoplasm from one organ or part of the body to another remote from the primary site.
Grading, Staging, and Metastasis:
|
| III | Distant metastasis Metastasis The transfer of a neoplasm from one organ or part of the body to another remote from the primary site. Grading, Staging, and Metastasis, significantly elevated tumor Tumor Inflammation markers |
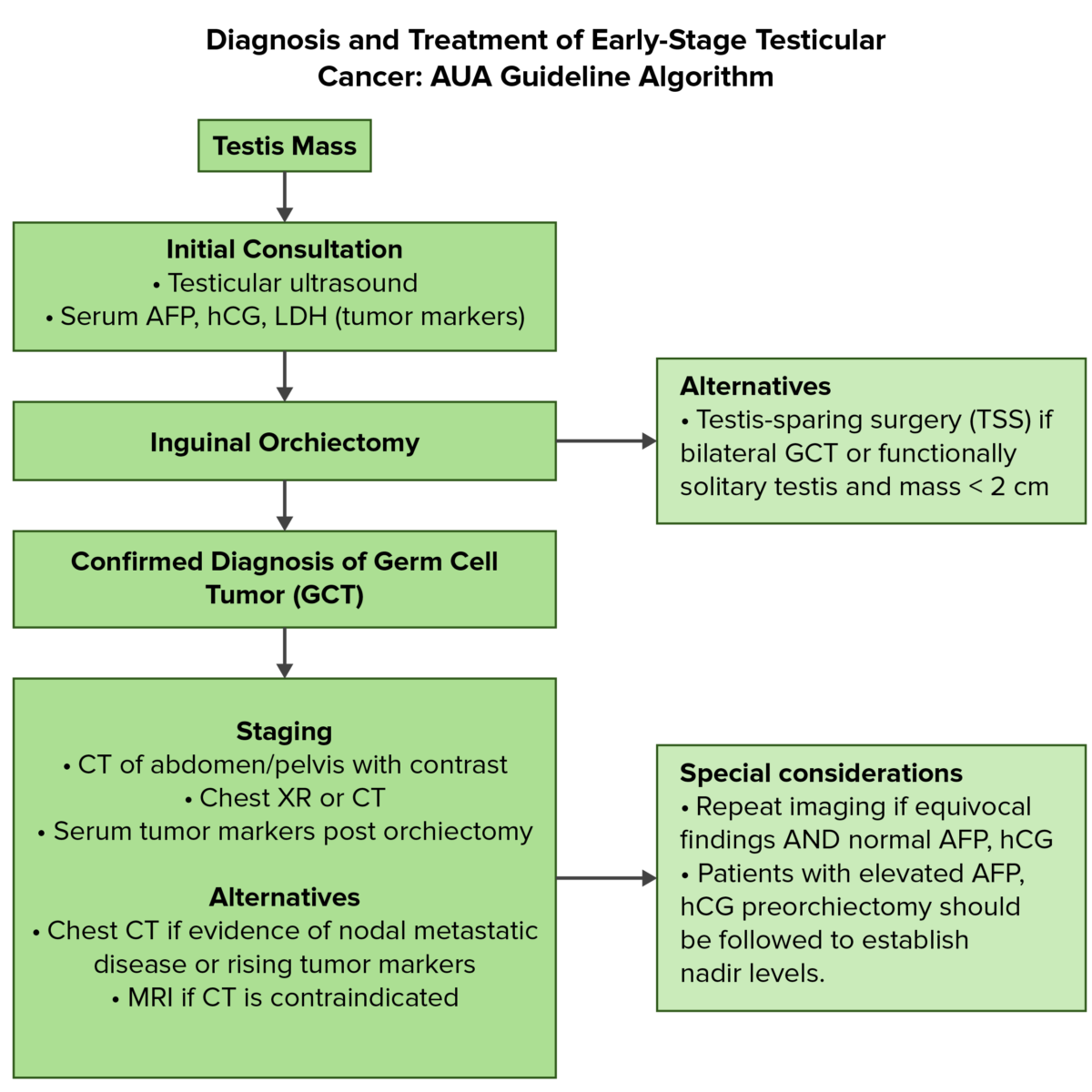
Overview of the diagnostic and initial management of testicular cancer:
AFP: alpha-fetoprotein
AUA: American Urological Association
Fertility preservation (i.e., sperm banking) should be discussed extensively with men of reproductive age before any treatment. Primary treatment is radical inguinal orchiectomy, followed by therapy, depending on the stage:
Fertility preservation (i.e., sperm banking) should be discussed extensively with men of reproductive age before any treatment. Primary treatment is inguinal orchiectomy, followed by therapy depending on the stage: