Poliomyelitis is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. This virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology is a member of the Picornaviridae Picornaviridae A family of small RNA viruses comprising some important pathogens of humans and animals. Transmission usually occurs mechanically. There are nine genera: aphthovirus; cardiovirus; enterovirus; erbovirus; hepatovirus; kobuvirus; parechovirus; rhinovirus; and teschovirus. Coxsackievirus family. It is a small, single-stranded, positive-sense RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology without a lipid envelope Envelope Bilayer lipid membrane acquired by viral particles during viral morphogenesis. Although the lipids of the viral envelope are host derived, various virus-encoded integral membrane proteins, i.e. Viral envelope proteins are incorporated there. Virology. Transmission occurs through the fecal–oral route and, occasionally, through respiratory aerosols Aerosols Colloids with a gaseous dispersing phase and either liquid (fog) or solid (smoke) dispersed phase; used in fumigation or in inhalation therapy; may contain propellant agents. Coxiella/Q Fever. The majority of patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship will be asymptomatic or have a mild, abortive presentation with flu-like symptoms Flu-Like Symptoms Babesia/Babesiosis. Those who develop nonparalytic poliomyelitis will develop signs and symptoms of aseptic meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis. A very minor proportion of patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship will progress to paralytic poliomyelitis, with neurologic progression (including asymmetric flaccid paralysis). The diagnosis is determined by the clinical presentation and can be supported by viral culture Viral culture West Nile Virus, PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), and serology Serology The study of serum, especially of antigen-antibody reactions in vitro. Yellow Fever Virus. Current antivirals are ineffective, and management is supportive. There are 2 vaccines available, which have almost eradicated this disease worldwide.
Last updated: Sep 19, 2022

RNA virus identification:
Viruses can be classified in many ways. Most viruses, however, will have a genome formed by either DNA or RNA. RNA genome viruses can be further characterized by either a single- or double-stranded RNA. “Enveloped” viruses are covered by a thin coat of cell membrane (usually taken from the host cell). If the coat is absent, the viruses are called “naked” viruses. Viruses with single-stranded genomes are “positive-sense” viruses if the genome is directly employed as messenger RNA (mRNA), which is translated into proteins. “Negative-sense,” single-stranded viruses employ RNA dependent RNA polymerase, a viral enzyme, to transcribe their genome into messenger RNA.
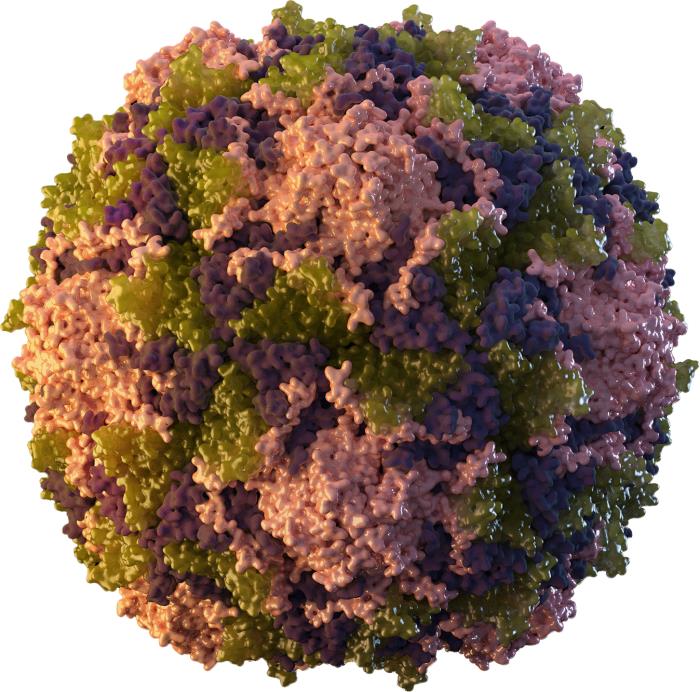
A 3-dimensional (3D) graphical representation of a tightly packed, icosahedral poliovirus particle
Image: “Poliomyelitis” by CDC. License: Public Domain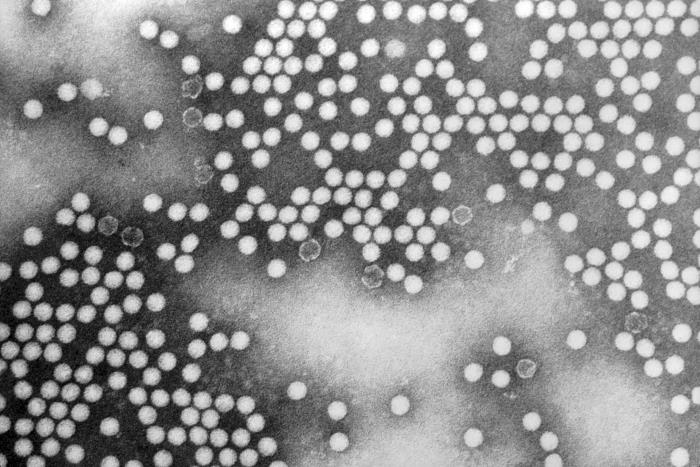
A transmission electron microscopic (TEM) image depicting numerous, round, poliovirus virions, which measure approximately 30 nm in diameter and exhibit icosahedral symmetry
Image: “A transmission electron microscopic (TEM) image of Poliovirus type-1 virions” by CDC. License: Public DomainPoliomyelitis is caused by 3 serotypes of poliovirus:
Humans are the only known reservoir Reservoir Animate or inanimate sources which normally harbor disease-causing organisms and thus serve as potential sources of disease outbreaks. Reservoirs are distinguished from vectors (disease vectors) and carriers, which are agents of disease transmission rather than continuing sources of potential disease outbreaks. Humans may serve both as disease reservoirs and carriers. Escherichia coli.
This highly contagious virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology is transmitted via:
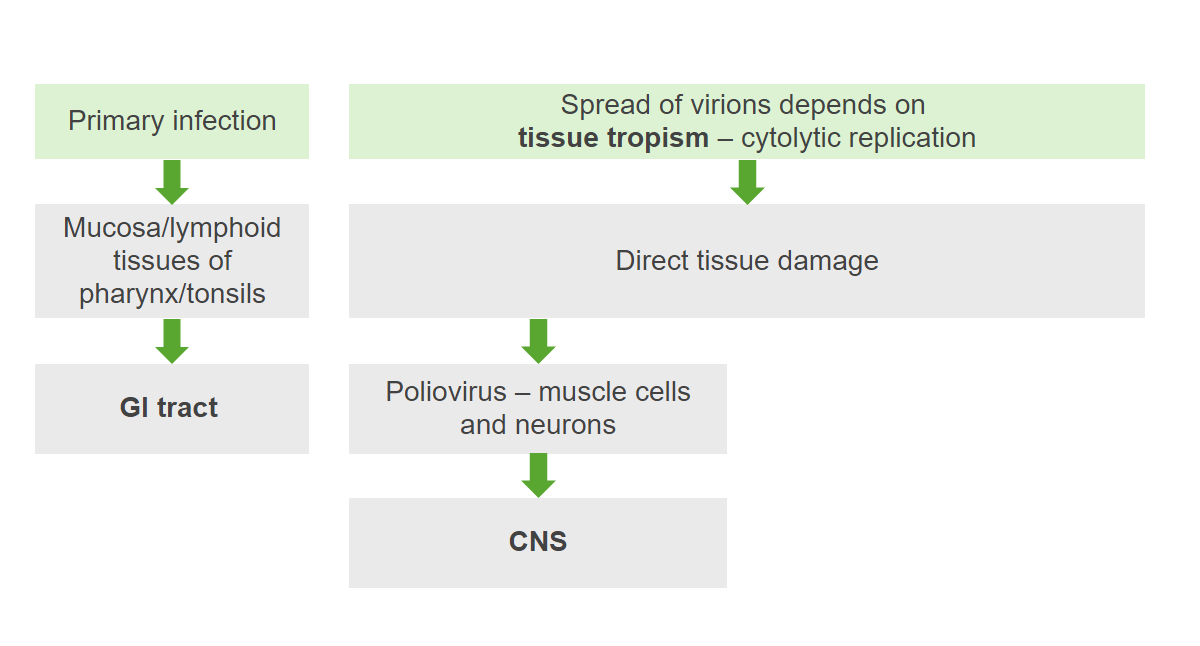
The pathogenesis of poliovirus:
The virus initially enters and infects lymphoid tissues. Viremia occurs, allowing eventual spread to the nervous system. Replication results in tissue damage and symptoms.
The majority of infected individuals are asymptomatic or develop a minor flu-like illness:
Approximately 4% of those infected will develop nonparalytic poliomyelitis. Presentation will be aseptic meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis after a prodrome Prodrome Symptoms that appear 24–48 hours prior to migraine onset. Migraine Headache similar to that of abortive poliomyelitis.
A minority of patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with nonparalytic poliomyelitis will progress to the paralytic form Paralytic form Rabies Virus of the disease, characterized by:
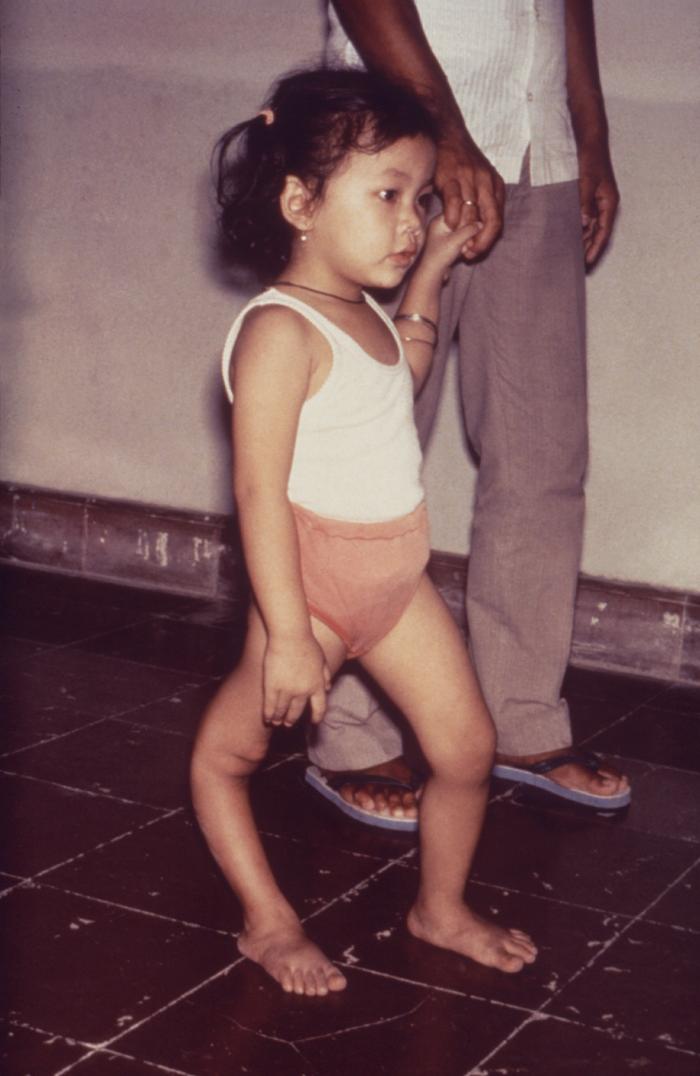
A young girl with a deformity of the right lower extremity as a consequence of paralysis from paralytic poliovirus infection
Image: “Paralytic poliovirus infection” by CDC. License: Public DomainPostpoliomyelitis syndrome manifests as worsening symptoms in poliomyelitis survivors. It can occur decades after the initial infection.
Diagnosis is based on clinical presentation and supported by the diagnostic workup.
Lumbar puncture Lumbar Puncture Febrile Infant:
Specific testing:
There is no effective antiviral Antiviral Antivirals for Hepatitis B therapy for poliomyelitis. Management is supportive.
Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with nonparalytic poliomyelitis make complete recoveries. For those with paralytic poliomyelitis:
There are 2 vaccines used:
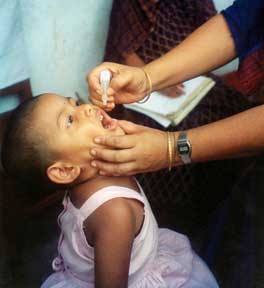
A young girl receiving the oral poliovirus vaccine
Image: “A child receiving an oral polio vaccine” by USAID. License: Public Domain| Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology | Coxsackievirus Coxsackievirus Coxsackievirus is a member of a family of viruses called Picornaviridae and the genus Enterovirus. Coxsackieviruses are single-stranded, positive-sense RNA viruses, and are divided into coxsackie group A and B viruses. Both groups of viruses cause upper respiratory infections, rashes, aseptic meningitis, or encephalitis. Coxsackievirus | Poliovirus | Echovirus Echovirus Echoviruses are single-stranded positive-sense RNA viruses belonging to the genus Enterovirus. Transmission is most commonly through the fecal-oral route. The majority of patients are asymptomatic. Patients who are symptomatic can exhibit a wide range of illnesses ranging from nonspecific URIs and exanthems to severe and life-threatening illnesses. Echovirus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics |
|
|
|
| Transmission |
|
|
|
| Clinical |
|
|
|
| Diagnosis |
|
|
|
| Management | Supportive | Supportive | Supportive |
| Prevention | Handwashing | Vaccination Vaccination Vaccination is the administration of a substance to induce the immune system to develop protection against a disease. Unlike passive immunization, which involves the administration of pre-performed antibodies, active immunization constitutes the administration of a vaccine to stimulate the body to produce its own antibodies. Vaccination | Handwashing |