Benign Benign Fibroadenoma prostatic hyperplasia Hyperplasia An increase in the number of cells in a tissue or organ without tumor formation. It differs from hypertrophy, which is an increase in bulk without an increase in the number of cells. Cellular Adaptation (BPH) is a condition indicating an increase in the number of stromal and epithelial cells within the prostate Prostate The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system. The gland surrounds the bladder neck and a portion of the urethra. The prostate is an exocrine gland that produces a weakly acidic secretion, which accounts for roughly 20% of the seminal fluid. gland ( transition zone Transition Zone Pediatric Gastrointestinal Abnormalities). Benign Benign Fibroadenoma prostatic hyperplasia Hyperplasia An increase in the number of cells in a tissue or organ without tumor formation. It differs from hypertrophy, which is an increase in bulk without an increase in the number of cells. Cellular Adaptation is common in men > 50 years of age and may greatly affect their quality Quality Activities and programs intended to assure or improve the quality of care in either a defined medical setting or a program. The concept includes the assessment or evaluation of the quality of care; identification of problems or shortcomings in the delivery of care; designing activities to overcome these deficiencies; and follow-up monitoring to ensure effectiveness of corrective steps. Quality Measurement and Improvement of life. The development of BPH involves modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors, which lead to anatomic obstruction and downstream effects on other organ systems. Clinically, patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship present with a combination of obstructive and bladder Bladder A musculomembranous sac along the urinary tract. Urine flows from the kidneys into the bladder via the ureters, and is held there until urination. Pyelonephritis and Perinephric Abscess storage symptoms. Diagnosis is made by determining the severity of voiding symptoms through a variety of non-invasive (voiding diary, history, physical examination) and invasive (cystoscopy, urodynamics, transrectal ultrasound imaging) tools. Treatment is multimodal with medical and surgical components (prostatectomy) utilized in combination.
Last updated: May 17, 2024
Benign Benign Fibroadenoma prostatic hyperplasia Hyperplasia An increase in the number of cells in a tissue or organ without tumor formation. It differs from hypertrophy, which is an increase in bulk without an increase in the number of cells. Cellular Adaptation (BPH) is a histologic diagnosis with an increase in the total number of stromal and epithelial cells within the transition zone Transition Zone Pediatric Gastrointestinal Abnormalities of the prostate Prostate The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system. The gland surrounds the bladder neck and a portion of the urethra. The prostate is an exocrine gland that produces a weakly acidic secretion, which accounts for roughly 20% of the seminal fluid. gland.
The overall size of the prostate Prostate The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system. The gland surrounds the bladder neck and a portion of the urethra. The prostate is an exocrine gland that produces a weakly acidic secretion, which accounts for roughly 20% of the seminal fluid. gland does not correlate with the degree of symptoms.
Benign Benign Fibroadenoma prostatic hyperplasia Hyperplasia An increase in the number of cells in a tissue or organ without tumor formation. It differs from hypertrophy, which is an increase in bulk without an increase in the number of cells. Cellular Adaptation occurs with bladder Bladder A musculomembranous sac along the urinary tract. Urine flows from the kidneys into the bladder via the ureters, and is held there until urination. Pyelonephritis and Perinephric Abscess outlet obstruction (BOO), leading to lower urinary tract Urinary tract The urinary tract is located in the abdomen and pelvis and consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The structures permit the excretion of urine from the body. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder and out through the urethra. Urinary Tract: Anatomy symptoms (LUTS), which can greatly affect quality Quality Activities and programs intended to assure or improve the quality of care in either a defined medical setting or a program. The concept includes the assessment or evaluation of the quality of care; identification of problems or shortcomings in the delivery of care; designing activities to overcome these deficiencies; and follow-up monitoring to ensure effectiveness of corrective steps. Quality Measurement and Improvement of life.
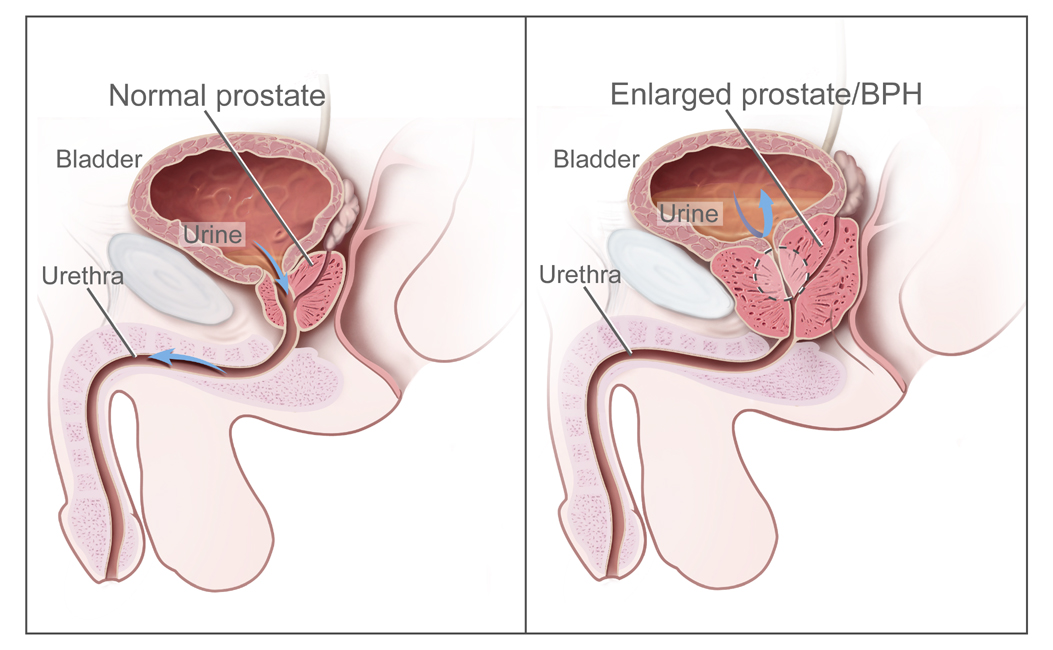
Illustration comparing the normal prostate (left image) and an enlarged prostate or BPH (right image), which is associated with bladder outlet obstruction
Image: “BPH” by National Institutes of Health. License: Public DomainPrevalence Prevalence The total number of cases of a given disease in a specified population at a designated time. It is differentiated from incidence, which refers to the number of new cases in the population at a given time. Measures of Disease Frequency of BPH increases with age:
Risk factors:
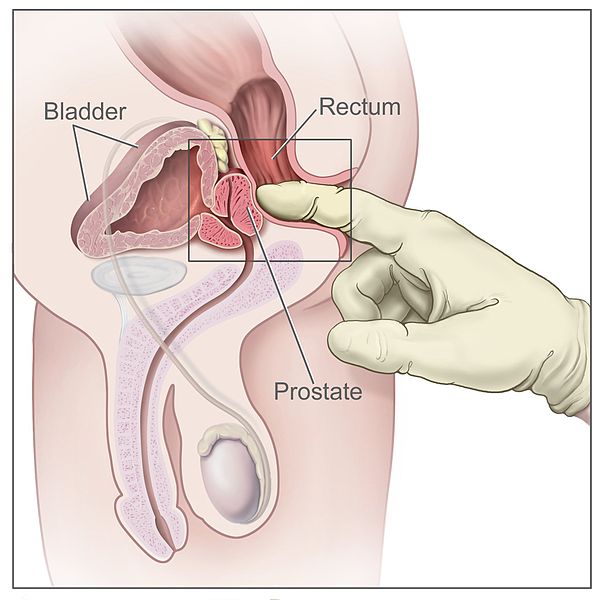
Digital rectal exam (side view of the male reproductive and urinary anatomy, including the prostate, rectum, and bladder):
The doctor inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum and feels the prostate to check for abnormalities.