Penile anomalies and conditions may be congenital Congenital Chorioretinitis or acquired and can affect the urethral opening, prepuce Prepuce The double-layered skin fold that covers the glans penis, the head of the penis. Penis: Anatomy, shaft, or glans or the penis Penis The penis is the male organ of copulation and micturition. The organ is composed of a root, body, and glans. The root is attached to the pubic bone by the crura penis. The body consists of the 2 parallel corpora cavernosa and the corpus spongiosum. The glans is ensheathed by the prepuce or foreskin. Penis: Anatomy. Examples include phimosis, paraphimosis, epispadias, hypospadias, balanitis, Peyronie disease, and priapism. The severity of clinical symptoms varies, but diagnosis of each of these conditions is usually based on the history and physical examination. Treatment varies from medical therapies to surgical intervention. These diagnoses are important to be aware of, since a few (such as phimosis and balanitis) are relatively common, while others (such as paraphimosis and priapism) can have severe complications if not treated in a timely fashion.
Last updated: Jul 21, 2023
The penis Penis The penis is the male organ of copulation and micturition. The organ is composed of a root, body, and glans. The root is attached to the pubic bone by the crura penis. The body consists of the 2 parallel corpora cavernosa and the corpus spongiosum. The glans is ensheathed by the prepuce or foreskin. Penis: Anatomy is made up of:
Penile conditions can be classified on the basis of the affected region of the penis Penis The penis is the male organ of copulation and micturition. The organ is composed of a root, body, and glans. The root is attached to the pubic bone by the crura penis. The body consists of the 2 parallel corpora cavernosa and the corpus spongiosum. The glans is ensheathed by the prepuce or foreskin. Penis: Anatomy:
Male baby with epispadias
Image: “Male baby with epispadias” by Department of Pediatric Urology, University Medical Center Regensburg, Germany. License: CC BY 2.0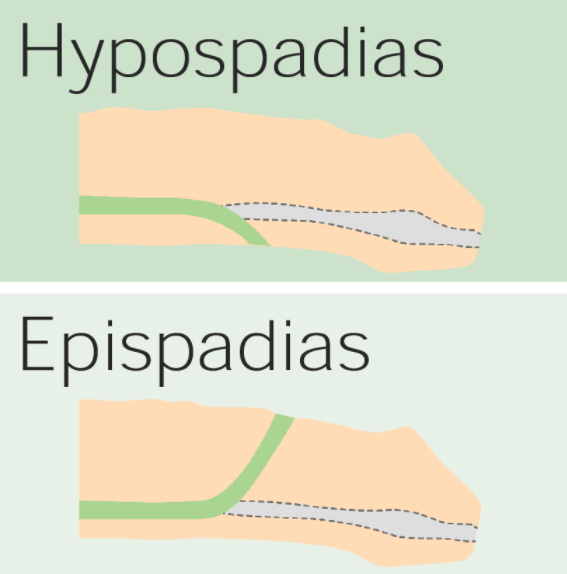
The difference between hypospadias and epispadias: Hypospadias results in an abnormal urethral opening on the ventral surface of the penis, whereas epispadias results from an abnormal opening on the dorsal surface.
Image by Lecturio.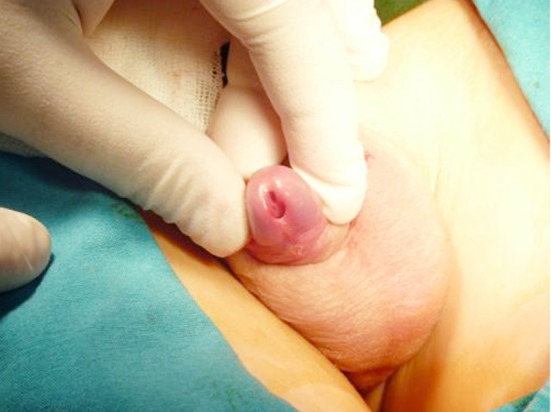
Glanular hypospadias
Image: “Glanular hypospadias is detected with the retraction of the foreskin” by Yesildag E et al. License: CC BY 3.0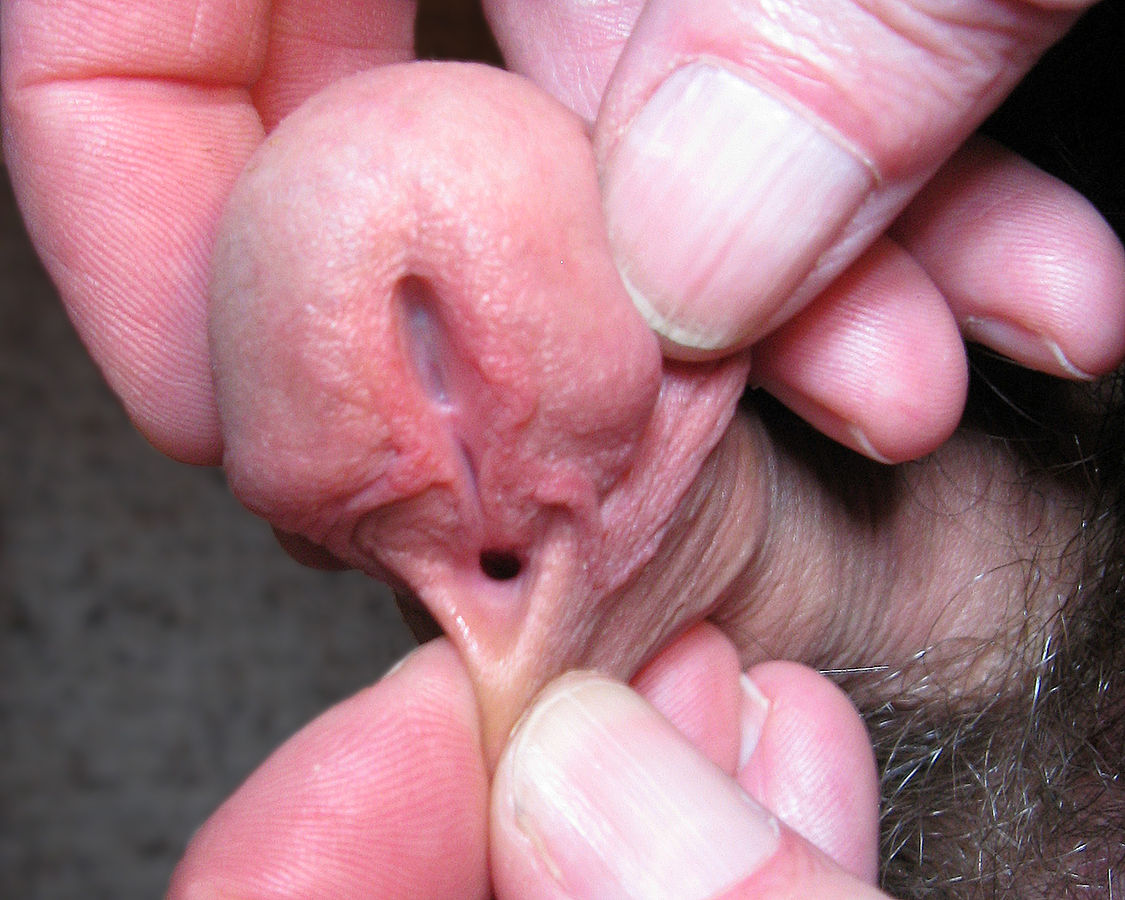
Abnormal opening on the ventral surface of the penis consistent with hypospadias
Image: “Depiction of a human penis with hypospadias” by Buddy. License: Public Domain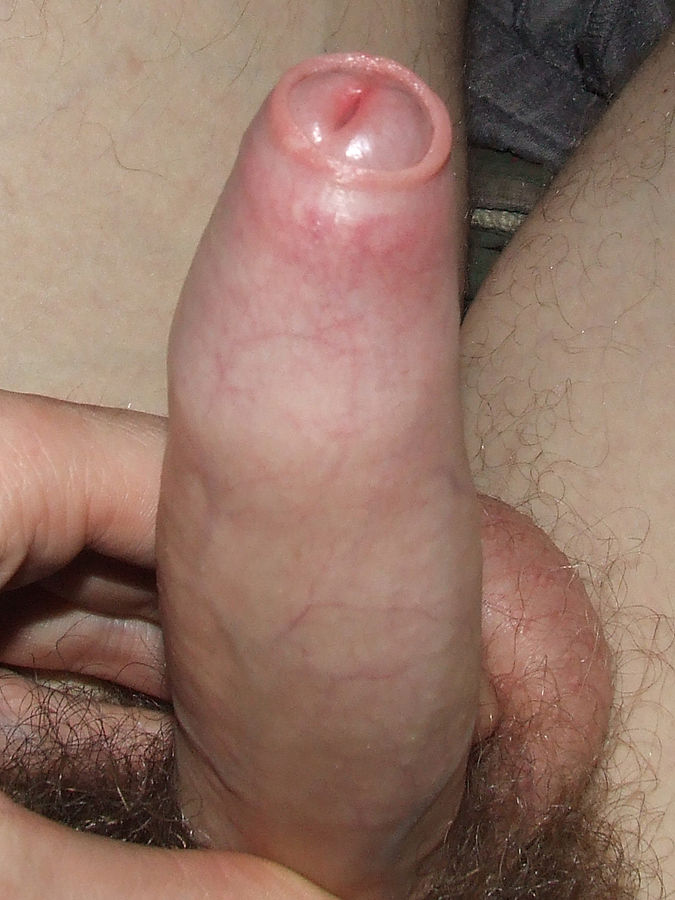
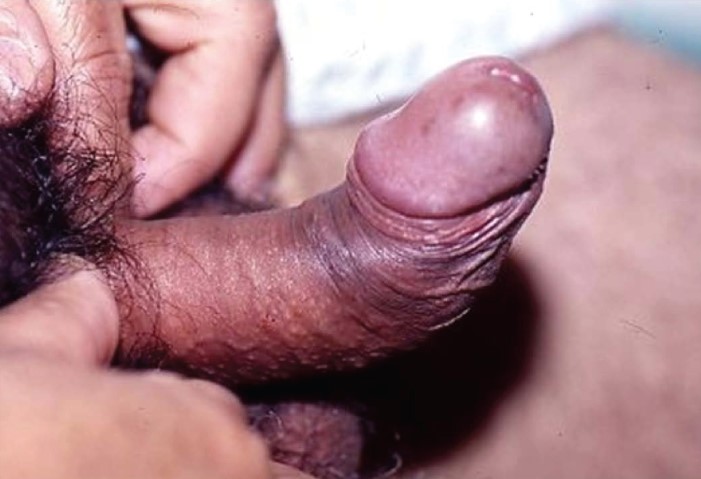
An erect penis with phimosis
Image: “Example of an erect penis with Phimosis. The foreskin will not retract.” by Andrew1985. License: Public Domain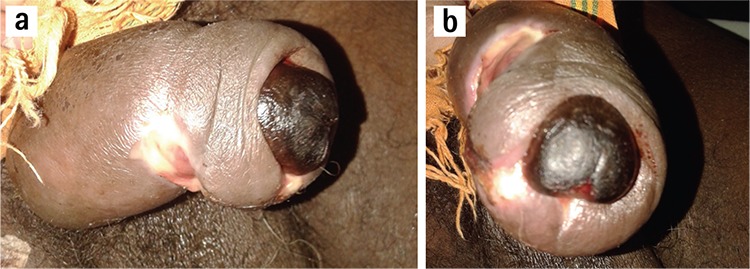
Paraphimosis complicated by glans gangrene:
This condition is caused by impairment of lymphatic and venous blood flow, leading to swelling and compromise of arterial blood flow.
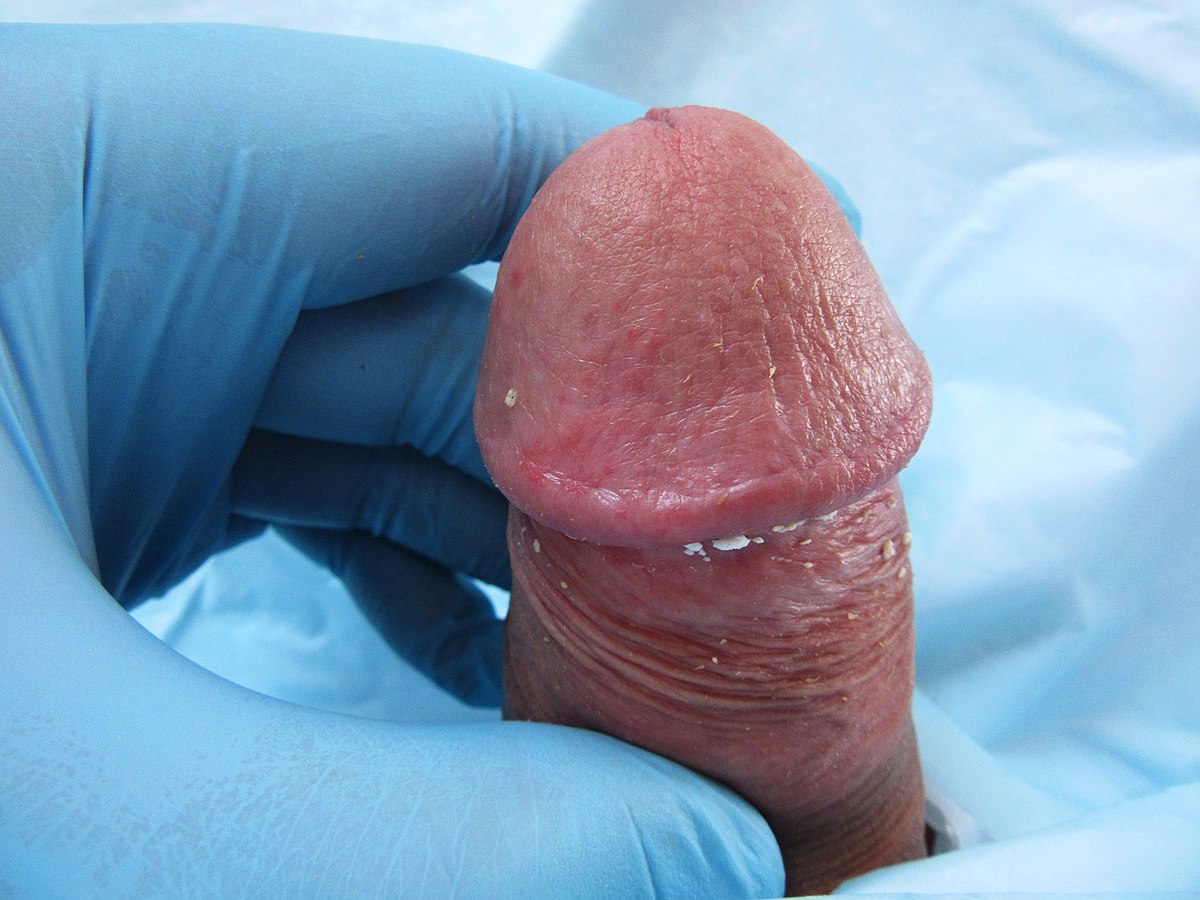
Erythema and edema of the glans penis consistent with balanitis
Image: “Balanitis caused by smegma” by MFN24. License: CC0 1.0Peyronie disease is a penile deformity Deformity Examination of the Upper Limbs caused by fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans/ scarring Scarring Inflammation of the tunica albuginea Tunica albuginea Penis: Anatomy.
Abnormal curvature of the penis secondary to Peyronie disease
Image: “Penile deformity secondary to Peyronie’s disease” by Tran VQ et al. License: CC BY 3.0The diagnosis is clinical.
Priapism is an abnormal, persistent erection Erection The state of the penis when the erectile tissue becomes filled or swollen (tumid) with blood and causes the penis to become rigid and elevated. It is a complex process involving central nervous system; peripheral nervous systems; hormones; smooth muscles; and vascular functions. Penis: Anatomy (usually > 4 hours) that is not associated with sexual stimulation.
The diagnosis is suspected on the basis of the history and physical exam. The following can help differentiate ischemic from nonischemic priapism:
Complications of ischemic priapism include: